Important Methods for Studying the Brain Examine an
advertisement
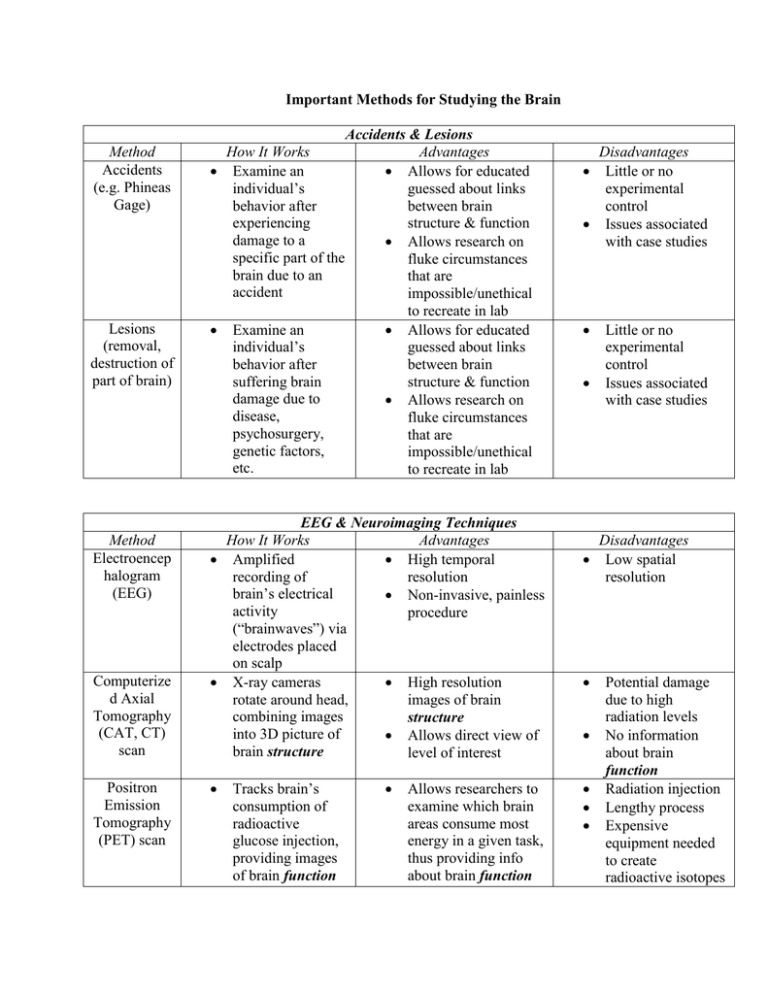
Important Methods for Studying the Brain Method Accidents (e.g. Phineas Gage) Lesions (removal, destruction of part of brain) Method Electroencep halogram (EEG) Computerize d Axial Tomography (CAT, CT) scan Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan Accidents & Lesions How It Works Advantages Examine an Allows for educated individual’s guessed about links behavior after between brain experiencing structure & function damage to a Allows research on specific part of the fluke circumstances brain due to an that are accident impossible/unethical to recreate in lab Examine an Allows for educated individual’s guessed about links behavior after between brain suffering brain structure & function damage due to Allows research on disease, fluke circumstances psychosurgery, that are genetic factors, impossible/unethical etc. to recreate in lab EEG & Neuroimaging Techniques How It Works Advantages Amplified High temporal recording of resolution brain’s electrical Non-invasive, painless activity procedure (“brainwaves”) via electrodes placed on scalp X-ray cameras High resolution rotate around head, images of brain combining images structure into 3D picture of Allows direct view of brain structure level of interest Tracks brain’s consumption of radioactive glucose injection, providing images of brain function Allows researchers to examine which brain areas consume most energy in a given task, thus providing info about brain function Disadvantages Little or no experimental control Issues associated with case studies Little or no experimental control Issues associated with case studies Disadvantages Low spatial resolution Potential damage due to high radiation levels No information about brain function Radiation injection Lengthy process Expensive equipment needed to create radioactive isotopes Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Strong magnetic field causes disorientation of atoms in brain; reorientation = signal as to soft tissue density (picture of brain structure) Type of MRI that detects amount of bloodflow in different brain regions (proxy for oxygen consumption; brain function) Allows researchers to examine brain structure without exposure to radiation involved with CT scan Non-invasive, painless procedure High spatial resolution (3-6 millimeters) Non-invasive, painless procedure Quick imaging process No information about brain structure Can be an uncomfortable, claustrophobic experience No information about brain function Can be uncomfortable, claustrophobic experience