The Cell
advertisement

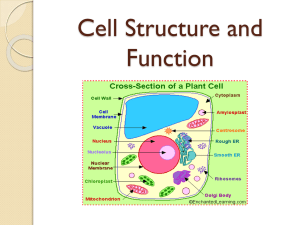
The Cell What is a Prokaryote? Prokaryote ? NO Nucleus or membrane bound organelles. “Pro” = “No Nucleus” A single celled organism Bacteria Cytoplasm Cell Membrane DOES have Cell Membrane, DNA (circular type), Ribosomes, Cytoplasm, and Cilia and/or Flagella What is a Eukaryote? Eukaryote ? What is a Eukaryote? All Plant, Animal, Fungi, Protista Cells!!! Have NUCLEUS and Membrane bound organelles “Eu” = “Yes Nucleus” What MUST all cells have? (Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes) Things What MUST ALL cells have? (Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes) 4 Things: DNA Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Ribosomes What 3 things does a Plant cell have that an Animal cell does NOT have? What 3 things does a Plant cell have that an Animal cell does NOT have? •Cell Wall •Chloroplasts •Large Vacuole Name the 3 parts of the Cell Theory Scientists who helped develop the Cell Theory List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life Cells come from existing, living cells All living things are made of 1 or more cells Who invented the microscope and saw the first living (live) cells in pond water and called them “wee beasties?” Who invented the microscope and saw the first living cells in pond water and called them “wee beasties?” Leeuwenhoek Who saw cork and named the chambers “Cells”? Who saw cork and named the chambers “Cells”? Hooke Sounds like cork (kind of) What did Schwann say? What did Schlieden say? What did Schwann say? What did Schleiden say? Schwann claimed that all animals are made of cells. Schleiden claimed that all plants are made of cells. Think: Schwann sounds like Swan the animal Think: Schlidin’ down the vine and vines are plants Who claimed that all cells must come from existing cells? Hint: Cows come from cows Cells come from cells Who claimed that all cells must come from existing cells (reproduce)? Way to Remember: Cows come from cows Cells come from cells Who did this experiment and believed in biogenesis? Who did this experiment and believed in biogenesis? Redi - Biogenesis Who did this experiment and believed in abiogenesis? Who did this experiment and did he believe in biogenesis or abiogenesis? Needham – Abiogenesis (He needed more information on how to do a good experiment) Who did this experiment and believed in biogenesis? Who did this experiment and believed in biogenesis? Pasteur - Biogenesis The cell’s FUNCTION! What are the four levels of cell organization starting from the smallest to largest? What are the four levels of cell organization starting from the cell? ___________ is when cells perform a specific function for an organism. Give at 3 least examples Cell Specialization is when cells perform a specific function for an organism. Give at 3 least examples Red blood cells blood cells Nerve cells What is the semi-permeable, phospholipid bilayer that regulates what goes in and out of a cell? What is the semi-permeable, phospholipid bilayer that regulates what goes in and out of a cell? Cell Membrane Cell Wall What 3 things pass through the cell membrane or cell wall easily? What 3 things pass through the cell membrane or cell wall easily? Carbon DioxideDiffusion H2O- Osmosis Oxygen - Diffusion What is located in the cell membrane to selectively allow things into and out of the cell? What is located in the cell membrane to selectively allow things into and out of the cell? Proteins & Protein Channels What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? ? What is the jelly-like substance between the cell membrane and the nucleus? Cytoplasm What is the control center of the cell? What is the control center of the cell (brain)? NUCLEUS What is the organelle that is inside the nucleus and makes ribosomes? What is the organelle that is inside the nucleus and makes ribosomes? Nucleolus What covers the outside of the nucleus and what are the holes called to allow ribosomes and RNA out? What covers the outside of the nucleus and what are the holes called to allow ribosomes and RNA out? Nuclear Membrane (Nuclear Envelope) and Nuclear Pores What is the genetic material that is inside the nucleus called when it is threadlike? What is the genetic material inside the nucleus called when it has condensed and preparing for cell division? What is the genetic material that is inside the nucleus called when it is threadlike? Chromatin (Hint: looks like spaghetti) What is the genetic material inside the nucleus called when it has condensed and preparing for cell division? Chromosome What is the powerhouse of the cell? What is the powerhouse of the cell? Mitochondria What makes proteins for the cell? Hint: ?????? What makes proteins for the cell? Hint: RIBOSOMES What is used for photosynthesis in the plant cell? What is used for photosynthesis in the plant cell? Chloroplasts What are chloroplasts, leukoplasts, and chromoplasts called? What are chloroplasts, leukoplasts, and chromoplasts called? Plastids What is the large sac in a plant cell (holds water) and small sac in an animal (used for storage) called? What is the large sac in a plant cell (holds water) and small sac in an animal (used for storage) called? What digests food and gets rid of unwanted things in a cell? ????????? What digests food and gets rid of unwanted things in a cell? ______________is a folded membrane and transports materials throughout the cell. ______________is a folded membrane and transports materials throughout the cell. Transportation of Proteins Transportation of Lipids & Carbs ____________ is used in packaging and transport out of cell? Hint: Think of sending a gold necklace to your friend through the mail. ____________ is used in packaging and transport out of cell? Hint: Think of sending a gold necklace to your friend through the mail. Golgi Bodies or Golgi Apparatus What are the microtubules covering the cell like hair used for movement? What are the microtubules that are whip-like and used for movement? What are the microtubules covering the cell like hair used for movement? What are the microtubules that are whip-like and used for movement? Cilia Flagella The movement of any molecule from HIGH → LOW concentration is called ________?________ The movement of any molecule from HIGH → LOW concentration is called Diffusion Movement of water across the membrane from High to Low is called ________. Movement of water across the membrane from High to Low is called Osmosis. What is movement of high to low concentration that needs a protein but DOES NOT need energy? What is movement of high to low concentration that needs a protein but DOES NOT need energy? Facilitated Diffusion What is movement of high to low concentration that needs a protein and needs energy? What is movement of high to low concentration that needs a protein and needs energy? ACTIVE TRANSPORT __________________ is when a large food particle is moved into the cell. ___Endocytosis________ is when a large food particle is moved into the cell. __________________ is when a large particle is moved out of the cell. ___Exocytosis_________ is when a large particle is moved out of the cell. Endocytosis and Exocytosis (moving big particles in or out of the cell) is also called _______ ________. Endocytosis and Exocytosis (moving big particles in or out of the cell) is also called _______ ________. Bulk Transport When the solute concentration inside and outside of the cell is equal. This is called______ and the cell (shrinks, swells, or stays the same)? When the solute concentration inside and outside of the cell is equal. This is called______ and the cell (shrinks, swells, or stays the same)? Isotonic Cell stays the same When the solute concentration outside the cell is higher than inside the cell it is called______ and the cell shrinks, swells, or stays the same? When the solute concentration outside the cell is higher than inside the cell it is called______ and the cell shrinks, swells, or stays the same? Hypertonic Cell shrinks When the solute concentration inside the cell is higher than outside the cell it is called______ and the cell shrinks, swells, or stays the same? When the solute concentration inside the cell is higher than outside the cell it is called______ and the cell shrinks, swells, or stays the same? Hypotonic Cell Swells and could Burst What happens to the cell in this situation? Where does water move in this situation? 93% H2O 75% H2O What happens to the cell in this situation? Cell Shrinks Where does water move in this situation? Water moves out Hypertonic Solution Water goes out 93% H2O 7% Solute 75% H2O 25% Solute You need to understand what happens when given water concentrations instead of solute concentrations. Name the 2 reasons cells cannot be the size of a basketball. Red Blood Cell Name the 3 reasons cells cannot be the size of a basketball. 1. Geometry: Volume increases faster than surface area which makes it hard for membrane to keep up with needs of the cell 2. Practical aspects: Nucleus can’t handle that big of a job. Be able to identify which organelles belong to Plant, Animal, or Prokaryotic Cells ! ORGANELLE PLANT ANIMAL Prokaryote Cell Wall Yes No Yes Cell Membrane Yes Yes Yes Nucleus Yes Yes No Nuclear Membrane Yes Yes No Cytoplasm Yes Yes Yes Endoplasmic Reticulum Yes Yes No Ribosome Yes Yes Yes Mitochondria Yes Yes No Lysosome No (uncommon) Yes No Chloroplast Yes No No Vacuole Yes (Large) Rare- very small No Golgi apparatus Yes Yes No Cilia No No Yes Be able to identify the organelles in plant and animal cells from various pictures in our notes and Trade & Grade review!!!! Understand the diffusion lab that we conducted in class. Iodine diffuses into bag because iodine is smaller than bag pores and stains starch black Starch too big to diffuse through bag pores so it stays in bag. You know this by the iodine/water in the cup not turning black.