The student will: identify parts of periodic chart chemical reactions
advertisement

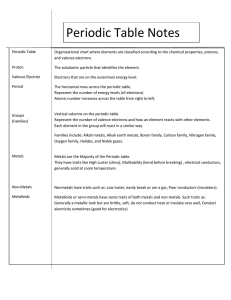
The student will: identify parts of periodic chart explain periodic law in relationship with chemical reactions calculate trends of periodic chart calculate trends according to location of element on periodic chart Chapter 5 p.123 Periodic Table Periodic means = Repeating pattern Dimitri Mendeleev Russian chemist, 1866, published in 1869 Mendeleev- discovered pattern by chemical properties---left empty spaces… 42 yrs later … Henry Mosely English chemist 1911 Modern definition of Atomic# = modern organization of Periodic Table. • PT divided into two sections • Metals / non-metals via stair steps • Metals on the left of stairs • Metals conduct electricity & heat • Non-metals on the right of stairs • Non-metals do not conduct electricity very well and heat only slightly. Most are gases and powders. • Metalloids • Elements touching the stair steps » Exclude Aluminum • Properties of both, “can’t make up their mind” • “Semi-conductors” ….used in computer chips • • • • Elements going sideways period Elements going down group or family Period numbers down side tell largest occupied energy level. Group numbers across the top tell number of valence electrons. • there are some deviations • transition elements, the group # equal the sum of the s & d electrons. * Important Concept Periodic Law :::::: Groups or families exhibit same characteristics. • Note: outer valence electrons determine chemical properties SO…..all elements in a group or family will have similar chemical properties. The physical & chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic number. • Official way to say it : • Group 1 Alkali Metals » Very reactive, explosive, does not exist pure in nature • Group 2 Alkaline-Earth Metals » Very reactive but not as active as group 1 does not exist pure in nature • Group 3-12 Transition Metals » Less reactive, some not reactive, good conductors of electricity, heat Group 17 Halogens Very reactive, gases Group 18 Noble Gases Not reactive, inert, Lanthanides Extremely similar, tedious to distinction Actinides Radioactive, short life • Group 1: s block “Alkali Metals” all elements in group 1 have 1 valence ehence… all have similar properties. Extremely reactive…..explosive Not found in pure state in nature Combines vigorously with non-metals Usually stored under kerosene Going down group lower melting point Li Na K Rb Cs Fr HYDROGEN : doesn’t share same properties as group 1 is placed above group 1 because it does have the 1s1 orbital filled. • Group 2 Alkaline-Earth Metals s2 block harder, denser, stronger too reactive to be found in purity in nature Be … Mg… Ca… Sr… Ba… emeralds….green fireworks white fireworks, very hard, Ca3PO4 = bones , CaCO3 = Concrete , Marble, limestone Chlorophyll in plants is calcium based Red fireworks Medicine tracking, white chalky stuff people drink, isotopes “ With a color pencil lightly color in groups 1 & 2 to color code the s block on your periodic block” • Transitional Metals groups 3-12 color code in each case the sum of outer s electrons and d electrons = group number • Fe, Co, Ni, = make steel, only these can make a magnet • Al = most abundant metal on earth • Fe = second abundant, most used #1 • Group 11 • Cu • Ag • Au = coinage metals, nonreactive ,can be pure on earth. Group 12 Zn = used in plating… ZnO Cd = rechargeable batteries Hg = poisonous, accumulates in bodies, thermometers • Non-metals » » » » » color code entire p block begin to fill p sublevel # of valence electrons = group# -10 Most are gases @ room temp 1 non-metal is a liquid at room temp = Br Poor conductors of electricity and heat • Group 17 = Halogens • F… most chemically reactive Use to etch glass and tooth decay • Cl … • Br … • I… disinfective …. Swimming pools lipstick, dyes thyroid medicine, purple vapor » Sublimination: solid gas » CO2: solid gas “never gets wet, never a liquid” • Diatomic Molecules = • 2 atoms of same element chemically combine in nature N2 O2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 H2 When writing these you must write them as diatomic !!!!! Or it will be wrong!!!! Noble Gases: group 18… inert ….filled energy orbital Laser Light shows, Neon lights Carbon 3 forms called allotropes p. 626 in book **Allotrope= same element different structural form l. Diamond….. Atoms in a pyramid 2. Graphite ….. Atoms in layers. pencil 3. Coal………….Atoms in a sphere…Fullerene 4. A fourth has been invented ….. carbonite periodic table based on carbon-12 Silicon sand, SiO2 ….. Glass, computer chips Nitrogen each breath is 80% N2, diatomic, fertilizers, TNT, dynamite • Phosphorus » Fertilizers, Match heads • Antimony & Bismuth » Added to other metals to lower melting point » Automatic fire sprinkler • Oxygen » 20% of air , diatomic, 2 allotropes » Ozone, O3 ….. How made ????? • Alloys: – Brass = Cu + Zn – Bronze = Cu + Sn – Sterling Silver = Cu + Ag – Pewter = Cu + Sn + Sb • Gold: • • • • 100% gold = 24 karat 92% gold = 22 karat….8% copper 58% gold = 14 karat …42% copper 50% gold = 12 karat ….50% copper • What property does copper add to the gold? • What makes your skin turn green with fake gold? The student will: identify parts of periodic chart explain periodic law in relationship with chemical reactions calculate trends of periodic chart calculate trends according to location of element on periodic chart