Reconstruction Review U.S. II 3 a, b, c, 4c ...
advertisement

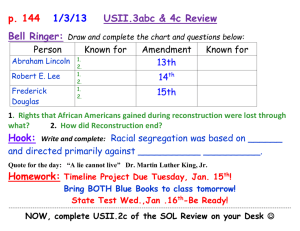
Reconstruction Review U.S. II 3 a, b, c, 4c Name _____________________ Period ____ USII.3 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of Reconstruction on American life by a) analyzing the impact of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution of the United States. 1. What is an Amendment? A way to add to or change the Constitution of the United States 2. Reconstruction Amendments 13th, 14th and 15th 3. The 13th Amendment __________. bans slavery in the United States and any of its territories 4. Which amendment gave all male citizens the right to vote, regardless of race? 15th Amendment 5. Which amendment granted citizenship to all persons born in the United States? 14th Amendment 6. In your own words define what each amendment does. How does it work today? Draw a picture to show how it works today or Give a written example of how it works today. 13th Amendment 14th Amendment 15th Amendment USII.3 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of Reconstruction on American life by b) describing the impact of Reconstruction policies on the South and North . 7. During Reconstruction many things changed. When a government makes a change and provides guidelines; it is called a new ________________ Policy 8. One change was the Civil Rights Act of 1866. It gave equal rights to ___________? African Americans 9. Another change was that the new freedmen most likely became ___________ and were given assistance and help from the _____________ _____________ sharecroppers, Freedman’s Bureau 10. Examples of Congress’s Reconstruction policies in the South □ □ □ □ Southern military leaders could not hold office Southerners Resented Northern Carpetbaggers African Americans could hold public office and political positions such as Congressmen Federal troops were placed in the South to reinforce the equal rights guaranteed to African Americans by Civil Rights Act of 1866 USII.3 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of Reconstruction on American life by c) describing the legacy of Abraham Lincoln, Robert E. Lee, and Frederick Douglass. 11. Which of the following were part of the Reconstruction period of history? Robert E. Lee, Abraham Lincoln, Frederick Douglass 12. Which president during Reconstruction supported amnesty, forgiveness and reconciliation? Abraham Lincoln 13. Who are? ________Robert E. Lee Confederate General, supported Reconciliation President of Washington College ________ Abraham Lincoln ________ Fredrick Douglass Union President and creator of the 10% plan Fought for voting rights for African Americans and women ***14. Which individual (Lee, Lincoln or Douglass) do you think impacted the future path of our nation the most and why? USII.4 The student will demonstrate knowledge of how life changed after the Civil War by c) describing racial segregation, the rise of “Jim Crow,” and other constraints faced by African Americans and other groups in the post-Reconstruction South. 15. What is Racial Segregation? The separation of African Americans and whites in public places 16. Gains made by African Americans during Reconstruction were lost almost entirely in the South because of__? black codes 17. Jim Crow Laws legalized segregation in the South. 3c3 Legal segregation was created as a result of Reconstruction and the passage of discriminatory laws in the South. Two leaders emerged to fight the battle for equality. ****18. Two leaders who fought for African American equality were W.E.B. Dubois and Booker T. Washington. Know 2-3 similarities. Know 2-3 differences