Evolution Glossary
advertisement
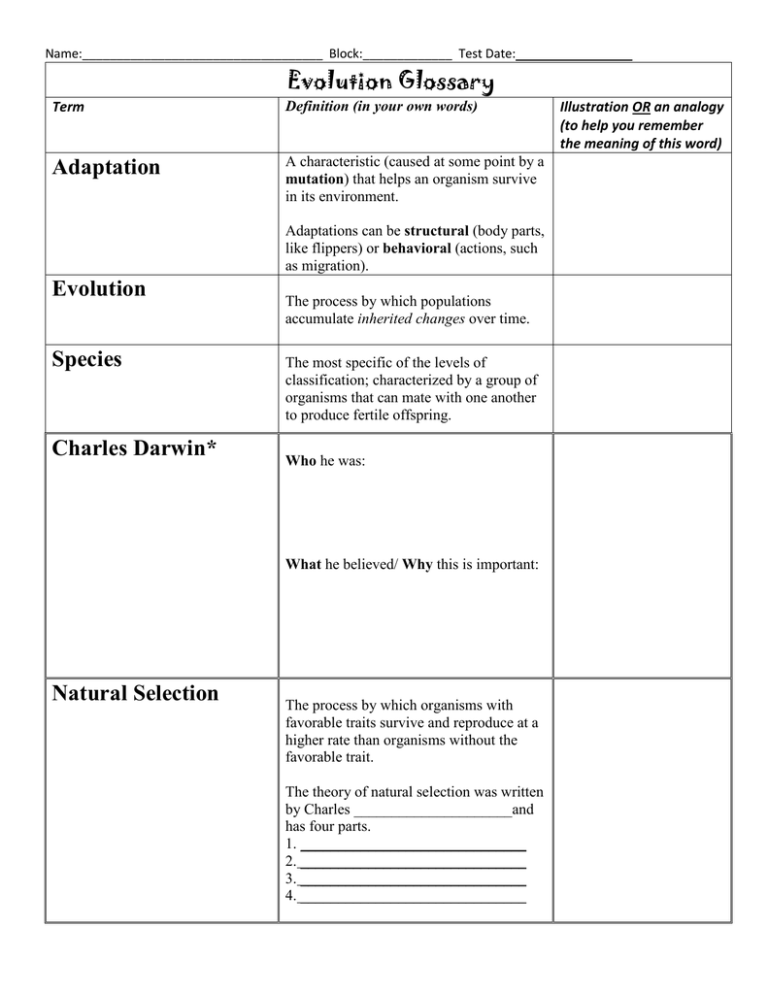
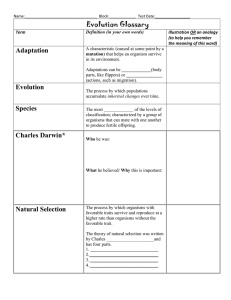
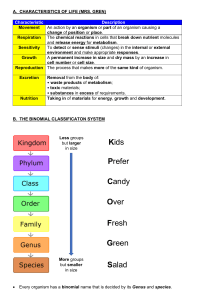
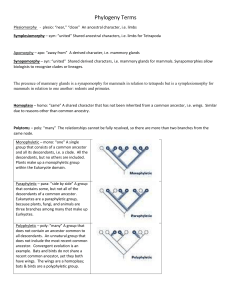
Name:___________________________________ Block:_____________ Test Date: Evolution Glossary Term Definition (in your own words) Adaptation A characteristic (caused at some point by a mutation) that helps an organism survive in its environment. Adaptations can be structural (body parts, like flippers) or behavioral (actions, such as migration). Evolution Species Charles Darwin* The process by which populations accumulate inherited changes over time. The most specific of the levels of classification; characterized by a group of organisms that can mate with one another to produce fertile offspring. Who he was: What he believed/ Why this is important: Natural Selection The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than organisms without the favorable trait. The theory of natural selection was written by Charles _____________________and has four parts. 1. ______________________________ 2. ______________________________ 3. ______________________________ 4. ______________________________ Illustration OR an analogy (to help you remember the meaning of this word) Name:___________________________________ Block:_____________ Test Date: Jean-Baptiste Lamarck* Who he was: What he believed: Generation Time The period between the birth of one generation and the birth of the next generation. Speciation The process by which two populations of the same species become so different that they can no longer interbreed (have babies). Extinct Describes a species of organism that has died out completely. Fossil Record A historical sequence of life indicated by fossils found in layers of the Earth’s crust. Analogous Structures (caused by convergent evolution) Structures in two different species that might look similar or even perform the same task but are NOT caused by a recent shared ancestor. (Example: bird wings and butterfly wings) Homologous Structures (caused by divergent evolution) Structures in two different species that look similar but usually have functions and are caused by a recent SHARED ancestor. (Example: front flippers in whales and arms in humans) Vestigial Structure The remnant of a once-useful anatomical structure. For example, humans have a tail bone because our species is descended from an ancestor species that had a tail.