Agenda 1. Persian Empire
advertisement

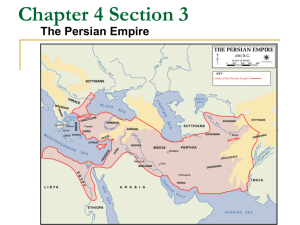
Agenda 1. Persian Empire Objectives Students will be able to… 26. Describe the major beliefs and traditions of Judaism. 27. Summarize the key aspects of the Persian Empire. Skills Objectives Students will be able to… S7. Analyze important features of political and thematic maps. 11/11/10 People of Mesopotamia • Hebrews • Phoenicians • Assyrians • All conquered by the Babylonians (the New Babylonians!) • Then by the Persians Assyrian Empire (New) Babylon Objective #27 Persian Empire Babylonians • King Nebuchadnezzar • Hanging Gardens (a Wonder of the World) • Forced the Hebrews to move to Babylon as slaves – Babylonian Captivity (also called the Exile) • [Objective 25] Persians • Conquered the Middle East, Egypt, modern-day Iran and Afghanistan, Asia Minor, and even into Europe 1. Where would you find the oldest part of the Persian empire? 2. When did the Persian empire reach its greatest extent? Cyrus the Great • Founder of the Persian Empire • Conquered many lands • Known for his tolerance of other cultures and religions • Allowed the Hebrews to return to and rebuild Jerusalem Cyrus the Great • Called “the Great” because of his conquests, and because people loved him • Persian Empire expanded easily, conquered peoples wanted to be a part of it Persian Tombs • Known as the “king of kings” Cambyses • Cyrus’ son. He’s not so great. • Cambyses is everything his father is not –Intolerant –Mean –Disliked • When he dies, the empire falls apart Rule of World History #4 Power will collapse without respect Darius • The winner of a mini-civil war was Darius • Not related to Cyrus, but carries on his tradition • Creates the largest empire in the world up to that time Darius • • • • Re-conquers the empire Restores tolerance Invades Greece Creates the Persian imperial achievements Persia’s Achievements • Imperial bureaucracy • The Royal Road Imperial Bureaucracy • Imperial = belonging to an empire • Bureaucracy = organizational structure in government that is in charge of running things • Darius built a really good one to manage his large empire The Royal Road • Connected the major Persian cities • Important for: –Communication (messenger system) –Trade –Moving armies 3. Where were the two endpoints of the Royal Road? Persian Religion • Called Zoroastrianism, named after the prophet Zoroaster • Monotheistic – Ahura Mazda • Based on conflict between good and evil • People choose sides and their soul is rewarded for choosing well The Story of Zoroaster He was placed by god in a Hamoa plant. He Laughed instead of crying at birth. He glowed so bright that the people became frightened of him and wanted to destroy him. They tried to burn him to death They tried to let animals stamped upon him They left him in the woods, where a mother wolf found and raised him. Then Angels took him up to heaven They taught him about the past, present, and future Zoroaster taught that the Persians that there were two powerful gods. One stood for truth (Ahura Mazda) and light. The other represented evil (Ahriman) and darkness. The two gods were in a constant struggle. Paradise awaited those who followed truth and light, and punishment for those who chose darkness. This was determined by a day of Judgment. Zoroaster wrote down these ideas in a book called the Avesta. The Persians left their mark in history. The Persians showed respect for other cultures. Their government brought order to Southwest Asia. Only Greece escaped Persian control. Exit Ticket Persia Writing! • Explain how the Persian Empire’s rulers fit Rule of World History #4 • Explain how the Hebrew Kingdoms (think Solomon) fit Rule of World History #1 The Rules of History (Thus far…) #1 Divided, you fall #2 Beware the nomads #3 He who controls trade, controls the world #4 Power will collapse without respect