Animals and Habitats Study Guide
advertisement

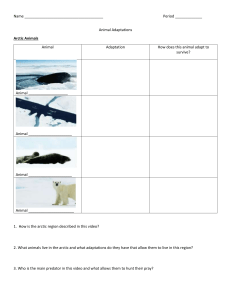
Animals and Habitats Study Guide Test is on Thursday, October 1st Identify living and non-living things. living- elephant non-living- rock Name the different land habitats (grassland, forest, rainforest, arctic tundra, and desert) and one water habitat (ocean). grassland- forest- rainforest- arctic tundra- desert- ocean- A habitat includes both living and non-living things. (living-Trees non-living-Rocks) Plants and animals are interdependent. This means that plants help animals and animals help plants. Example: Plants help animals by giving them food and shelter. Animals help plants by carrying seeds to different places. A food chain begins with the sun providing food for plants. The bigger animals are at the top of the food chain. (sun – plant – bug – bird – snake) An adaptation is a change an animal makes to survive. Identify three different animal adaptations. (camouflage, hibernation, migration) camouflage- hibernation- migration- o Camouflage is a way for animals to hide from predators and blend in with their surroundings. (ex. chameleons, arctic fox, arctic hare) o Hibernation is when animals sleep through the winter (ex. bears, squirrels, bats). Animals hibernate because the weather is cold and food is scarce. o Migration is when animals move to another place when it is colder and food is scarce. (ex. birds, whales, Monarch butterflies) Fossils give scientists information about plants and animals that lived on Earth many years ago. Virginia’s state fossil is called Chesapecten Jeffersonius.






![cWTTgcT]c^UcWT]^afTVXP] Pc[P]cXRRdaaT]cXbeTahbcPQ[T R[X](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/018089929_1-c3a93d850d5a512554ffede057d4cc20-300x300.png)