Chapter 4 Overview Duiker & Speilvogel Pericles: Funeral Oration- ideals of
advertisement

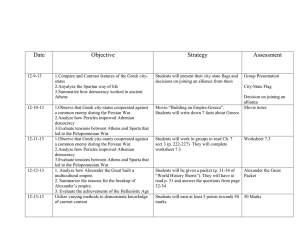
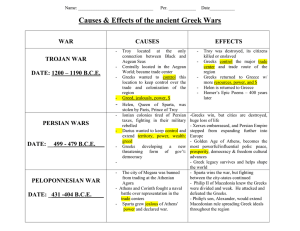
Chapter 4 Overview Duiker & Speilvogel Pericles: Funeral Oration- ideals of democracy and importance of the individual Early Greece o Geography- mountainous terrainisolating, sea trading Minoan Crete o 2000-1450 BCE = height o Around 2800 BCE Bronze tools/ weapons o Palace at Knossos o Bull-leapers (gymnasts) o Why did they decline? Invasion? Mycenaeans o 1600-1100 BCE= height o Homer o Invasion by the Dorians? Dark Age (1100-750BCE) o Migration due to declining population and falling food production o Iron replaced bronze o Adoption of Phoenician alphabet Homer o Based Iliad and Odyssey on oral tradition of the Trojan War o “the gods strong and incalculable; that the quality of a man matters more than his achievement, that violence and recklessness will still lead to disaster, and that this will fall on the innocent as well as on the guilty.” o Homer gave an idealized pastcornerstone of education Greek City-States (c750-500BCE) o Polis= small but autonomous political unit, town and countryside Acropolis= fortified hill Agora= market and assembly (AGORAPHOBIC) Classes w/in polis: Adult males (full political rights), women and children (citizens w/ no political rights), noncitizens (slaves and resident aliens) New Military- hoplites (heavily armed) Phalanx formation Colonization (750-550BCE) o Causes: poverty, land hunger, growing gulf between rich and poor, overpopulation and development of trade o Effects: Establishment of colonies, spread of culture throughout Mediterranean region, increased trade and industry Govt. o Monarchy-Oligarchy-TyrannyDemocracy o Tyrants- usurpers of power in a coup d’etat- upheld public works projects to enhance their popularity Sparta o Peloponnesus- conquered the Laconians and subjected theme to serfdom “HELOTS”- bound to the land o Created a military state to control Laconian and Messenian Helots o Babies judged at birth- defective- left to die o Boys- wet-nursed- taken away at 7 to military barracks- military trainingjoined army at 20, lived at Barracks until 30-could retire at 60. o Could marry and visit wife at night, but couldn’t get caught o Spartan women unique- had more rights- trained in wrestling and gymnastics to make them strong and bear healthy children- married later o Spartan Govt. (oligarchy) 2 kings- military affairs and supreme priests Gerousia= council of elders Ephors= supervised education Apella= assembly of all male citizens o isolationist o Leader of Peloponnesian League o Spartans valued their strength as justification for their militaristic ideals and regimented society Athens o Monarchy-Oligarchy (7thcBCE)Tyranny-Democracy o 7thcBCE- political and social discontent- rival factions w/in aristocracy- many farmers sold into slavery when they couldn’t pay debts o 594BCE- Solon- reforms- cancelled land debts, outlawed new loans based on human collateral and freed people from slavery o Tyrants: Pisistratus & Clisthenes Created new Council of 500 chosen by lot Classical Greece (500-338BCE) o Greece vs. Persia Ionian colonies revolt against Persians 499BCE aided by Athenian navy 490BCE Persian king Darius attacked Greece Battle of Marathon Xerxes renewed plans for invasion of Greece Battle of Thermopolae- Leonidas (Spartan king) 9,000 Greeks and 300 Spartans held off Persians for 2 days 479BCE Persian army defeated at Platea o 478-477BCE Delian League founded w/ Athens o “Age of Pericles”- height of Athenian power and the culmination of its brilliance as a civilization o Athens was sacked and burned, Greek naval fleet won decisive victory over Persian navy at Salamis. o 479BCE Greeks defeated the Persians at Plataea Athenian Empire o Athens formed the Delian League Age of Pericles o Assembly “will of the people”= all male citizens over 18- passed all laws and made financial decisions on war and foreign policy o Direct Democracy o Pericles expanded suffrage: lowerclass citizens eligible for public offices formerly closed: state pay for office-holders o City magistrates chosen by lot o “Generals”=directors of policy (10 officials)= elected by public vote o Ostracism- person receiving 6,000 votes could be exiled for 10 years o Used treasury of Delian League to rebuild Athens The Peloponnesian War (431-404 BCE) o Sparta v. Athens o Athen’s plan to stay behind walls but plague struck o Athens defeated= walls torn down, navy disbanded, empire destroyed o Interfighting b/w Athens, Sparta, and Thebes weakens the Greek citystates while Macedonia became stronger. Culture of Classical Greece o Herodotus (484-425BCE) History of the Persian Wars Central theme struggle b/w Greeks and Persians for Greek freedom Divine intervention in Greek victory o Thucydides (460-400BCE) Greatest historian of ancient world Scientific, methodical, and objective account of Pelop. War o Greek Drama 1st were tragedies- suffering of hero (tragic flaw) ex: Hubris o Aeschylus (525-456BCE) 1st tragedian Oresteia Trilogy- evil acts breed evil acts- Reason Triumphs o Sophocles (496-406BCE) Oedipus Rex- man is fated to kill father and marry his mother o Euripedes (485-406BCE) The Bacchae Critical of view that war was glorious- showed war as brutal and barbaric Greek Comedy o Aristophanes (450-385 BCE) The Clouds, Lysistrata Comic but effective message against the Peloponnesian War (women have sex strike until war is ended) The Arts: The Classical Ideal o Architecture- the Temple o Doric- Ionic- Corinthian columns o Parthenon- Temple of Athena Sophists o Wandering teachers o Truth is relative to everyone Socrates o Socratic Method o Sentenced to death for corrupting the youth of Athens- hemlock Plato o The Republic o Ideal state: Population divided into 3 groups o Upper-class – Philosopher-Kings o Men and women have same education and equal access to all positions Aristotle o Student of Plato, tutor to Alexander the Great o Book: Politics: constitutional govt. o Marriage impt for mutual support o Women biologically inferior to men and therefore should be subordinate to men in marriage Greek Religion o Social and practical o Civic cult necessary for well-being of state o 12 Olympian gods (Zeus, Hera, Athena, Apollo, Aphrodite, Poseidon, etc) o Each polis had a patron god o Afterdeath spirits to a gloomy underworld- Hades o Ritual important along w/ prayer and sacrifices o Oracles (at Delphi) Daily Life o Males part of public life o Slavery common o Limited arable land- trade very important especially for grain o Women as wives, primary duty to have children o Homosexuality accepted The Rise of Macedonia o Philip II (359-336BCE)- King of Macedonia Built efficient army and conquered the Greeks He was assassinated o Alexander the Great (336-323BCE) Became king of Macedonia at 20 Invaded the Persian Empire Asia Minor-Syria, Palestine, Egypt- Mesopotamia (Babylon)Persepolis-Indus River His troops mutinied at Indus River, forced to turn back On return trip, Alexander died in Babylon Legacy: Hero or Villain? Hellenistic Era “to imitate Greeks” o “Hellenic” culture= Greek culture o Extension of Greek language and ideas to non-Greek world of Middle East o Spreading of Greek language, art, architecture, and literature o Urban centers key for diffusing Greek culture Non-Greeks restricted from high positions so that Greeks could maintain their dominance Ex: Alexandria in Egypt Many Greek colonists moved to the Middle East Economic and Social Trends o Agriculture o Commerce increased trade between west and east o Key trade item= grain o New opportunities for women o Education for upper class women o Ptolemaic rulers in Egypt= return to kings marrying own sisters Culture in Hellenistic World o Hellenistic sculptures tried for more emotional and realistic art rather than idealized o Menander (342-291BCE)= New Comedy “Pretty Woman” Stories o Polybus (203-120BCE)= chief historian of Hellenistic Age A Golden Age of Science o Separation of science from philosophy o Archimedes (287-212 BCE)= famous scientist Worked on geometry in spheres and cylinders Pi Science of hydrostatics Archimedian screw Philosophy o Epicurus (341-270BCE)- founder of Epicureanism Human beings were free to follow self-interest as a basic motivating force. Happiness was goal of lifepursuit of pleasure Pleasure= freedom from emotional turmoil, freedom from worry Remove from public activity Friendship important o Stoicism- founded by Zeno (335263BCE) Happiness, the supreme good, could only be found by living in harmony with the will of God You could bear whatever life offered Public service important and noble Religion in Hellenistic World o Decline in popularity of traditional Greek Olympian Religion o Mystery cults= individuals could pursue a path to salvation and achieve eternal life by being initiated into a union with a savior god or goddess who had died and risen again. Name: _________________________ Period: _______ Date: __________ Chapter 4 Reading Quiz 1. Name the two famous Greek historians and the subject of each of their famous works. Herodotus- known as the “Father of History” wrote Histories about the Persian Wars…included the Gods favoring the Greeks as the main reason for their win over the Persians. Thucydides- known as a scientific historian…wrote a History of the Peloponnesian War in which he included statistics, and was much more systematic in his account. 2. Who was Philip II? (Time Period, Location, Key Achievements). (359-336 BCE/ 4th century BCE) King of Macedonia who invaded Greece, and conquered the Greeks…he was assassinated and his son, Alexander the Great took over. 3. List two similarities and two differences between Sparta and Athens. Similarities Both City-States Both polytheistic Patriarchal Both had rule by oligarchies at one point Joined together to fight the Persians in the Persian Wars Differences Athens was focused on intellectual pursuits Sparta was organized as a militaristic society Athens was surrounded by a wall…for the Spartans, their people were their wall Fought against each other in the Peloponnesian War Women had more rights in Sparta