Do now: If it’s broke you should fix it,... with “fixing” the Articles of Confederation?
advertisement

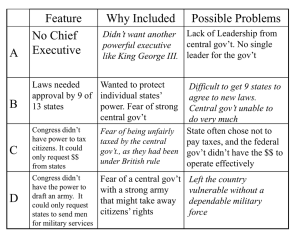
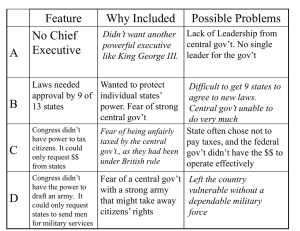
Do now: If it’s broke you should fix it, right? Are their any dangers with “fixing” the Articles of Confederation? Today, I will be able to evaluate the effectiveness of the Articles of Confederation and explain how the Northwest Ordinance benefited the U.S. If you have not taken the quiz on 6.4/6.5, you must do so by Friday 9 January 2015. If you did not turn in your 7.1 homework, do so now. Grades will be update tomorrow around 3:00 pm. ***** The Grading Period Ends 21 January 2015 (Wednesday) Complete 7.2 Qs 1-6. 5 Jan: Crash Course Review of the AmRev 6 Jan: The “Articles of Confederation” homework 7 Jan: The Failure of the A.O.C. and the need for a more effective document 8 Jan: The Constitutional Convention homework 9 Jan: Many Compromises (possible homework) Each state was guaranteed "its sovereignty, freedom, and independence.“ Each state had one vote in Congress, which meant that small states had as much power as large states. Laws passed by Congress required approval by 9 of the 13 states. Amendment of the Articles required unanimous approval. **So… each state was allowed to act as their own independent country; however, were loosely united. Think of it this way: each state is still a family, but extended family like your 5 cousin removed (hey, I think were related, but I’m not sure how…) Created a central government (a legislature called Congress that would make laws). Leader of the Congress was elected and called the President, acts similar to the Speaker of the House does today). 2 to 7 members per state, only 1 vote per state Term = 1 year Powers Protect the seas Declare war Informally help to settle disputes between states Coin money (states could as well) Appoint military officials Indian relations No Executive to carryout the laws passed No Judiciary to formally settle all disputes between states No common currency, made it difficult to trade Had to ask states for money and soldiers if necessary 9 out of 13 states to pass a law, instead of a simple majority which would be 7. **Essentially, the federal government has to beg the states for virtually everything, and the states can say no to almost any request. Suggested by George Washington and headed by James Madison. Held Sept of 1786 Parties involved: NJ, NY, PA, DE, VA Reason: To discuss disputes regarding trade between the states. At this point, virtually each state had their own currency, so did Congress. What does that mean? If you wanted to buy goods from PA and you lived in VA, you would have to exchange for VA $ for PA $ your currency. **Difficult to conduct business When: August 1786 to February 1787 Why: Aggressive tax and debt collection Political corruption Parties involved: Farmers from MA, a lot of AmRev veterans State government and tax collectors Other information: Taxes were raised during an economic depression (terrible idea), also Remember people aren’t particularly keen on paying taxes in the first place Actions: State raised taxes during a depression State began seizing farm land from those that didn’t pay their taxes or didn’t pay back their loans Farmers organized and attacked government buildings and officials MA militia finally raised and rebellion is put down After the Annapolis Convention and Shay’s Rebellion people began to realize that the A.O.C. need fixed, so they agreed to meet in Philadelphia May 1787. 1787, guaranteed basic right to settlers, and outlawed slavery in those territories. 60,000 settlers and a Constitution statehood Provided a clear and easy way to settle newly acquired territory, allowed 5 new states to enter the union OH, IN, IL, MI, and WI Allows the federal government the ability to generate some revenue without having to ask the states for $.