P h i l
advertisement

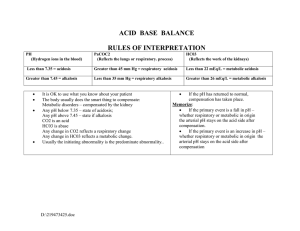
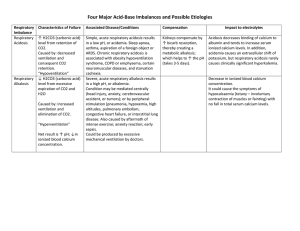
Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Lecturer : Dr Awni Khrais Coordinator : Dr Reiad Ramadane Internal Examiner : Dr Reiad Ramadane Department of Clinical Pharmacy Student Name: Course Name: Physiology 2 Course Number:0511220 Final Exam ……..///////// Student Number: Semester of Academic Year 2009 /2010 Date: 20/1/2010 Duration. 120 min Information for Candidates 1. This examination paper contains 70… questions in .9.. pages, totalling 50… marks. 2. The marks for parts of questions are shown in round brackets. Notes to Candidates 1. You should attempt all questions. 2. You should write your answers clearly Part I. Basic Notions Objectives. The aim of the questions in this part is to evaluate the required minimal student knowledge and skills. Answers in the pass category represent the minimum acceptable standard (34…. marks). QUESTIONS/////// Regarding adrenal gland, minaralocorticoids are secreted from A- Zona glomerulaza B- Zona fasciculate C- Zona reticulate D- Medulla Aldosteron secretion A- Decreases secretion of potassium B- Causes depletion of fluid C- Decreases renal absorption of sodium D- Involves with rennin- angiotensin system Glucocorticoids secretion cause the following except A- Protein catabolism B- Decrease glucogenesis C- Increase blood pressure D- Has immunosuppressive effect Catacholamine include the following A- Adrenaline B- Norephidrine C- Dopamine D- All of the above 1 Catacholamines secretion cause the following except A- Alfa adrenoreceptor causes vasoconstriction B- Beta adrenoreceptors cause vasodilatation C- Increase blood pressure D- Decrease heart rate Hyperactivity of adrenal gland is characterised by the following except A- Striae of abdomen B- Depression of immune system C- Osteoporosis D- Hypoglycaemia Corticosteroid side effect resulted in producing A- Weight loss B- Dehydration C- Acne D- Anaemia The most common causes of hyperfunction of adrenal gland is A- Excessive secretion of ACTH B- Tumor of adrenal gland C- Prolonged glucocorticoid administration D- Adenoma of Zona glomerulosa Adrenal hypofunction is associated with the following except A- Muscular weakness B- Loss of weight C- Anaemia D- Constipation Phaeochromocytoma is associated with the A- Tumor of chromaffine cells B- Hypotension C- Hypoglycaemia D- Reduced metabolic rate Lctotrophs cells of anterior pituitary gland secrete A- Growth hormone B- Prolactine C- TSH D- ACTH Gonadotophs cells of adenohypophysis secrete A- FSH B- TSH C- ACTH D- T3 2 The following hormone induces ovulation A- GH B- LH C- FSH D- TSH Causes of hypopituitarism include A- Pituitary tumor B- Head injury C- Hypothalamic dysfunction D- All of the above Hypopituitary feature include the following A- Insensitivity to cold B- Excessive Prolactine C- Excessive ACTH secretion D- Hypotension GH deficiency in children causes A- Dwarfism B- Diminished muscle mass C- Obesity D- Premature atheroma Giantism A- Arises in children before epiphysis have fused B- Arises in adult life C- Occurs with excess production of TSH D- All of the above Insulin is secreted by the following pancreatic cells A- Alfa cells B- Beta cells C- Delta cells D- None of the above Type I insulin dependent A- It is due to α cells destruction B- Occurs at any age C- Usually the onset before puberty D- May occur during pregnancy Complication of diabetes mellitus include all the following except A- Ketoacidosis coma B- Renal failure C- Nero-retinopathy D- Weight gain (overweight ) 3 Goitre is associated with disorder of A- Increase thyroid hormone secretion B- High TSH C- Increase iodine intake D- Lack of iodine Hypothyroidism better treated with A- Catacholamines B- Acetylecholine C- Thyroxin D- All of the above Diabetes Insipidus is associated with abnormal secretion of A- Prolactine B- Antidiuretic hormone C- Glucose metabolism D- Insulin The neocerebellar syndrome involve the following except A- Hypotonia B- Asthenia C- Dysmetria D- Loss of involuntary movement control Static tremor is seen in A- Liver disease B- Parkinson's disease C- Hypothyroidism D- Neocerebellar syndrome Auditory sensory area is located in A- Temporal lobe B- Parietal lobe C- Frontal lobe D- Occipital lobe Visual sensory area is located in A- Temporal lobe B- Parietal lobe C- Frontal lobe D- Occipital lobe Metabolic characteristic of basal ganglia include the following except A- Copper content is high B- Oxygen consumption is high C- Glucose utilization is high D- Metabolic utilisation is low 4 Dopamine is secreted from A- Globus pallidus B- Cudate C- Substantia Nigra D- Putamen Disease of basal ganglia include the following except A- Chorea B- Athetosis C- Rigidity D- Decrease muscle tone Daily intake of sodium is about A- 12 g B- 10 g C- 8.5 g D- 5.5 g Reabsorption of sodium occur in the following except A- Proximal convoluted tubule B- Collecting tubule C- Distal convoluted tubule D- Loop of Henle In Addison's disease there will be A- Decrease sodium in ECF B- Hypertension C- Decrease calcium in ECF D- None of the above In heart failure oedema may occur because A- Decrease excretion B- Reduced aldosteron secretion C- Reduced sodium intracellular fluid D- None of the above Part II. Familiar Problems Solving Objectives. The aim of the questions in this part is to evaluate that the student has some basic knowledge of the key aspects of the lecture material and can attempt to solve familiar problems (19… marks). QUESTION. In case of haemorrhage A- There is complete sodium reabsorption by renal tubule B- There is increased hypotension and vasodilatation of renal vessels C- The amount of filtered sodium is increased D- All of the above All may occurs in Mineralocoricoid deficiency except A- Hypotension B- Excessive sodium excretion C- Circulatory collapse D- Hypervolaemia 5 In women, water retention may occur with increased secretion of A – Cortisol B – Estrogen C - Glucocorticoid D – Mineralocoricoid Polyuria occurs in A- Diabetes mellitus B- Renal failure C- Decreased manitol and urea D- All of the above Hyponatraemia may occur in A- Cold weather B- Increased aldosteron secretion C- Excessive sweating and severe vomiting D- All of the above Symptoms of hyponatremia involve the following EXCEPT: A- High blood pressure B- Hypovolemia C- Anorexia D- Loss of skin elasticity Failure to inactivate aldosteron may occur in : A- Lung disease B- Renal disease C- Liver disease D- All of the above Death may occur in sever hyponatremia with : A- High blood pressure B- Sever oedema C- Sever cellular dehydration D- Stimulation of thirst centre In ascending limbs of nephrone: A- Chloride is passively reabsorbed B- Chloride is actively reabsorbed and sodium follows passively C- Sodium is actively reabsorbed following chloride reabsorption D- All of the above Hypochloraemia may occur in: A- Prolonged use of nasogastric tube B- Diabetes insipidus C- Renal failure D- Heart failure 6 Metabolic alkalosis may occur with: A- persistence vomiting B- Dehydration C- Hypochloraemia D- Hyponatremia Potassium ions have all the following EXCEPT: A- Is 3.5-5 meq/lit in plasma B- Mainly absorbed from small intestine by active transport C- Is the main cation in the extracellular fluid D- The dietary requirement is around 3.5mg Potassium will be completely reabsorbed in: A- Loop of Henle B- Proximal convoluted tubules C- Distal convoluted tubule D- all of the above Potassium is important for: A- Tissue growth and repair B- Contraction of skeletal but not smooth muscle C- Maintain extracellular osmolality D- Maintain extracellular PH Hypokalaemia occur in the following EXCEPT: A- Sever diarrhea B- Prolonged vomiting C- Decreased aldosteron excretion D- Large dose of digitalis All may occur in hypokalaemia EXCEPT: A- Paralytic ileus B- Hypotension C- Increased muscle and vascular tone D- Heart block Prolonged use of spironolactone may cause: A- Hyperkalemia B- Hypokalemia C- Hyponatremia D- Hypernatremia Hyperkalemia may occur in A- Acidosis B- Alkalosis C- Increased aldosteron secretion D- All of the above Neurological symptoms of hyperkalemia include: A- Cardiac disturbance B- ECG abnormalities C- Tingling D- Increased muscle tone 7 QUESTIONS///////// Part III. Unfamiliar Problems Solving Objectives. The aim of the questions in this part is to evaluate that the student can solve familiar problems with ease and can make progress towards the solution of unfamiliar problems, and can set out reasoning and explanation in a clear and coherent manner (.16….. marks). QUESTION Ventricular fibrillation occurs when potassium serum level exceeds : A- 5 mEq/liter B- 7 mEq/liter C- 11 mEq/liter D- All of the above Production of acetoacetic acid, in diabetes mellitus is due: A- Incomplete oxidation of fatty acid B- Over production of lactic acid C- Over production of glucose D- Only occur in type I diabetes Respiratory system regulates PH by keeping normal arterial level of: A- CO2 Concentration B- Oxygen concentration C- Bicarbonate D- All of the above Corticospinal tract lesion may be associated with the following EXCEPT: A- Spasticity B- Hypertonia C- Babinisk's sign D- Hyporeflexia Causes of hyperventilation involve the following EXCEPT: A- Inhibition of respiratory centre in brain stem B- Hypoxia C- Pulmonary D- Excessive artificial respiration Best way to correct acid-base balance resulted from salicylate poisoning is to measure: A- Urea S.L B- Creatinine serum level C- Blood PH measurement D- All of the above Carpopedal spasm (tetany) may result from: A- Hypocalcaemia B- hypercalcaemia C- Respiratory acidosis D- Metabolic acidosis Metabolic acidosis may occur in hypofunction of : A- Thyroid gland B- Adrenal gland C- Hypofunction of pituitary gland D- All of the above 8 Common tests used to diagnose metabolic acidosis involve all EXCEPT: A- Plasma urea B- Creatinine serum level C- Ketone bodies in urine D- Blood gases saturation PCO2 less than 30mmHg may cause: A- Metabolic acidosis B- respiratory acidosis C- Respiratory alkalosis D- Respiratory acidosis The primary disorder in metabolic acidosis is: A- Increase in bicarbonate B- Reduced bicarbonate C- Increase formation of ammonia D- Decrease production of non-volatile acid Metabolic acidosis, may occur in all EXCEPT: A- Sever hyperglycaemia B- Asthma(status asthmaticus) C- Sever starvation D- All of the above Dehydration may cause: A- Respiratory alkalosis B- Respiratory acidosis C- Metabolic acidosis D- Metabolic alkalosis In respiratory acidocis A- Always there is increased pco2 B- The degree of compensation is adequate in status asthmatics C- The renal production of bicarbonate is high in bronchopneumia D- Bicarbonate. co2 ratio is normal Cardiac disturbances in respiratory acidosis may be A- Bradycardia B- Tackycardia C- Delirium D- Hallucination In respiratory acidosis . the following may occur A- Hypercalicaemia B- Hypokalaemia C- Hyponatraemia D- Hypocalicaemia 9