Mgt 4310 Week 4
advertisement

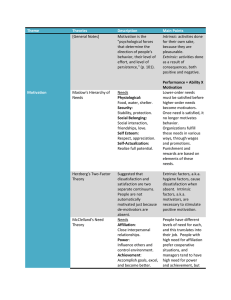
Mgt 4310 Week 4 Motivation An internal state Manager’s motivate employees by creating an environment where motivation is aligned to organizational goals. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self-actualization Self-esteem Social Belonging Security Physiological Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Self-Actualization The need to develop one’s true potential and skills (creative, autonomous tasks) Self-Esteem The need for feelings of adequacy, competence, and confidence (awards, prestigious titles, promotions) Belongingness The need for social interaction, affection, friendship (opportunities to interact, supportive supervision) Safety The need for security, freedom from anxiety, order (job security, comfortable work environment, adequate pay) Physiological The needs for survival, such as, food, water, shelter (minimum pay and existence level support) Aldefer’s ERG Theory Needs – needs satisfied by material substances Existence Needs – the need for meaningful social relationships Relatedness Needs – need for developing one’s potential Growth Social Reinforcement Theory Increase desirable behavior by: following with a desirable consequence (Positive Reinforcement) • Or removing an undesirable consequence (Negative Reinforcement) Social Reinforcement Theory Decrease undesirable behavior by: following with a undesirable consequence (Punishment) • Or removing the desirable consequence (Extinction) Hertzberg Intrinsic motivation and Extrinsic Motivation Job Design • Job Breadth, Job Enlargement (variety) • Job Depth, Job Enrichment (responsibility) Equity Theory Perceived Ratio Comparisona Employee’s Assessment Outcomes A Inequity (Underrewarded) < Inputs A Outcomes A Inputs B = Inputs A Outcomes A Inputs A aPerson Outcomes B Outcomes B Equity Inputs B > Outcomes B Inequity (Overrewarded) Inputs B A is the employee, and person B is a relevant other or referent. Expectancy Theory Ability Motivation Effort Performance Outcomes (rewards) A person’s motivation is a function of: A. Effort-to-performance expectations B. Performance-to-outcome expectancies C. Perceived valence of outcomes Motivation Equals = Valence (Value of Outcome) Effort (E > P) Performance Expectancy (E) (probability of Effort leading to Performance) Influenced by Ability (P > O) Reward Outcome Instrumentality (I) (probability of Performance leading to Reward Outcome) Implications of expectancy (Nadler and Lawler) Understand outcomes valued by employees Define desired behaviours (measurable) Make sure performance is reachable Link performance to outcomes Look for conflicting expectancies (interfering outcomes) Make rewards significant enough to be motivate Check for equity Goal-Setting Theory Setting specific goals increases performance Difficult goals result in higher performance Feedback causes higher performance than nonfeedback Goals must be accepted by the individual people are more committed to goals they set themselves and make public Social Cognitive Effects: Self-Fulfilling Prophecy When our expectations about another person cause that person to act in a way that is consistent with our expectations. Steps: Expectations formed about future performance Behaviour toward the person is consistent with our expectations Effects are produced on the person’s beliefs (selfefficacy), motivations and performance Behaviour fulfills expectations and reinforces original perceptions Creating a Motivation Model Independent variable – a predictor variable (e.g. effort). Predicts outcomes. Normally found at the beginning of your model. Dependent variable – an outcome or criterion variable (e.g. performance). Found at the end of your model. Moderator variable – variables that will effect the relationship between the independent and dependent variables (e.g. ability). Normally placed at the edges of the model with links to the independent and dependent variables. Mediator variable – a variable that links the independent and dependent variables. Found between the independent and dependent variable. The only link between the independent and dependent variable is through the mediator, otherwise the independent variable has no link to the dependent variable. Ability Effort Performance Satisfaction Job Characteristics Model Job enrichment Combine tasks Establish client relationships Reduce supervision Increase autonomy and decision making Have direct feedback on performance Recognizing Contributions Build self-confidence through high expectations Connect performance to rewards Use a variety of rewards Be positive and hopeful Within groups of about 5 members, use the process theories to: Develop a recommendation to present to the class on the way that you can motivate yourself and your classmates. • Make sure that you can explain the link to the theory or theories • Remember the instructor is not the sole initiator of motivation • Ideas that can be comfortably managed will be implemented Focus on whole not the individual Issues Concentrating rewards on the Stars Concentrating outside not inside Self-fulfilling prophecy gone wrong Ignoring the culture