Torque problem 9-33
advertisement
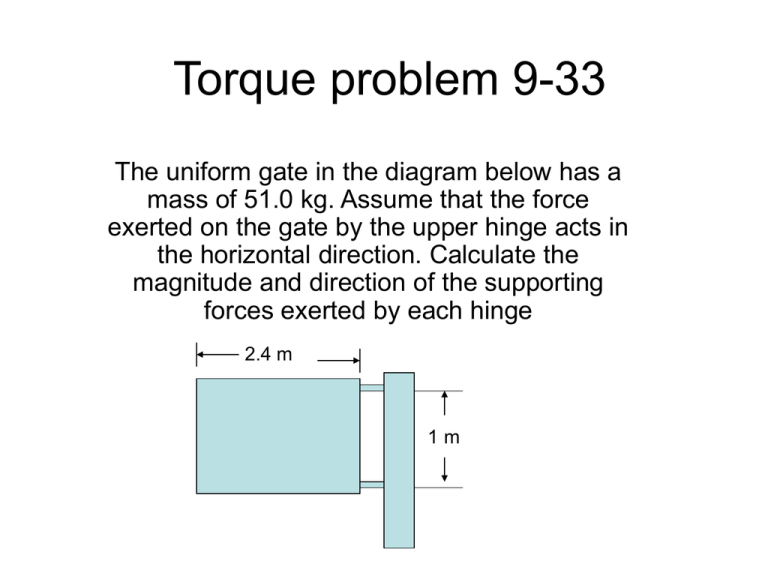
Torque problem 9-33 The uniform gate in the diagram below has a mass of 51.0 kg. Assume that the force exerted on the gate by the upper hinge acts in the horizontal direction. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the supporting forces exerted by each hinge 2.4 m 1m • Use static equilibrium net Torque = 0 • Choose the pivot point at the lower hinge • Gate torque at its center of mass Fup 1.2m d1 1m FG Pivot point NET = = FG d1 – Fup (1m) = 0 • Find d1 • d12 = (1.2)2 +(0.5)2 • d1 = 1.3 m Fup 1.2m FG 1m d1 Pivot point Find FG • Find angle 1.2m Cos = 1.2/1.3 = 0.923 1.3 m = cos-1(0.923) = 22.620° Pivot point • Find FG and component perpendicular to d1 1 2 FG FG = 51 kg 9.81 m/s2 = 500 N + 2 = 90 and 1 +2 = 90 = 1 FG = FG cos = 500N 1.2/1.3 = 461.8 N NET = = FG d1 – Fup (1m) = 0 • D1 = 1.3 m • FG = 461.8 N FG d1 = Fup (1m) Fup = 461.8 N 1.3m/1m = 600 N Find Fdn • Apply equilibrium conditions to forces FNET = F = 0 F is a vector so FX = 0 FY = 0 600 N 1.2m d1 1m 500 N For lower hinge FX = - 600 N FY = 500 N Therefore the magnitude of Fdn is ((500)2 + (-600)2)1/2 = 781 N For the direction, the opposite side is 500 N and the adjacent side is 600 N = tan-1(500/600) = 39.8 ° above the horizontal