RENEWABLE ENERGY
advertisement

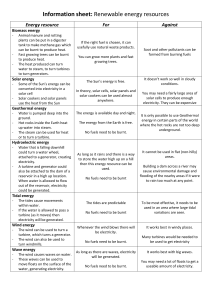
RENEWABLE ENERGY Solar Energy Power from the sun Produced by nuclear fusion reactions in the sun’s core Passive Solar Heating: Uses the sun’s energy to heat something directly Oriented according to the yearly movement of the sun Active Solar Heating: Energy from the sun is gathered by collectors & used to heat water or to heat a building Photovoltaic Cells: Convert the sun’s energy into electricity Energy is stored in batteries which supply electricity when the sun is not shining Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Wind Power Converts the movement of wind into electrical energy Fastest growing energy source in the world Cost has declined Problem with transporting electricity Biomass Using plant material, manure & any other organic matter as an energy source Methane Produced when bacteria decompose organic wastes Can be burned to generate heat or electricity Alcohol Produced by fermenting fruit or agricultural waste (ex: ethanol from corn) Hydroelectricity Produced from the flow of moving water 20% of the world’s electricity Water in a reservoir is released to turn a turbine, which generates electricity Expensive to build, relatively inexpensive to operate Doesn’t contribute to acid rain like burning fossil fuels does Dams last longer than most fossil fuel power plants do Changes a river’s flow & can disrupt ecosystems Geothermal The energy from heat in the Earth’s crust Power plants pump heated water or steam from rock formations and use the water or steam to power a turbine that generates electricity Water must be managed carefully so it is not depleted Geothermal heat pumps can be used to both heat & cool homes Geothermal Conservation Around the Home