Enzymes Regulate cell chemisty
advertisement
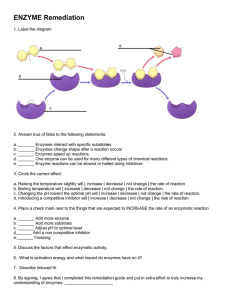
Enzymes Regulate cell chemisty Enzymes • Enzymes- are biological catalysts, or chemicals that accelerate a chemical reaction without itself being affected by the reaction. Enzymes • Groups of enzymes work together to carry out a given metabolic function. • This process must be regulated in order to allow the cell to meet its changing needs for energy. Enzymes • Enzymes - are vital to such bodily functions as digestion Large Insoluble Molecule Type of Enzyme Small Soluble Product Carbohydrate (e.g. Starch) Carbohydrase Simple Sugars (e.g. glucose) Protein Protease (e.g. pepsin) Amino Acids Fat/Lipids Lipase Glycerol and Fatty Acids Enzymes • 1.Enzyme – usually end in ase • Amylase -enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars (saliva) • Lactase – enzyme that breaks down sugar to produce energy • Enzymes often associate with other molecules to get the job done done….. Enzymes 2. Cofactor Aid in the action of the enzyme • Non-protein • link to enzymes / presence is essential to the activity of those enzymes Enzymes • Cofactors work by changing the shape of an enzyme • Specificity Enzymes • 3. Substrate In an enzymatic reaction, the reactant that the enzyme acts upon is: – Substrate Lactase Lactose Galactose Glucose Enzymes • A number of variables effect enzyme activity: • Temperature • pH Enzymes Heat-sensitive enzyme Controls Melanin • Less enzyme activity in warmer areas (lighter) • More enzyme activity in cooler areas(darker) • The enzyme the determines melanin optimal temp is below 103