Headache or facial or neck pain attributed to arterial dissection (ICHD-6.5.1)
advertisement
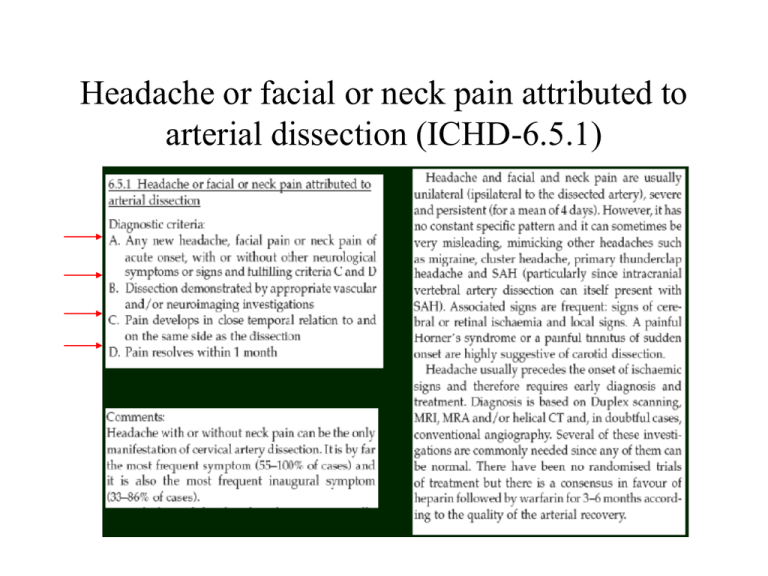
Headache or facial or neck pain attributed to arterial dissection (ICHD-6.5.1) Cervical Spine Adjusting and the Vertebral Artery Arterial dissection Unveiling the Risks • Head Position – Dental procedures – Ceiling Painting • Sports Activities – Wrestling – Judo – Treadmill running • Accidents – Motor vehicle accidents – Falls – Airbag or seatbelt trauma • Neck Trauma – Cervical manipulation – Abuse – Incredibly, even sea wave induced trauma – Hand-held massager • Leisure Activities – Roller coasters – Yoga • Infection – Narrowing of blood vessel – Bouts of violent coughing These factors can cause an arterial dissection which result in a secondary stroke About Stroke and dissection.. • • • • 3,000 VADs per year (700,000/yr in USA). 1 of every 233 strokes is related to a VAD. 75% of VAD related strokes make a good recovery. 5% of VAD related strokes result in death. • 13% of stroke and under-diagnosed (CSC). • Incidence of 2.5~3/100,000 (carotid), and 1~1.5/100,000 (vertebral) (CSC=Canadian Stroke Consortium) Genetic factors? • Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.(rubber man syndrome) • Fibromuscular dysplasia. • Ultrastructural connective tissue abnormality. • Homocystinaemia. • Marfan’s syndrome. • Cystic medial necrosis. • Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. Two risks is relevant to dissection: trauma+ CTD (CSC) Arterial Dissection • Occurs when there is breakdown in the vessel wall of the artery causing blood to flow into the tissue layers instead of into the lamina and clot formation. (Norris et al, 2000) • Typically, the subsequent stroke is secondary to the dissection. Subintimal vs. Subadventitial Vessel lumen Aneurysm Types of Arterial Dissection 2 specific types – Carotid Artery Dissection (CAD) – Vertebral Artery Dissection (VAD) Normal Dissected Carotid artery dissection (CAD) • CAD are 3-5 times more prevalent than VAD. • Presenting signs and symptoms include: – – – – – – – Unilateral headache. Local pain. Ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome. Dysarthria and Dysphagia. Memory impairments. Hemiparesis. Visual impairment involving one field of vision. (retinal occlusion may be a heralding symptom of dissection in some cases) (Campellone et al, 2004) CAD • Classic triad: =Unilateral headache. =Ipsilateral partial Horner’s syndrome. =Contralateral hemispheric findings--aphasia, neglect, visual disturbance or hemiparesis. • Diagnosis is via angiography (CTA,MRA).