Female Anatomy 1
advertisement

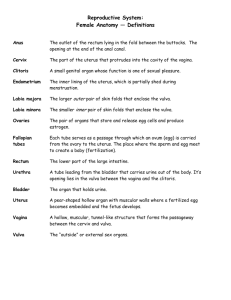
Female Anatomy 1 Vulva 2 Vulva 3 Vulva 4 Vulva 5 Vulva 6 Female Genital Exam Use a hand mirror to look at your genitals Identify the various parts Look for any unusual bumps or coloring Think about your feelings regarding your genital anatomy. Do it on a regular basis 7 Vulva External genitals Mon veneris Labia majora and minora Clitoris 8 Clitoris 9 Clitoris Homologus to penis Same # of nerve endings as the head of penis Only purpose is sexual arousal Most common method of self stimulation & orgasm 10 Underlying structures 11 Clitoris photo 12 Underlying structures Vestibular bulbs Bartholin’s glans 13 Pelvic floor muscles 14 Kegel Exercises Urinary control after childbirth Increases genital sensitivity Increases sensation during intercourse Technique of doing exercises 15 Internal structures (summary) Vagina Vasocongestion = lubrication Grafenberg (G) spot Cervix Uterus Ovaries 16 Vagina, Uterus, Ovaries 17 Uterus & Ovaries 18 Vagina Vaginal opening has highest concentration of vaginal musculature Inner 2/3 = fewest nerve endings Changes during intercourse Orgasmic platform 19 Vaginal lubrication The first sign of sexual arousal Occurs within 10 – 30 seconds after effective physical or psychological stimulation Seeps through the vaginal walls as vasocongestion occurs. 20 Other vaginal lubrication Saliva Water-based lubricant Lubricated condoms Not Vaseline 21 Chronic vaginitis Due to Birth control pills Antibiotic medication 22 Bartholin’s glands Located on either side of the vaginal opening Produces fluid Function unknown Possibly to lubricate entrance to vagina 23 Hymen Use is largely unknown Types Imperforate hymen 24 Female Anatomy (Cont.) 25 Grafenberg (G) spot Location http://mama.indstate.edu/users/nizrael/grafenberg. html Female counterpart to male prostate gland Female ejaculation 26 Cervix Cervical cancer - increases risk due to Genital warts Having several male sexual partners First intercourse at an early age Cigarette smoke 27 Uterus Endometrioses Cells from uterine lining implant in abdominal cavity 28 Ovaries 40,000 to 400,000 innature ova at birth 300 - 450 mature in a woman’s lifetime Ovaries are endocrine glands Produce sex hormones Estrogen and progesterone 29 Fallopian tubes 30 After release from ovary, eggs viable for 24-48 hours for fertilization 31 Breasts 32 Breasts Size Fatty tissue determines size Unrelated to milk or sensitivity Preoccupation with size Surgical alternatives Enlargement Reduction http://www.plasticsurgerypa.com/index.cfm?event=ProductView&CategoryID=33& SubcategoryID=29&ProductID=251 http://www.plasticsurgerypa.com/index.cfm?event=ProductView &CategoryID=33&SubcategoryID=30&ProductID=114 Lift http://www.plasticsurgerypa.com/index.cfm?event=Subcategory 33 View&CategoryID=33&SubcategoryID=43 Silicon Gel Breast Implants 34 Breast exams Self-exam Does Mammogram = better Not not reduce fatalities recommended for women under 40 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) = Best 35 Mammogram 36 Menstruation Menarche Onset = 11 - 15 years Menstrual synchrony Women living together develop similar cycles 37 Menstrual synchrony Synchronized menstration Apparently based on the sense of smell 38 Menopause Permanent cessation of menstruation Hormone replacement therapy Benefits Protects against Osteoporoses Cardiovascular disease Loss of vaginal lubrication KY Risks May increase estrogen dependent breast cancer Endometrial cancer 39