Testing Figures for Exam III
advertisement
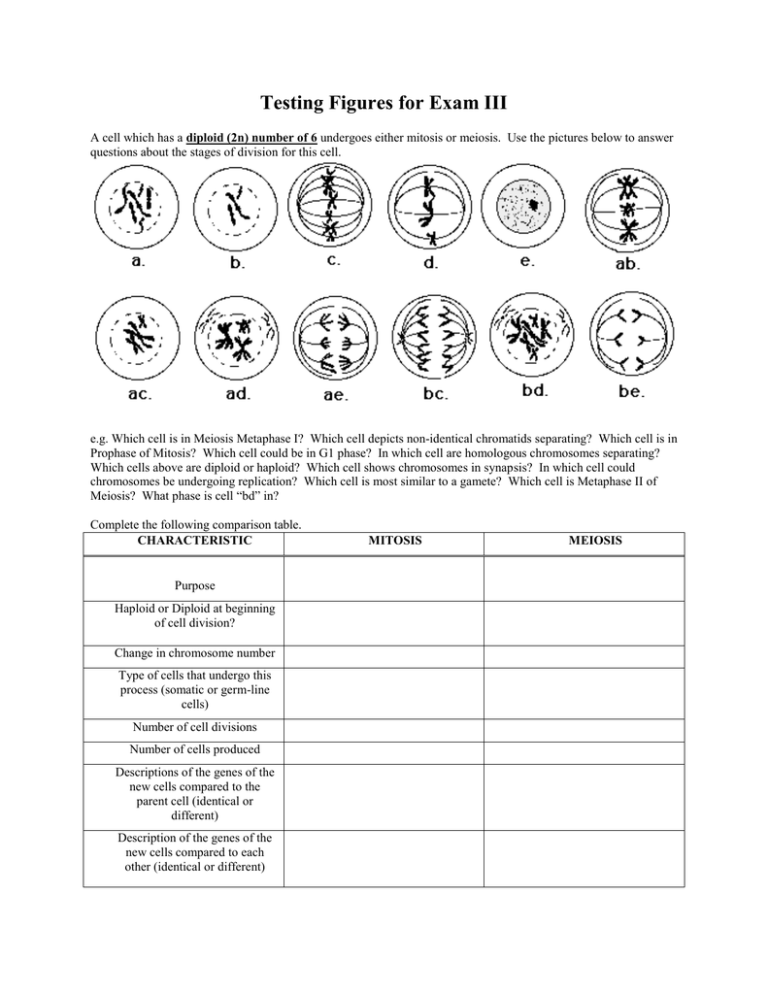
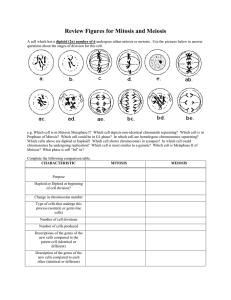
Testing Figures for Exam III A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. e.g. Which cell is in Meiosis Metaphase I? Which cell depicts non-identical chromatids separating? Which cell is in Prophase of Mitosis? Which cell could be in G1 phase? In which cell are homologous chromosomes separating? Which cells above are diploid or haploid? Which cell shows chromosomes in synapsis? In which cell could chromosomes be undergoing replication? Which cell is most similar to a gamete? Which cell is Metaphase II of Meiosis? What phase is cell “bd” in? Complete the following comparison table. CHARACTERISTIC Purpose Haploid or Diploid at beginning of cell division? Change in chromosome number Type of cells that undergo this process (somatic or germ-line cells) Number of cell divisions Number of cells produced Descriptions of the genes of the new cells compared to the parent cell (identical or different) Description of the genes of the new cells compared to each other (identical or different) MITOSIS MEIOSIS Key Words Cohesion Adhesion Heat capacity Universal solvent Acid Alkaline/Basic Hydroxyl group Amino group Carboxyl group Phosphate group (Aldehyde and Ketone) Peptide Amino acid Peptide bond Polar Non-polar Hydrophobic Hydrophilic Triglyceride Fatty Acid Glycerol Fat Oil Saturated C-C bond Unsaturated C-C bond Nucleotide Deoxyribonucleotide Ribonucleotide DNA RNA Nucleic Acid Double stranded helix Single stranded Nitrogenous base Monosaccharide/simple sugar Disaccharide Polysaccharide/complex sugar Cellulose Starch Chitin Murein/peptidoglycan Glycogen Fructose Sucrose Glucose Hormone Sterol/steroid Photosynthetic pigment cholesterol Insulation Energy storage Catalyst Structural support Mitochondrion Chloroplast lysosomes Golgi body Endoplasmic reticulum Hypotonic Hypertonic Diffusion Passive transport Active transport Faciliated transport Plasmolysis Salt Ionic bonds Covalent bonds Hydrogen bonds Solubility Light absorption Light reflection Calvin Cycle (light indpt) Light dependent reactions NAD+/NADH FAD+/FADH2 Equation for cell resp. Equation for photosynth. Pyruvate ADP + P ATP Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron transport chain ATP synthase/mill Hydrogen ion reservoir Permeable/impermeable Membrane channel proteins Fermentation Ethanol and CO2 Yeast and fermentation Human muscle cells & ferm. Bacteria and fermentation Lactic acid Matrix of mitochondrion Inner membrane Outer membrane Carbon dioxide Role of H2O in cell resp and photosyn. Enzyme Substrate Product Energy-requiring reaction Energy-liberating reaction Enzymes and pH, temp. Functions of protein Functions of lipids Functions of carbos Functions of nucl. Acids Parts of a nucleotide Competitive inhibitor Non-competitive inhibitor