Moon Project
advertisement

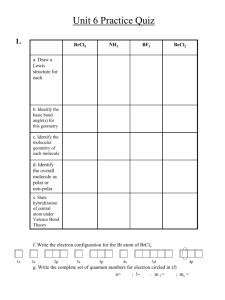
Moon Project • Because we have had so few clear nights, the Moon project deadline is extended one week until February 25. • Locate the Moon with respect to the STARS on the star map (NOT the horizon) – You need to find star patterns you recognize in the sky and on the map to determine where the Moon is – Depending on the time of night you look the Moon will be in different parts of the sky, but on a single night always close to the same stars. Announcements • Exams will be returned Wednesday. Scoring office results did not come until late today and there are some corrections needed. • Future assignments will be graded, but you are encouraged to take them until you get a perfect score. We record your last attempt. • Assignment for Wednesday is in two parts: – Part A: Astronomy Place tutorial “Light & Spectroscopy” done on Astronomy Place – Part B: Planet assignment 1 on Angel Objectives • Describe the process of emission and absorption of photons by atoms • Relate the photon energy and wavelength to the temperature of the source • Explain why each element’s atoms emit & absorb photons with only certain colors, energies, wavelengths Emission & Absorption of Light • The most common confusion mentioned was how different elements emit & absorb different color light • The second most common confusion was about thermal radiation Today we will discuss these two issues. MOST IMPORTANT • Electrons Emit & Absorb Photons of Light • Energy is CONSERVED – When an electron emits a photon, the electron loses the energy the photon carries off – When an electron absorbs a photon, the electron gain the energy the photon had Temperature • Measures motion of atoms (& molecules, ions, nuclei, electrons) • Hotter = moving Faster kT = 1/2 m v2 k=number m=mass T=temperature v=speed Not a required equation How do Atoms gain Energy 1. Absorbing a Photon 2. Colliding with another atom, electron or ion • • Hot gas Electric current (demo) Thermal Radiation 1. Hotter -> Brighter emit more radiation per unit area. Stephan-Boltzmann Law 4 E = T 2. Hotter -> Bluer emit bluer (higher energy) photons Wien Law max = 2.9 x 106 / T(K) [nm] 3. Bigger -> Brighter (more photons) Thermal Radiation Atom electron nucleus p+n proton neutron e- Energy Levels Atoms are not the same as planetary systems Only certain Orbits (Energy Levels) are allowed an electron in an atom. Like an elevator - can stop only at the floors, not in between Energy Levels E n e r g y E3 E2 E1 Absorption: e- in lower energy orbit absorbs a photon & jumps to higher energy orbit Emission: e- in higher energy orbit jumps to lower energy orbit & emits a photon Absorption & Emission of Light Interaction of Light with Matter Hydrogen • Remember that each electron is only allowed to have certain energies in an atom. • Electrons can absorb light and gain energy or emit light when they lose energy. • It is easiest to think of light as a photon when discussing its interaction with matter. • Only photons whose energies (colors) match the “jump” in electron energy levels can be emitted or absorbed. Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum). By studying the spectrum of an object, we can learn its: 1 Composition 2 Temperature 3 Velocity Emission Spectra • The atoms of each element have their own distinctive set of electron energy levels. • Each element emits its own pattern of colors, like fingerprints. • If it is a hot gas, we see only these colors, called an emission line spectrum.