Ryan High School Schedule 1—8:50-9:45 2A/2B—9:51-11:20
advertisement
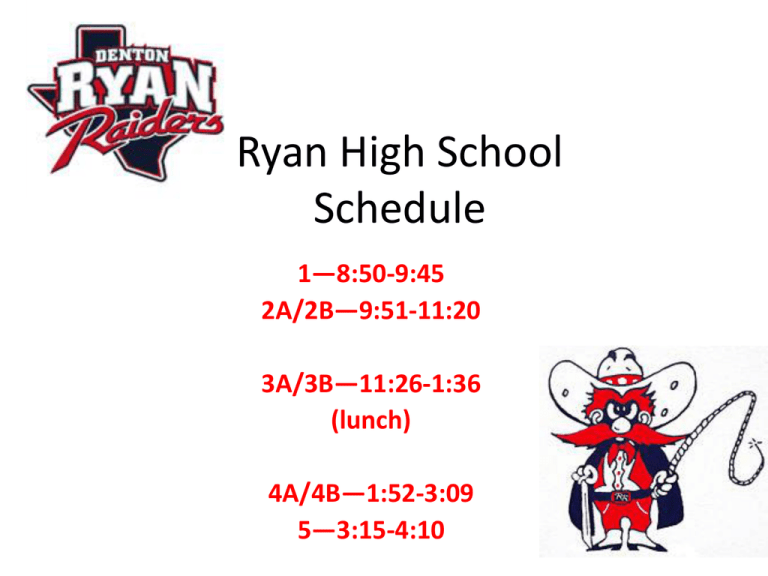
Ryan High School Schedule 1—8:50-9:45 2A/2B—9:51-11:20 3A/3B—11:26-1:36 (lunch) 4A/4B—1:52-3:09 5—3:15-4:10 Alma Mater • • • • • • • • We are Ryan High School strong And to you we sing this song Ryan Raiders we’ll be true Ryan Raiders through and through We sing to you our own proud school For without a doubt in victory we’ll shout Faith and hope anew, we are true Ryan Raiders we love you Fight Song • We are the Raiders of Ryan High • We keep our spirit and our banners high • For we are mighty and powerful and we are strong • And we pledge our loyalty all the daylong • For we are one for all and all for one • Until victory we have won • Yes we will go…fight..and we will win • For Ryan High our dear old friend Junior Year • Best year in high school and this is why… • You enter as sophomores, but you leave as • SENIORS! Welcome to United States History Class Ms. Calabrese Syllabus and Class Description See History Alive Chapter 1, page 1 U.S.: What do you remember from 8th grade U.S. History class? • Full name and class block in upper right hand corner • Survey handout with questions and matching • Survey History Alive textbook Chapters 1-7 Calabrese Strengths: • Connectedness • Context • Input • Intellection • Harmony HISTORY: WHAT IS IT? WHY DO WE NEED TO STUDY IT? HOW DO WE LEARN ABOUT IT? “There is no such thing as an uninteresting life.” Mark Twain “There is a relation between the hours of our life and the centuries of time.” Ralph Waldo Emerson “The first important step in anyone’s education is to know your own people.” Chaim Potok, The Chosen (224) “All history is gossip.” JFK “Those who can’t remember the past are condemned to repeat it.” George Santayana “History is a guide to navigation in perilous times.: “History is who we are and why we are the way we are.” David McCullough, author and historian “We can disagree without being disagreeable.” President Barack Obama U.S. History • History is the study of the past to help understand the present and prepare for the future • The U.S. is a unique “experiment” in a democratic republic • Our “founding fathers” were influenced by ideas of the Enlightenment Bloom’s Taxonomy—how we learn Alexis de Tocqueville • French historian who visited the U.S. in the 1830s • In Democracy in America, he wrote about American “exceptionalism” notably: freedom of the press mix of religions movement within social classes Alexis De Tocqueville identified five values leading to America’s success as a constitutional republic 1. Liberty 2. Egalitarianism (equality) 3. Individualism 4. Populism 5. Laissez-faire (leave things alone!) So does history ever change? • Yes—interpretations of past events can change • The events considered important or unimportant often reflect cultural bias • Historiography is the study of how history is learned • Emphasis can be placed on different ideas and events reflected in current events when viewing past events Historical Sources • Primary Sources—eyewitnesses • Secondary Sources—2nd hand information • Is the source reliable? • Who is behind the source? • Is there a bias? Can you still use it? Who takes care of our sources? • • • • • • • Librarians Archivists Scholars Historians Curators Collectors Re-enactors Are these primary or secondary sources? • • • • • • • • • Political cartoon News article Textbook Diary Your teacher Photograph Your parent Picture album Map More sources • • • • • • • • • • TV show Documentary You-Tube Website Furniture Bullet Rock Painting Portrait Shopping catalog • • • • • • • • • Comic book Magazine Toy Movie poster War recruitment poster Movie Clothing Weapon Campaign button “Brushes with History” • Personal connections or memories • Classes at school • Personal experiences • Family stories • People You are a witness to history—consider your personal timeline • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1997—NASA lands a probe on the surface of Mars 1998—Impeachment of President Clinton 1999—Space Shuttle Discovery docks with International Space Station 2000—closest presidential election in history 2001—Terrorist attack on the U.S. on September 11 2002—invasion of Afghanistan 2003—invasion of Iraq 2004—Re-election of Bush 2005—Hurricane Katrina 2006—Airplanes ban liquids of over 4 oz. on flights 2007—Beginning of the Great Recession 2008—World-wide financial crisis, election of Obama 2009—Tea Party Formed 2010—Osama Bin Laden killed by U.S. Seals 2011---Occupy Wall Street 2012—Re-election of Obama 2013—Government shut-down 2014—Ebola Virus in Dallas, Texas 2015—Started U.S. History with Ms. Calabrese Six Degrees of Separation • • • • • • • • • President Obama President Bush JFK Elvis Marilyn Monroe Princess Diana Frank Sinatra 9-11 Victim General Patton AP Test--Format See other power point on themes periods





