Note Taking Guide Topic # 3035 Natural Selection
advertisement

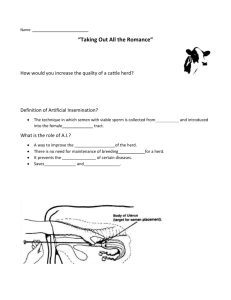
Note Taking Guide Topic # 3035 Natural Selection I. What is evolution? ¨ A change in the ________ makeup of a population with time. ¨ It is a two-step process 1. Development of genetic variability in the population. 2. Natural selection of those variations which are ____________ for survival. Example through lecture Let's say a population of black spotted cattle--BB-- eventually turn into a population of white spotted cattle--bb-- over a period of years. II. Genetic variability Assuming that a population starts out with the same genetic makeup, all new genetic material in that population will arise by mutation. 1. A ___________ is a random inheritable event. 2. Let's take our black spotted cattle as an example; for some reason the chromosomes that code for black spots are mutated. This mutation Changes the BB to Bb. Now with the b gene in the herd, White spotted cattle can arise. Variation in the chromosomes also occurs when an egg and a sperm ________. Both carry unique traits from the parents into one individual, forming an individual which varies from either parent. 1. This variation is normally a __________ event. 2. In our example, let's say two mutated animals mate with one another. Let's look at their offspring. III. Natural selection In a population certain individuals may be genetically _________ suited for the environment than others. If the environment is such that it favors these individuals then these are the individuals that will _________ to have offspring and pass their genetic makeup to their offspring. As long as the environment does not again change then these individuals will become the "__________" population. The sequence of events that leads to a certain characteristic being "selected" be the environment is called ____________ _____________. Let's design a little scenario to demonstrate natural selection It has been 50 years since the first mating of our mutated cattle. Over the years the once all black spotted herd is now about 75% black spotted and about 25% white spotted. A new disease has also mutated during this time period. A disease known as Bovine Black Spotitis. The disease is not fatal, but any black spotted bull or cow is sterile. The disease spreads quickly through the herd and within six months time all black spotted cattle are sterile. What will eventually happen to the herd? Answer Only the whit cattle will be able to reproduce, eventually producing a completely herd of white spotted cattle. IV. Use of genetic variability and natural selection in producing improved livestock. As livestock managers, we can take advantage of natural genetic _______________ in livestock. Braham cattle (Bos indicus) are know for their heat tolerance, due to the fact they have adapted to the hotter climate of Asia and Africa. Bos taurus (European cattle) does not have this characteristic. By intentionally mating Brahman cattle to European (like the Angus) we take the role of "natural selectors" by determining the matings that will take place. (we could call this unnatural selection) 1. This mating produces the "Brangus" breed. It has better carcass characteristics than the Brahman. It has better heat resistance than the Angus. 1. A similar mating between Brahman and Shorthorn cattle has produced the Santa Gertrudis Breed.