Name_____________________________________________________ Period _____ Christmas Break Assignment
advertisement

Name_____________________________________________________
Christmas Break Assignment
Period _____
Algebra II
Equations Packet
This assignment is to be completed by you over Christmas break. You are to record your answers on this
sheet of paper. All of your work must be written neatly in the packet. If your work is not shown for every
problem, you will receive no credit. This assignment will be counted as a quiz and you will also take an
exam on this material after the break. This assignment is due on Monday January 3, 2011 in class. This
means you must bring it to class, not leave it at home or in your locker. If it is not in class on Monday,
you will lose points for each day it is late. If you need to ask any questions, please feel free to e-mail me.
1. ______________
2. ______________
3. ______________
4. ______________
5. ______________
6. ______________
7. ______________
8. ______________
9. ______________
10. ______________
11. ______________
12. ______________
13. ______________
14. ______________
15. ______________
16. ______________
17. ______________
18. ______________
19. ______________
20. ______________
21. ______________
22. ______________
23. ______________
24. ______________
25. ______________
26. ______________
27. ______________
28. ______________
29. ______________
30. ______________
Equations
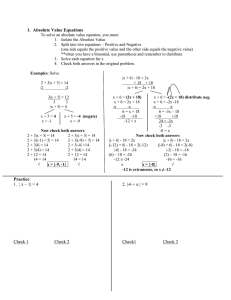
1. Absolute Value Equations
To solve an absolute value equation, you must:
1. Isolate the Absolute Value
2. Split into two equations – Positive and Negative
(one side equals the positive value and the other side equals the negative value)
**when you have a binomial, use parenthesis and remember to distribute
3. Solve each equation for x
4. Check both answers in the original problem.
Examples: Solve
|x + 6| - 18 = 2x
+ 18 + 18
|x + 6| = 2x + 18
2 + 3|x + 5| = 14
-2
-2
3|x + 5| = 12
3
3
|x + 5| = 4
x+5=4
x = -1
x + 5 = -4 (negate)
x = -9
Now check both answers
2 + 3|x + 5| = 14
2 + 3|x + 5| = 14
2 + 3|(-1) + 5| = 14
2 + 3|(-9) + 5| = 14
2 + 3|4| = 14
2 + 3|-4| =14
2 + 3(4) = 14
2 + 3(4) = 14
2 + 12 = 14
2 + 12 = 14
14 = 14
14 = 14
√
x = {-9, -1}
√
x + 6 = (2x + 18)
x + 6 = 2x + 18
-x
-x
6 = x + 18
-18
-18
-12 = x
x + 6 = -(2x + 18) negate
x + 6 = -2x -18
-x
-x
6 = -3x – 18
+18
+18
24 = -3x
-3 -3
-8 = x
Now check both answers
|x + 6| - 18 = 2x
|x + 6| - 18 = 2x
|(-12) + 6| - 18 = 2(-12)
|(-8) + 6| - 18 = 2(-8)
|-6| - 18 = -24
|-2| - 18 = -16
(6) – 18 = -24
(2) – 18 = -16
-12 ≠ -24
-16 = -16
x
x = {-8}
√
-12 is extraneous, so x ≠ -12
Practice:
1. | x – 1| = 4
Check 1
Check 2
2. |-6 + a | = 9
3. 2|2x – 4| = 86
Check 1
Check 2
4. |-5x| + 4 = -11
Check1
Check 1
Check 2
Check 2
|𝑥+4|
Check 1
Check 2
6. -4|b – 2|-9 = -37
Check 1
7. |x + 6| = 2x
Check 1
Check 2
8. |2x + 12| = 7x – 3
Check 1
9. |2x – 6| - x = 3
Check 1
Check 2
10. |4x + 5| + 3x = 10
5.
10
=1
Check 1
Check 2
Check 2
Check 2
2. Radical Equations
To solve a radical equation:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Isolate the radical on one side of the equation
Square or both sides of the equation
Solve the remaining equation for x
Check answer in the original problem. (Extraneous Roots)
Model Problem 1: Solve: 3 = √𝑥 − 1
2
(3)2 = (√𝑥 − 1)
9=x–1
10 = x
Check: x = 10
3 = √𝑥 − 1
3 = √10 − 1
3 = √9
3 = 3 √ Check
Model Problem 2: Solve: √3𝑥 + 1 − 1 = 𝑥 − 4
√3𝑥 + 1 = 𝑥 − 3
2
(√3𝑥 + 1) = (𝑥 − 3)2
3x + 1 = x2 – 6x + 8
0 = x2 – 9x + 8
0 = (x – 8) (x – 1)
(x – 8) = 0 (x – 1) = 0
x=8
x=1
Check: x = 8
√3𝑥 + 1 − 1 = 𝑥 − 4
√3(8) + 1 − 1 = 8 − 4
√24 + 1 − 1 = 4
√25 − 1 = 4
5–1=4
4 = 4 √ check
Practice: Solve each radical equation and check.
11. √−8 − 2𝑥 = 4
Check
x=1
√3𝑥 + 1 − 1 = 𝑥 − 4
√3(1) + 1 − 1 = 1 − 4
√3 + 1 − 1 = −3
√4 − 1 = −3
2 – 1 = -3
-1 = -3 x Reject!
12. √𝑥 − 4 = −12
Check
13. √2𝑥 − 6 = √3𝑥 − 14
Check
(hint: If a radical is on both
sides of the equation, square
both sides, then solve)
14. √𝑥 + 1 + 2 = 4
Check
15. √8𝑥 = 𝑥
Check
16. 𝑥 = 4 + √2𝑥 − 8
Check
17. 𝑦 = √6𝑦 + 16
Check
18. √2𝑥 − 7 = 𝑥 − 3
Check
19. −3 = √37 − 3𝑥 − 𝑥
Check
20. √3𝑥 − 8 + 1 = 3
Check
3. Solving Equations with Fractional Exponents
To solve you must:
1. Isolate the expression containing the exponent (the base)
2. Raise both sides of the equation to the reciprocal of the exponent (Give both sides a
new exponent: the reciprocal)
3. Solve for x
4. Check in the original
3
Example 1: Solve
54 = 2𝑥 2
REMEMBER:
3
2
54 = 2𝑥
2
2
Fractional Exponents represent
𝑃𝑂𝑊𝐸𝑅
radicals. 𝑅𝑂𝑂𝑇
3
27 = 𝑥 2
2
3 2
2
(27)3 = ( 𝑥 2 )3
9=x
2
3
273 = ( √27 )
= 32 = 9
−1
EXAMPLE 2: Solve:
5 = 3 + 4𝑎 6
a is the base! We must isolate it.
−1
6
−1
6
2 = 4𝑎
1
2
= 𝑎
Raise each side to the reciprocal power
The reciprocal of
1 −6
( )
2
=𝑎
26 = a
64 = a
−1
6
is -6
Negative exponents: flip the base,
exponent becomes positive
5
EXAMPLE 3: Solve:
-3 + (8 − 2𝑥)4 = 29 The base is (8 – 2x)! Isolate!
5
(8 − 2𝑥)4 = 32
4
5 5
4
Reciprocal Power!
4
((8 − 2𝑥) ) = (32)5
5
8 − 2𝑥 = ( √32)4
8 − 2𝑥 = 16
−2𝑥 = 8
𝑥 = −4
Now, solve for x!
Practice:
3
−3
21. 𝑥 4 + 6 = 33
22. 𝑥 2 =
1
1
729
3
23. 11 = 2𝑥 2 − 3
24. (𝑛 − 27)2 = 64
3
25. 26 = -1 + (27𝑥)4
5
26. 3125= (−1 – 18x)3
−3
27. 4𝑏 4 + 20 =
3
21
28. -54 = 10- (x – 10)2
2
5
29. -5126 = -6 - 5(3𝑥 + 22)3
3
30. 3646 = 1 + 5(4𝑥 + 17)2