Children and Their Basic Needs
advertisement

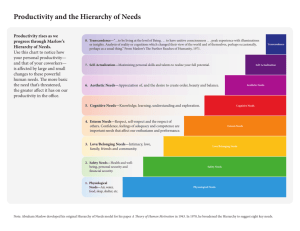
I Just Didn’t Know Children and their most basic needs. Who Am I and What am I doing Here? Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Physiological Lowest level – life sustaining needs: Air Food Bodily comforts Physiological Physiological - seeks coping information in order to meet basic needs. Information that won’t help an individual meet those basic needs in a short time is ignored. Safety/Security Out of danger, stability, dependency, protection, freedom from fear, anxiety and chaos. Safety/Security Safety – seeks help information. Needs help in seeing how they can be safe and secure. Belonging and Love Needs Affiliated with others Being accepted and loved Belonging and Love Needs Belonging and Love – seeks enlightening information searching for ways to feel like they belong and are loved. Self-Esteem Self-Evaluation – to achieve, be competent, gain approval and recognition. Self-Esteem Self-Esteem – seeks empowering information-looking for ways to develop their ego. Self-Actualization Be all that you can be. To know. To understand. Self-Actualization Edifying information Lower-academic achievement Seemingly not interested in school. Self-Actualization “In a neighborhood where the jobs people hold owe little to their education, it is natural for children as they grow older, to regard school as a brief prelude to work rather than as an avenue to their future opportunities” Plowden Report of 1967 Self-Actualization Who attends high poverty and high minority schools? Who are our lowest achieving student? Who is more likely to be taught by under-qualified teachers? Self-Esteem Needs Perceived competence is only acquired through successful experiences Success build success Failure builds failure Self-Esteem Needs Repeated Failure Low achievement expectancy. Low academic self concept. Self-Esteem Needs If people don’t expect to succeed, they seldom put forth the effort needed for success Low Expectation Low Effort Belonging and Love Needs “If children are brought up in love, they learn to love.” Belonging and Love Needs Economic hardships influence how parents interact with their children. (Hashima and Amato, 1994). Children who are poor are more likely to be victims of child abuse. (Jaudes and Voohis, 1995). Belonging and Love Needs Schools seldom fulfill this need so these children may not identify with school. Absenteeism Non-compliance Disruptiveness Inattentiveness (Fixin and Cox, 1992) Belonging and Love Needs Most frequently cited reason for dropping out of school. (Quigley, 1992). So, how do they fulfill this need? Safety Needs Toxic Homes + Toxic Environments = Toxic Lives Twice as likely to live in over-crowded and substandard housing. Low Income Indoor Pest Indoor Pollutants (Evans & Kantrowitz) (Am. Housing Survey) Safety Needs Low-income, ethnic minority children are more likely to live in environments with toxic waste (Evans & Kantrowitz, 2002). Safety Needs Critical Mass When many poor households are lumped up together, a critical mass is created. As more stable, middle-class households move away, a chain reaction begins. Social meltdown, rising crime rates, high levels of drug abuse and alcoholism, accelerated family breakdown --- neighborhood deterioration-ignites. Bad neighborhoods destroy good people. (Rusk Report,1996) Safety Needs SES Neighborhood All-cause mortality Cardiovascular risk Cardiovascular disease (Smith, et al. 1998) Injury with mortality (Cubbin, LeClere, and Smith, 2000) Crime Fear of environment (Wandersman and Nation, 1998) Externalizing and Internalizing Behavior Problems Children become sexually active earlier. (Leventhat and Brooks Gunn, 2000) Child Abuse The younger the child, the more likely to be abused. CDF, 2000. Increased exposure to trauma. Twice as likely to die before their 1st birthday. (Duncan & Brooks-Gunn, 1997) Physiological Needs Air, water, shelter Birth weight Nutrition Health care