Modern Theory of Evolution

TOPIC : Evolution
AIM : Explain the today ’ s theory of evolution.
Do Now : 1. Copy the topic and aim.
2. Complete # 6 on the back of your Natural
Selection reading notes
HW : “How did Mammoths Go Extinct” article ( This will be collected and graded.
)
6. There are 2 types of worms: worms that EAT AT
NIGHT (nocturnal) and worms that EAT DURING THE
DAY (diurnal). Birds eat during the day and seem to be eating only the diurnal worms while the nocturnal
worms are in their burrows. Each spring when the worms reproduce, that have about 500 babies but only
100 of these ever become old enough become old enough to reproduce.
• Favorable adaptation: Eating at night (not caught by birds)
• Unfavorable adaptation:
Eating during the day
• If speciation were to occur, which adaptation would the species have?
Nocturnal worms
A
B
C
D
E
F
1. Identify the type of rock fossils are located in.
Sedimentary rock
2. Identify the layer with the oldest fossils. F
3. Identify the layer with the most complex fossils.
A
4. Identify the layer with the youngest fossils. A
5. Identify the layer with the least complex fossils.
F
1. What kind of evidence for evolution does this represent?
Similarities in embryological development
2. What does this evidence suggest?
These species evolved from a common ancestor.
Identify the part of the theory of Natural Selection represented in the diagram below. Support your answer.
• Speciation
• One species of finch evolved into many species of finches.
What environmental factor caused the speciation of finches?
• The source of food on each island.
Review :
1. Explain the theory of Natural Selection.
2. Explain what Darwin meant by the term overproduction .
3. Explain what organisms compete for and what the result of competition is.
4. Explain what Darwin says about variation .
5. Describe ‘Survival of the Fittest.’
6. Describe speciation .
Sources of
•
Sexual Reproduction genetic
•
Genetic engineering variation in a
•
Selective breeding species
•
Mutations (changes in
DNA)
• Migration : moving into or out of an area
Rate of
Evolution
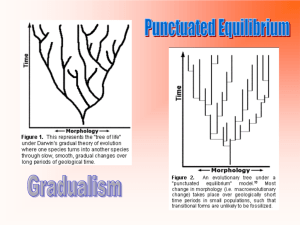
1. Gradualism:
• Evolution occurs SLOWLY &
CONTINUOUSLY through time
2. Punctuated Equilibrium
• Sudden changes in a species after long period of no change
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zjR6L38yReE
• Ex: Bacteria have evolved resistant to certain antibiotic
Punctuated Equilibrium Today
• Penicillin has been in use since 1943. It originally came from the fungus
Penicillium.
• 1947: Species of bacteria that cause pneumonia and other infections already had developed resistance to the drug.
• By the 1990s, several disease-producing bacteria had become resistant to penicillin and many other antibiotics.
• When penicillin was used to kill bacteria, those with the penicillin-resistant variation survived, reproduced, and passed this trait to their offspring.
• Over a period of time, this bacteria population became penicillin-resistant.
GRADUALISM
PUNCTUATED
EQUILIBRIUM
• *BOTH THEORIES SEEMED
TO HAVE OCCURRED
DURING EARTH ’ S
HISTORY*
Which organisms
• Those that reproduce at a very fast rate have
–Ex: bacteria, insects
evolved quickly?
Extinction
As long as species have been evolving, species have been going extinct. It is estimated that over 99.9% of all species that ever lived are extinct . The average lifespan of most species is 10 million years , although this varies widely between taxa.
There are a variety of causes that can contribute directly or indirectly to the extinction of a species or group of species.
Most simply, any species that cannot survive or reproduce in its environment and cannot move to a new environment where it can do so, dies out and becomes extinct . Extinction of a species may come suddenly when an otherwise healthy species is wiped out completely, as when toxic pollution renders its entire habitat unlivable; or may occur gradually over thousands or millions of years, such as when a species gradually loses out in competition for food to better adapted competitors.
In the natural course of events, species become extinct for a number of reasons, including but not limited to:
• extinction of a necessary host, prey or pollinator
• inter-species competition
• inability to deal with evolving diseases
• Sudden changing environmental conditions
Recently, HUMANS have become an additional cause of extinction for some species, by being a mega-predator or by transporting animals and plants from one part of the world to another.
(e.g., livestock released by sailors onto islands as a source of future food, rats escaping from boats). In most cases, introducing these invasive alien species , can affect native species directly by eating them, competing with them, and introducing pathogens or parasites that sicken or kill them or, indirectly, by destroying or degrading their habitat.
• Very little variation in a
What can
species
cause extinction?
• Major environmental change
• If adaptation no longer favorable all organisms die extinction
Let ’ s summarize…
1. Identify some sources of variation.
Sexual repro, genetic engineering, selective breeding, mutations, migration
2. Identify the theory in which there is no evolution for a long period of time followed by brief periods of change.
Punctuated equilibrium
3. Identify TWO THINGS can cause a species to become extinct?
• No variation within a species
• Major environmental change the species cannot adapt to
Which population of organisms would be in greatest danger of becoming extinct?
(1) A population of organisms having few variations living in a unchanging environment.
(2) A population of organisms having few variations living in an changing environment.
(3) A population of organisms having many variations living in a unchanging environment.
(4) A population of organisms having many variations living in an changing environment.
Which statement could best be inferred from the information in this diagram?
(1) Evolution does not involve gradual change.
(2) Evolutionary changes can result in extinction.
(3) Evolution begins with plants.
(4) Evolution produces organisms that all fill the same niche.
1. Identify the common ancestor.
Species A
2. Identify species that have become extinct.
Species C, D, H, L, O, P
3. Identify the species that have not become extinct.
Species J, K and M
Which statement about the rates of evolution for different species is in agreement with the theory of evolution?
(1) They are identical, since the species live on the same planet.
(2) They are identical, since each species is at risk of becoming extinct.
(3) They are different, since each species has different adaptations that function within a changing environment.
(4) They are different, since each species has access to unlimited resources within its environment.
Which concept is not a part of the theory of evolution?
(1) Present-day species developed from earlier species.
(2) Some species die out when environmental changes occur.
(3) Complex organisms develop from simple organisms over time.
(4) Change occurs according to the needs of an individual organism to survive.
Fossil records indicate that between 80 and
60 million years ago the structure of the horned dinosaur underwent rapid changes separated by long periods of stability. This pattern of change best illustrates the concept of
(1) use and disuse
(2) punctuated equilibrium
(3) gradualism
(4) enzyme specificity
A key concept in the modern theory of evolution explains
(1) how new organs arise according to the needs of an organism
(2) how variations occur within a species
(3) the continued increase in the human population
(4) the presence of asexual reproduction within a species
Some scientists suggest that the extinction of dinosaurs resulted from sudden global weather changes caused by the impact of an asteroid on
Earth. This event most likely promoted the evolution of new species of animals. These ideas best support the concept of
(1)punctuated equilibrium
(2) use and disuse
(3) gradualism
(4) geographic isolation
The diversity within the wild bird species in the diagram below can best be explained by which process?
(1) natural selection (3) ecological succession
(2) asexual reproduction (4) mitotic cell division
Which concept would be correctly placed in box X?
(1) use and disuse
(2) variation
(3) transmission of acquired traits
(4) changes in nucleic acids
Which statement is not part of the concept of natural selection?
(1) Individuals that possess the most favorable variations will have the best chance of reproducing.
(2) Variation occurs among individuals in a population.
(3) More individuals are produced than will survive.
(4) Genes of an individual change to adapt to a changing environment
According to the theory of natural selection, why are some individuals more likely than others to survive and reproduce?
(1)Some individuals pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes.
(2)Some individuals are better adapted to exist in their environment than others are.
(3)Some individuals do not pass on to their offspring new characteristics they have acquired during their lifetimes.
(4)Some individuals tend to produce fewer offspring than others in the same environment.
Charles Darwin proposed that organisms produce many more offspring than can possible survive on the limited amount of resources available to them. According to
Darwin, the offspring that are most likely to survive are those that
(1.) are born first and grow fastest
(2.) are largest and most aggressive
(3.) have no natural predators
(4.) are best adapted to the environment
Darwin's studies of finches on the
Galapagos Islands suggest that the finches' differences in beak structure were most directly due to
(1.) acquired characteristics in the parent finches
(2.) the size of the island where the finches live
(3.) mating behaviors of the different finch species
(4.) adaptations of the finches to different environments