Normal flora of human body
advertisement

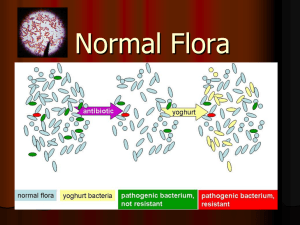
Assist Prof Microbiology Syed Yousaf Kazmi Define and classify normal microbial flora of human body Explain the beneficial role of microbial flora Explain the disease causing ability & clinical importance of microbial flora Population of microorganisms that inhabit the skin and mucous membranes of healthy normal persons (also called commensals) Commensals are organisms that derive benefit from another host but do not damage that host Internal organs/ cavities are sterile Two groups: ◦ The relatively fixed type of org ◦ The transient flora –org that inhabit the skin or mucous membranes for hours, days, or weeks IMPORTANT ◦ Staphylococcus epidermidis LESS IMPORTANT ◦ Staphylococcus aureus, Corynebacterium (diphtheroids), various streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, anaerobes (e.g., Propionibacterium), yeasts (e.g., Candida albicans) low pH, the fatty acids in sebaceous secretions, and the presence of lysozyme-eliminate nonresident microorganisms CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE ◦ Staph epidermidis imp cause of infective endocarditis ◦ Propionibacterium and Peptococcus-situated in the deeper follicles in the dermis-cause of acne ◦ Candida albicans-can enter into blood through I/V lines, drips that can result in systemic candidiasis NOSE ◦ Staph aureus -Imp cause of Staph aureus infections ◦ Other-S. epidermidis, Corynebacterium (diphtheroids), various streptococci MOUTH ◦ Viridans streptococci-cause of sub-acute endocarditis ◦ Strep mutans- cause of dental plaques ◦ Gingival crevices-Various anaerobes, e.g., Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, streptococci, Actinomyces israeli THROAT ◦ Viridans streptococci, Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria species Muhammad Talha 58-years-old man, smoker presents with shortness of breath, cough, expectoration of rusty colored sputum. His Chest X-rays showed consolidation of right lower lobe of lung. Sputum and blood culture isolated Strep pneumoniae. The most likely source of this pathogen in this patient is a. From another patient in community b. Patient’s own GIT flora c. Patient’s own throat flora d. Ingestion of contaminated water from community e. None of the above Correct Answer: c SMALL INTESTINE – Duodenum, jejunum and upper ileum- Enterococci and lactobacilli – Lower ileum, ceacum and large intestine- Fecal flora LARGE INTESTINE – Approx 96-99% fecal flora are Anaerobes – Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium spp, Clostridium spp (C perferingens), Anaerobic lactobacilli, Anaerobic streptococci (Peptostreptococci) – 1-4% are Coliform (e.g. E. coli, Klebsiella ), Enterococci, Pseudomonas – Candida in 10% population – Minor trauma e.g. sigmoidoscopy, enema etc-bacteremia in 10% Lactobacillus-maintains acid pH of vagina and prevent overgrowth of pathogens e.g. Candida albicans Intake of antimicrobials supress Lactobacillus- Candida vaginitis B. fragilis, Clostridium perfringens, C. albicans E. coli, group B streptococci-may colonize in certain ♀ CLINICAL IMPORTANCE Group B streptococci-imp cause of neonatal sepsis in newborn Recurrent UTI in ladies colonized by E coli A 25-years-young lady reported with upper respiratory tract infection. General practitioner prescribed Tab Co-amoxiclav for 3 days. On 4th day, lady experienced itching, thick curdy discharge from vagina. Gram stain of the discharge reveal numerous pus cells and gram positive budding microorganism. The cause of this infection is most likely due to: a. Fecal contamination of vagina b. Recto-vaginal fistula c. Antimicrobial intake d. Catheterization e. Per-vaginal exam Correct Answer: c The nonpathogenic resident bacteria interfere colonization by pathogenic bacteria by: ◦ Competition for receptors or binding sites on host cells, ◦ Competition for nutrients, ◦ Mutual inhibition by metabolic or toxic products ◦ Mutual inhibition by antibiotic materials or bacteriocins ◦ Other mechanisms The intestinal bacteria produce several B vitamins and vitamin K Development & function of the mucosal immune system Certain bacteria metabolize dietary carcinogens Microbial flora are low pathogenicity org Outside these anatomical barrier-cause disease Suppression of normal flora-allows pathogenic organism to overgrow & cause disease e.g. Candida vaginitis, Pseudomembranous colitis by Clostridium difficile Important cause of endogenous infections e.g. Strep pneumoniae pneumonia, Cervicofacial Actinomycosis etc. • Muhammad 24-years-young met a RTA. He sustained multiple injuries and was hospitalized. At laparotomy, it was found that there was a laceration in ascending colon 50 cm from ceacum. The laceration was stiched but three days later, he experienced pain right side of abdomen and fever. USG revealed pus collection near stitched laceration of ascending colon. The most likely organisms to be isolated will be 1. Vibrio cholerae and Staph aureus 2. Strep pyogenes 3. Mycobacterium tuberculosis 4. Mixed normal gastrointestinal flora 5. Neisseria meningitidis Correct Answer: 4