Growth & Replication of Bacteria
advertisement
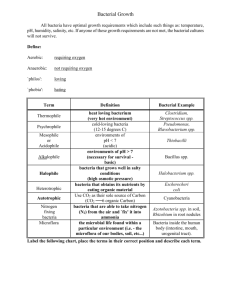
GROWTH & REPLICATION OF BACTERIA Assist Prof Dr. Syed Yousaf Kazmi OBJECTIVES 1. Explain growth requirements of bacteria 2. Relate bacterial growth curve to survival and spread of bacteria 3. Identify bacterial methods of replication and its clinical significance GROWTH REQUIREMENTS • Bacteria reproduce by binary fission • Despite rapid growth time in many bacteria e.g. 10 min for E coli, the population of microorganisms in the biosphere is roughly constant • Growth is counterbalanced by death -depletion of nutrients/ accumulation of toxic comp Binary Fission In Bacteria GROWTH REQUIREMENTS A. PHYSICAL REQUIREMENTS 1. Temperature • Psychrophiles cold-loving bacteria- Grow between -5o to 15o C e.g. Listeria monocytogenes, Flavobacterium spp. • Thermophiles heat-loving bacteria-Grow between 45oC and 70oC e.g. Bacillus stereothermophilus • Mesophiles optimum growth temperature between 25oC and 45oC Most pathogenic bacteria 2. pH • Neutrophiles grow best at a pH range of 5 to 8. Most bacteria • • Alkalophiles grow best at a pH above 8.5 e.g. Vibrio cholerae Acidophiles grow best at a pH below 5.5. e.g. Lactobacillus acidophilus MCQ • A lady brought soft cheese from Panda store at Majmaah and placed it in refrigerator. Five days later, she consumed soft cheese and developed diarrhea and vomiting. Given that the contamination of the pathogen occurred at home, which organism will most likely be the pathogen? a. Escherichia coli b. Listeria monocytogenes c. Bacteroides fragilis d. Streptococcus pyogenes e. Clostridium tetani Correct Ans: b GROWTH REQUIREMENTS 3. Oxygen requirements • Obligate aerobes grow only in the presence of oxygen e.g. M. tuberculosis • Obligate anaerobes grow only in the absence of oxygen e.g. Bacteriodes fragilis • Facultative anaerobes grow with or without oxygen e.g. E. coli • Microaerophiles require a low conc of O2 (2% to 10%) for growth e.g. Campylobacter spp., Helicobacter spp. • Aerotolerant anaerobe are Anaerobic, but tolerates exposure to oxygen e.g. Clostridium perfringens • Capnophilic prefers increased carbon dioxide levels e.g. Neisseria spp. Two enzymes superoxide dismutase and catalase required to combat free radicals generated during resp 2O2+2H+ →H202+O2, 2H202 →2H2O +O2 MCQ A microbiology student noticed that Thioglycollate culture broth tube was very turbid at the surface and clear in the rest of the tube. She can conclude that the 1. Broth is sterile. 2. Organisms cannot tolerate oxygen. 3. Organisms are aerobes 4. Organisms should be put in a candle jar. 5. Organisms are facultative anaerobes Correct Ans: 3 GROWTH REQUIREMENTS 4. Tonicity • • • Isotonic Growth at isotonic atmosphere: Most bacteria Osmo-tolerant Tolerate growth at high salt conc: e.g. Staph aureus, Halophiles Grow at very high salt conc e.g. some Vibrio spp B. Nutritional requirements • • • • • Carbon source Autotroph, Heterotroph Minerals e.g. Iron very imp for bacterial survival, utilize siderophores to chelate iron Water Trace elements Growth factors like heme, nicotinamide, purines etc. required for fastidious org e.g. Hemophilus spp, Group B strep etc. BACTERIAL GROWTH CURVE • Bacteria are said to undergo exponential growth (logarithmic growth) 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 20 , 2 1 , 2 2 , 2 3 , 2 4 , 25 • 1 bacterium will produce 16 bacteria after 4 generations • The doubling time for Escherichia coli is 20 min, while it is 24 hrs for Mycobacterium tuberculosis • One E. coli will produce over 106 org in 7 hrs • Doesn't happen due to toxic metabolites/ loss of nutrients BACTERIAL GROWTH CURVE BACTERIAL GROWTH CURVE 1. Lag phase Vigorous metabolic activity occurs but cells do not divide Few minutes up to many hours 2. Log (logarithmic) phase • • Rapid cell division occurs Lactam drugs act during this phase when cells are making peptidoglycan 3. Stationary phase • Nutrient depletion or toxic products growth slows till number of new cells produced = the number of cells that die 4. Death phase • Decline in the number of viable bacteria MCQ • A student wish to study the effect of an antimicrobial that inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis of bacteria. In which phase of the growth curve should he observe the maximum effect of the antimicrobial? 1. 2. 3. 4. Lag phase Log phase Stationary phase Death phase MCQ • A butcher developed a non healing ulcer on his left forearm after lacerated wound during his work at shop. The ulcer had erythematous and edematous edges with black necrotic central scab. The infective form of this disease developed in which stage of the growth curve of this pathogen? 1. 2. 3. 4. Lag phase Log phase Stationary phase Death phase CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS OF GROWTH CURVE OF BACTERIA • Cholera is a disease that can kill within 12 h, whereas tuberculosis takes months to develop • Result of C/S for V cholerae in 48 hrs while it takes weeks for M tuberculosis • Length of the lag phase and rates of exponential growth in different circumstances make predictions and contribute to safety standards for storage in the food industry