Cardiovascular System (CVS) Cardiac Vascular Arteries
advertisement
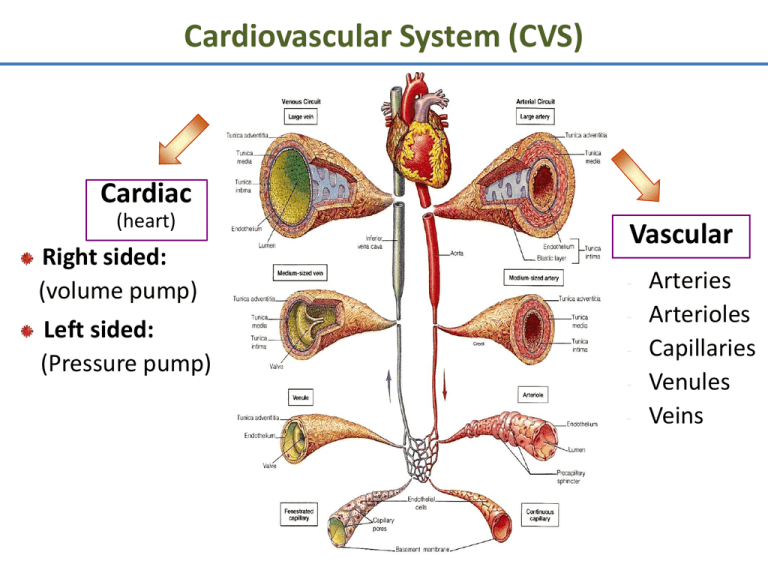
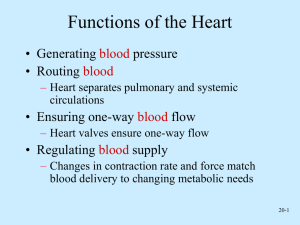
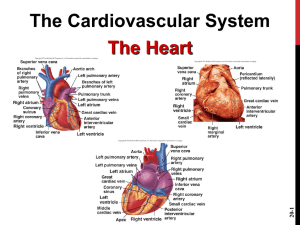
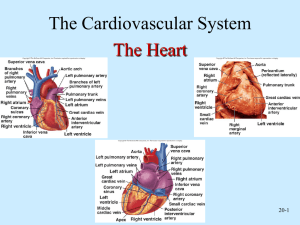
Cardiovascular System (CVS) Cardiac (heart) Right sided: (volume pump) Left sided: (Pressure pump) Vascular - Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Functions of Cardiovascular System I. Primary (main) Function of the Heart: ♥ Acts as a muscular pump: in order to maintain adequate level of blood flow throughout CVS by pumping blood under press into vascular system. ♥ Responsible for the mass movement of fluid in body. Functions of Cardiovascular System II. Secondary functions: 1. Transportation: • • • • Delivers O2 to tissues, & brings back CO2 to lungs. Carries absorbed digestion products to liver & tissues. Carries metabolic wastes to kidneys to be excreted. Distribution of body fluids. Functions of Cardiovascular System II. Secondary functions: 2. Regulation: • • • • Hormonal: carries hormones to target tissues to produce their effects. Immune: carries antibodies, leukocytes (WBCs), cytokines, & complement to aid body defense mechanism against pathogens. Protection: carries platelets, & clotting factors to aid protection of the body in blood clotting mechanism. Temperature: helps in regulation of body temperature, by diverting blood to cool or warm the body. Anatomy of the Heart Position: located behind sternum. Hollow, muscular organ. Anatomy of the Heart ♥ Consists of 2 separate pumps that maintain unidirectional flow of blood; the Lt & Rt hts. ♥ Left heart pumps oxygenated blood Systemic circulation. ♥ Right heart pumps deoxygenated blood Pulmonary circulation. ♥ Each pump contains 2 chambers: an atrium & a ventricle. ♥ 2 Atria: ■ ■ Chambers of the Heart ♥ 2 Ventricles: Thin-walled chambers. Receive blood returning to heart. ■ ■ ■ Thicker, muscular walls. Pump blood from heart. Each has same capacity & pumps same volume of bl in a given period of time. Chambers of the Heart ♥ Atria & ventricles are separated into 2 functional units by a sheet of fibrous connective tissue, which gives attachment to the valves. Valves of the Heart ♥ 2 Atrioventricular (AV) valves: ■ One way valves. ■ Allow bl to flow from atria into ventricles. ■ Tricuspid (Rt) & Mitral (Lt). ♥ 2 Semilunar valves : ■ One way valves. ■ At origin of pulmonary artery & aorta. ■ Pulmonary (Rt) & Aortic (Lt). ■ Open during ventricular contraction. Valves of the Heart: Remember ■ Vs are at entrance & exit of each ventricle. ■ Vs allow bl to flow in only ONE direction. ■ When AV-vs open, semilunar-vs close & vice versa. ■ Opening & closing of vs occur as a result of press differences. ■ AV cusps are held by chordae tendineae to papillary muscles. Atrioventricular & Semilunar Valves Types of Circulations Pulmonary and Systemic Circulations ■ Pulmonary circulation: – Bl pumped from RV through the lungs & back to the ht. ■ Systemic circulation: – Oxygen-rich bl pumped to all organ systems to supply nutrients from LV ■ Rate of bl flow through systemic circulation = flow rate through pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary Circulation • Moves blood to and from the lungs • Pulmonary trunk – Arises from right ventricle • Pulmonary arteries – Branches of pulmonary trunk which project to lungs • Pulmonary veins – Exit each lung and enter left atrium Systemic Circulation: Arteries • Aorta – From which all arteries are derived either directly or indirectly – Parts • Ascending, descending, thoracic, abdominal • Coronary arteries – Supply the heart Systemic Circulation: Veins • Return blood from body to right atrium • Major veins – Coronary sinus (heart) – Superior vena cava (head, neck, thorax, upper limbs) – Inferior vena cava (abdomen, pelvis, lower limbs) • Types of veins – Superficial, deep, sinuses Fetal Circulation Heart Walls: 3 Distinct Layers 1. Endocardium: the innermost layer of the ht. 2. Myocardium: the thickest main layer, consists of cardiac ms. 3. Pericardium (epicardium): the thin, outer covering or external membrane around the ht. Physiology of Cardiac Muscle ■ Cardiac muscle tissue forms 2 functional syncytia: atria, & ventricles. The heart is composed of 2 major types of cardiac muscle: 1: Contractile cells. 2: Autorhythmic (or automatic) cells. Contractile cells: Contract when stimulated, in same way as skeletal ms except for longer duration. Heart : Conducting Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Sinoatrial (SA) node. Internodal pathways. Atrioventricular (AV) node. Bundle of His. Rt & Lt bundle branches. Purkinje fibers. Heart : Conducting Tissues ♥ Conduction pathway: – – – – – – Sinoatrial (SA) node. Internodal pathways. Atrioventricular (AV) node. Bundle of His. Rt & Lt bundle branches. Purkinje fibers. ♥ Stimulation of Purkinje fibers cause both ventricles to contract simultaneously. Heart : Conducting Tissues ■ SA- node & to a lesser extent AVnode contain small round cells called ‘P cells’ which are probably the actual pacemaker cells. ■ At AV- node, very small no. of intercalated discs & gap junctions delay transmission of impulse. Cardiac Cycle • Heart is two pumps that work together, right and left half • Repetitive contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) of heart chambers • Blood moves through circulatory system from areas of higher to lower pressure. – Contraction of heart produces the pressure Cardiac Cycle Regulation of the Heart • Intrinsic regulation: Results from normal functional characteristics, not on neural or hormonal regulation – Starling’s law of the heart • Extrinsic regulation: Involves neural and hormonal control – Parasympathetic stimulation • Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate, acetylcholine secreted – Sympathetic stimulation • Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate and force of contraction, epinephrine and norepinephrine released Cardiac Innervations ■ Autonomic Nervous System: I: Sympathetic Nervous System division. II: Parasympathetic Nervous System division. Cardiac Innervations I: Sympathetic Nervous System: ■ Sympathetic nerves that reaches heart originates from POSTGANGLIONIC FIBERS (upper thoracic, paravertebral, ganglia) releases NORADRENALINE. ■ Mainly supplies: – SA-node, – Atrial myocardium, – AV-node, – Ventricular myocardium. Cardiac Innervations II: Parasympathetic Nervous System: ■ Parasympathetic nerve (vagus) that reaches ht originates from PREGANGLIONIC FIBERS (T1 to T5) releases ACETYLCHOLINE. ■ Mainly supplies: – SA-node, – Atrial myocardium, – AV-node. EKG EKG Heart Sounds • First heart sound or “lubb” – Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systole • Second heart sound or “dupp” – Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longer • Third heart sound (occasional) – Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and detected near end of first one-third of diastole