Lec2

Introduction to Networks and the Internet
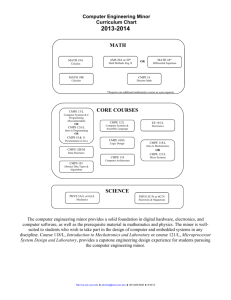
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
1
Data Communication Model
Network
Source
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Destination
2
Simplified Communication Model
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
3
Simplified Data Communications
Model
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
4
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
5
Components
• End systems (or hosts),
• Routers/switches/bridges, and
• Links (twisted pair, coaxial cable, fiber, radio, etc.).
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
6
Components (cont’d)
• Source
– generates data to be transmitted
• Transmitter
– Converts data into transmittable signals
• Transmission System
– Carries data
• Receiver
– Converts received signal into data
• Destination
– Takes incoming data
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
7
• Transmission.
• Signal Generation.
• Synchronization.
Key Tasks
• Error detection and correction.
• Addressing and routing
• End-to-end Recovery.
• Security.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
8
• Transmission.
• Signal Generation.
• Synchronization.
Key Tasks
Physical Layer
• Error detection and correction.
Data Link Layer
• Addressing and routing Network Layer
• End-to-end Recovery.
Transport Layer
• Security.
Application Layer
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
9
Networking
• Point to point communication not usually practical
– Devices are too far apart.
– Large set of devices would need impractical number of connections.
• Solution is a communications network.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
10
Simplified Network Model
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
11
Connecting End Systems
Dedicated link
Multiple access / shared medium
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
12
Connecting End Systems (cont’d)
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
13
Shared Communication
Infrastructure
A stream of packets from sender to receiver.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
14
Types of Data Networks
• Several ways to classify data networks.
• For example, according to “ coverage ”.
– Local Area Networks (LANs) typically provide networking capabilities within a building, campus.
• Typically within 5-mile radius.
– Wide-Area Networks (WANs) span greater geographic distances (e.g., world-wide).
– Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) span more restricted distances, e.g., geographic regions (e.g., Los Nettos network in Southern
California, etc.)
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
15
The Internet
Backbone
Regional
Stub
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
16
Types of Networks (cont’d)
• Classification according to type of connection .
– Dedicated link.
– Shared medium (multiple access).
– Switched point-to-point.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
17
Types of Networks (cont’d)
• Classification according to topology …
• What is network topology?
– The way network elements are interconnected.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
18
Network Topologies: Examples
Ring
Star
Irregular
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Tree
Bus
19
More Concepts…
• Network protocols.
• Layering.
• Network/protocol architecture.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
20
Network Protocols
• Diplomats use rules, called protocols , as guides for formal interactions.
• A communication protocol is a set of rules that specify the format and meaning of messages exchanged between computers across a network.
• A set of related protocols that are designed for compatibility are called protocol suite.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
21
Human and Computer Protocols
Human Protocol Computer Protocol
Hi
Hi
Got the time?
2:00
Web client open connection
OK send me data
Web server
< data > time
22
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Layering
• What is it?
• Building complex systems is hard!
– Approach: “Divide and conquer”.
– Split job into smaller jobs, or layers .
• Analogy to other fields.
– Building a house: digging, foundation, framing, etc.
– Car assembly line…
• Basic idea: each step dependent on the previous step but does not need to be aware of how the previous step was done.
23
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Analogy: Air Travel
• The problem: air travel.
• Decomposed into series of steps:
Arrival at airport
Check-in
Boarding
Takeoff
Departure from airport
Baggage claim
Deplane
Landing
Traveling
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
24
More on the air travel analogy…
Arrival
Check-in
Departure
Baggage claim
Boarding
Takeoff
Deplane
Landing intermediate air traffic sites
Airplane routing Airplane routing
Traveling
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
25
Protocol Architecture
• Task of communication broken up into modules
• For example file transfer could use three modules
– File transfer application
– Communication service module
– Network access module
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
26
Simplified File Transfer
Architecture
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
27
A Three Layer Model
• Application Layer
• Transport Layer
• Network Access Layer
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
28
Network Access Layer
• Exchange of data between the computer and the network
• Sending computer provides address of destination
• May invoke levels of service
• Dependent on type of network used (LAN, packet switched etc.)
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
29
Transport Layer
• Reliable data exchange
• Independent of network being used
• Independent of application
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
30
Application Layer
• Support for different user applications
• e.g. e-mail, file transfer
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
31
Layered Protocol Design
• Layering model is a solution to the problem of complexity in network protocols
• The model divides the network protocols into layers , each of which solves part of the network communication problem
– Each layer has its own protocol!
• Each layer implements a service to the layer above
– Relying on services provided by the layers below.
32
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Layers
• Layers are the different components that need to be designed/implemented when designing/implementing networks.
• Each layer responsible for a set of functions.
• Top layer relies on services provided by bottom layer.
• Layer makes it service available to higher layer through an interface .
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
33
Network/Protocol Architecture
• Set of layers, what their functions are, the services each of them provide, and the interfaces between them.
• A.k.a, protocol architecture or protocol stack.
• Examples:
– ISO-OSI 7 layer architecture.
– TCP-IP architecture (Internet).
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
34
Protocol Data Units (PDU)
• At each layer, protocols are used to communicate.
• At the source, control information is added to user data at each layer, a.k.a., encapsulation.
• At the receiver, control information is stripped off at each layer going up the stack, a.k.a., decapsulation.
35
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Operation of a Protocol
Architecture
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
36
Example 1: ISO OSI
Architecture
• ISO: International Standards Organization
• OSI: Open Systems Interconnection.
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data link
Physical
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
37
Layers of Interest in ISO Model
• Layer 7: Application
– Application-specific protocols (e.g. ftp, http, smtp)
• Layer 4: Transport
– Delivery of data between computers (end-to-end).
• Layer 3: Network
– Data routing across a network.
• Layer 2: Data Link
– Reliable transmission over physical medium.
• Layer 1: Physical
- Transmission of bits between two nodes.
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
38
Example 2: TCP/IP
Architecture
• Model employed by the Internet.
TCP/IP
Application
Transport
Internet
Network
Access
Physical
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data link
Physical
ISO OSI
39
TCP/IP Protocol Architecture
CMPE 150- Introduction to Computer Networks
40