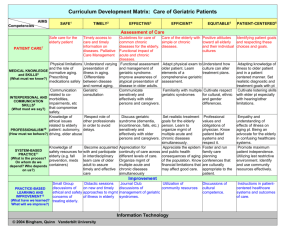
approach to elderly patients

Approach to elderly patient
Dr. Mansour Alzahrani
Objectives
• Demonstrate medical assessment including history taking and physical examination of an elderly patient.
• Assess functional, psychological and social domains of an elderly patient.
• Incorporate the family in the care of an elderly patient.
Medical assessment
• Review medical records
geriatric syndromes and its risk factors
• Medication history
Current and past
• Nutritional evaluation
What are the risk factor of GS
• older age
• baseline cognitive impairment
• baseline functional impairment
• impaired mobility
Geriatric syndromes
• pressure ulcers
• incontinence
• falls
• functional decline
• delirium
More over…
• Sensory impairment
• Dentition
• Mood
• Memory
• Pain
• Visual and hearing assessments
Medication history
• Review all medication including OTC
• Drug allergies or previous adverse drug reactions
• Polypharmacy > 4 drugs (is it good or bad?)
• Ask the family members to bring all medications including supplements in 1st visit.
• Ask the patient to read label, open container and recognize his/her medications
Nutritional evaluation
• The type, quantity, and frequency of food.
• Assess for malnutrition and undernutrition
• weight loss 5% in last month or 10% in last 6 months.
• Ability to chew and swallow
Psychological Assessment
• Mini-mental exam. For dementia.
• Geriatric Depression Scale for depression which include 5 questions:
1. Are you basically satisfied with your life?
2. Do you often feel bored?
3. Do you often feel helpless?
4. Do you prefer to stay home rather than going out and doing new things?
5. Do you feel pretty worthless the way you are now?
◦ More than 2 yes +ve
Social Assessment
• Patient’s living situation and social support.
• Address the potential hazards that increase risk of fall
Functional status
• It reflects pt ability to carry on the physical and social tasks necessary for usual activities.
• It has three components:
●Activities of daily living (ADLs)
●Instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs)
●Advanced activities of daily living (AADLs)
Activities of daily living
• self-care activities include: bathing, dressing, toileting, transferring, maintaining continence, and feeding.
• Inability to do these activities indicate need for a caregiver.
Instrumental activities of daily living
• These include: using the telephone, shopping, doing housework, doing laundry, preparing meals, driving, taking medications, and managing money.
• Dependency is higher in this level of activities.
Advanced activities of daily living
• occupational, recreational, and travel activities
• But the inability to do such activities could be due to health issue or personnel preference
Physical examination
• Assess mobility
• Hearing
• Visual
• MMS
“Get up and Go”
• ONLY VALID FOR PATIENTS NOT USING AN
ASSISTIVE DEVICE
• Get up and walk 10ft, and return to chair
• Seconds
• <10
• <20
• 20-29
• >30
Rating freely mobile mostly independent variable mobility assisted mobility
Can the family play a role in elderly care?