Lab 1 -2 - THEORY AND PROBLEMS GENETICS
advertisement

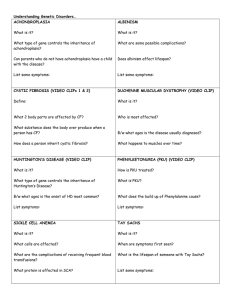
THEORY AND PROBLEMS GENETICS 1) In humans, alkaptonuria is a Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disease that results from a recessive gene. Two normal parents produce a child with PKU. (a) What is the probability that a sperm from the father will contain the PKU allele? (b) What is the probability that an egg from the mother will contain the PKU allele? (c) What is the probability that their next child will have PKU? (d) What is the probability that their next child will be heterozygous for the PKU gene? 2) In a family of seven children, what is the probability of obtaining the following numbers of boys and girls? (a) All boys (b) All children of the same sex (c) Six girls and one boy (d) Four boys and three girls (e) Four girls and three boys 3) What is the probability of rolling one six-sided die and obtaining the following numbers? (a) 2 (b) 1 or 2 (c) An even number (d) Any number but a 6 |Page1 4) What is the probability of rolling two six-sided dice and obtaining the following numbers? (a) 2 and 3 (b) 6 and 6 (c) At least one 6 (d) Two of the same number (two 1s, or two 2s, or two 3s, etc.) (e) An even number on both dice (f) An even number on at least one die 5) The following two genotypes are crossed: AaBbCcddEe X AabbCcDdEe. What will the proportion of the following genotypes be among the progeny of this cross? (a) AaBbCcDdEe (b) AabbCcddee (c) aabbccddee (d) AABBCCDDEE |Page2 6) The LM and LN alleles at the MN blood group locus exhibit codominance. Give the expected genotypes and phenotypes and their ratios in progeny resulting from the following crosses. (a) LMLM X LMLN (b) LNLN X LNLN (c) LMLN X LMLN (d) LMLN X LNLN (e) LMLM X LNLN 7) Give the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios for the following crosses for ABO blood types. (a) IAi X IBi (b) IAIB X IAi (c) IAIB X IAIB (d) ii X IAi (e) IAIB X ii 8) A woman has blood type A MM. She has a child with blood type AB MN. Which of the following blood types could not be that of the child’s father? Explain your reasoning. a) b) c) d) e) George O NN Tom AB MN Bill B MN Claude A NN Henry AB MM |Page3 9) In this chapter we considered Joan Barry’s paternity suit against Charlie Chaplin and how, on the basis of blood types, Chaplin could not have been the father of her child. (a) What blood types are possible for the father of Barry’s child? (b) If Chaplin had possessed one of these blood types, would that prove that he fathered Barry’s child? 10) In humans, alkaptonuria is a metabolic disorder in which affected persons produce black urine. Alkaptonuria results from an allele (a) that is recessive to the allele for normal metabolism (A). Sally has normal metabolism, but her brother has alkaptonuria. Sally’s father has alkaptonuria, and her mother has normal metabolism. (a) Give the genotypes of Sally, her mother, her father, and her brother. (b) If Sally’s parents have another child, what is the probability that this child will have alkaptonuria? (c) If Sally marries a man with alkaptonuria, what is the probability that their first child will have alkaptonuria? |Page4 Research topics Group A 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Sickle-cell disease Haemophilia A Red-green colorblindness Osteogenesis imperfecta Cystic Fibrosis (CF) Klinefelter’s Syndrome Turner’s Syndrome Down Syndrome Edward’ Syndrome Inborn error of metabolism Group B Taste.11 Cleft chin.12 Dimple .13 Earlobe.14 Earwax .15 Freckle .16 Thumb .17 Eye color.18 Human hair color .19 Tongue.20 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Phenylketonuria (PKU) Albinism Polydactyly Brachydactyly Hemochromatosis |Page5 |Page6