ReviewforA PIFinalExam,2012.doc
advertisement

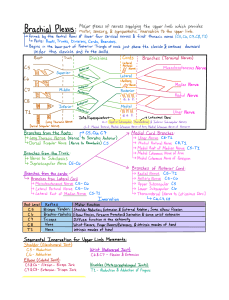
A&P1: Review for Final Exam Dr. Solti; 2012 The Final Exam will have 100 questions, 2 points apiece, divided approximately as follows: 50 questions from Chs 1-8 10 questions from Chs 10, 11, 12 40 questions from Chs 13, 14, 15 Chapters 1- 12: Study previous review sheets, quizzes, notes, and textbook Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves General characteristics of s.c. S.C. anatomy: protective structures, spaces, basic pattern of s.c., 2 enlargements; conus medullaris, filum terminale; cauda equina Gray matter: inner part of s.c., divided into gray horns: dorsal/ posterior; ventral/anterior; commissures White matter: outer part of s.c. ; organized into 3 white columns or tracts: dorsal, ventral, lateral CT coverings of spinal nerves: endoneurium, perineurium, epineurium 31 total spinal nerves: C1-C8, T1-T12, L1-L5, S1-S5, C1. Know the locations they innervate Know distribution of spinal nerves; rami, plexus Cervical plexus: phrenic nerve, phrenic nerve damage, innervates diaphragm Brachial plexus: supplies shoulders and upper limbs/arms: know 5 major branches of brachial plexus; brachial anesthesia; radial nerve damage, ulnar nerve damage; median nerve damage Lumbar plexus: femoral nerve; supplies thighs, abdomen, qudriceps Sacral plexus: sciatic nerve; supplies buttocks, and lower limbs Dermatome PNS Disorders: sciatica, neuritis, polyomyelitis, Myasthenia gravis Reflexes 5 components of reflex arc Stretch reflex Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves 4 Major parts of the brain (cerebrum, diencephalon, brainstem, and cerebellum) Protective coverings of the brain; 3 layers of meninges and their functions CSF: location, synthesis, functions, reabsorbed Blood-brain barrier A&P1: Review for Final Exam (continued) Dr. Solti; 2012 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves (continued): Functions of all parts of the brain, specifically: Cerebrum: 3 basic regions (cerebral cortex, cerebral white matter, basal nuclei), gyri, sulci, fissures, corpus callosum, hemispheres, 4 lobes, central sulcus, precentral sulcus, postcentral sulcus 3 functional areas of cerebral cortex: sensory areas, motor areas (Brocas speech area), association areas (Wernicke's area) Hemispheric lateralization Diencephalon (3 structures) Thalamus (of diencephalon); intermediate mass Hypothalamus (of diencephalon); infundibulum, mammillary bodies Epithalamus (of diencephalon); pineal gland Brainstem (3 regions) Medulla oblongata (of brainstem); pyramids, decussion Pons (of brainstem); "bridge", reticular formation Midbrain (of brainstem): tectum, superior/inferior colliculi; substantia nigra; Parkinson's Disease Cerebellum; vermis, folia, arbor vitae, cerebellar peduncles; 3 lobes (anterior, posterior, flocculonodular) Limbic System: hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus Reticular Formation System (in pons of brainstem) Brain waves Cranial nerves: 12 pairs, know the mnemonic and the names of the nerves Specifically know trigeminal (V) nerve , vagus (X) nerve, accessory (XI) nerve Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic NS and Autonomic NS Autonomic NS: functional generalizations; preganglionic neurons, postganglionic nurons 2 divisions: Sympathetic and parasympathetic Sympathetic/"Fight or flight" responses Parasympathetic/"At rest" responses Influence of brain on ANS Neurotransmitters of ANS Influence of drugs on ANS