Three.MesoEgypt.doc
advertisement

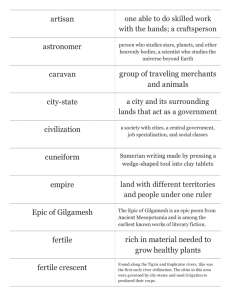
Topic Three: Mesopotamia and Egypt: The First Bronze Age Civilizations Mesopotamia, The Land Between Two Rivers I. 4000 to 3000 B.C. in the delta region of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, the first urban cities form. A. Flooding of the rivers allow for more food production, more population. 1. The urban areas were not politically unified, but individual city-states that trade/compete with each other 2. Because of the large populations, need method of food distribution -> bureaucracy 3. Bureaucracy leads to record keeping -> writing 4. earliest writing in Mesopotamia dates to ca. 3200 B.C. B. Civilization is now underway 1. definition of civilization II. Sumer, the First Civilization 3000 to 1763 B.C., in delta region A. By 3000 B.C. the Bronze Age starts 1. Each urban area is politically a city-state, mostly built of mud-brick, very little stone 2. In the center of the city are palaces and temples, ziggurats 3. Each city-state is dedicated to a particular god/goddess 4. The Sumerians don’t last very long, but they give their culture, religion and institutions to suceeding civilizations B. Concept of Monarchy 1. Priest-King who is intermediary between gods and the populace 2. Also has to lead the army because of almost constant warfare between city-states C. Polytheistic Religion 1. Many gods, anthropomorphic, and have flaws 2. Gods are not very nice, have specialized group to try and figure out the will of the gods 3. No real afterlife, no rewards/no punishment, life meant to be endured 4. No moral codes, no right or wrong, roleof humans is to serve the gods D. Engineering 1. Developed hydraulic engineering because the Tigris and Euphrates floods unpredicably (flood story) 2. also provide water for crops in the dry season 3. engineering will develop complex math, Mesopotamians have a base 60 counting system 4. survives today in our geometry and time systems 5. important because farmers have to feed non-farming urban population E. Writing 1. Cuneiform or wedge-shaped writing 2. syllabic language, starts as pictographs 3. write on clay tablets with reed pens, to make “permanent”, bake them 4. have schools to learn writing, only a very few III. Akkadian Empire, 2350 to 1763 B.C. A. Develops north of Sumerians, Semitic speaking peoples (Semite comes from Shem, son of Noah) 1. First true “empire”, city-state is Akkad, use cuneiform, but adapt to their own language 2. there is cross-over of Akkadian and Sumerian language B. Sargon II, the Great 1. responsible for the creation of the Akkadian Empire 2. conquers many of the Sumerian city-states, also goes west to modern-day Lebanon C. Narim-Sin, grandson 1. conquers Ebla, in Syria D. results are that Mesopotamian art and culture will spread throughout the Middle East E. by ca. 2100 B.C. the Sumerian have won independence from the Akkadians IV. Babylonians A. Amorites 1. group of Semitic speaking peoples on the borders of Mesopotamia, nomadic 2. eventually start settling down within Mesopotamia, build a city called Bab-Ilim 3. disliked by the other Mesopotamians, including the Akkadians (called vermin) 4. fourth king of the Babylonians, Hammurabi, builds an empire B. Hammurabi, 1792 to 1750 B.C. 1. rules 160 square miles when he becomes king, goes on to conquer both Sumer and Akkad 2. most famous for his law code, Code of Hammurabi, survives on steles 3. comprehensive law code, from price controls to consumer rights 4. adopt Sumerian cuneiform, but again in Babylonian 5. also adopted the Sumerian gods, but put the Babylonian god Marduk above them all 6. Hammurabi’s successors not able to keep control, in 1534 B.C. a group called the Kassites establish control over the Babylonian empire, but adopt Babylonian do difficult to piece history together 7. new type of government structure with Hammurabi, instead of the city-state, have a kingdom very confusing and upsetting to the rest of Mesopotamia V. Mesopotamian Society and Culture A. Society 1. Three main social classes: upper, lower and slaves, but not locked into your social class 2. slavery not bases on race and not perpetual, slaves had rights 3. women have rights B. Housing and Diet 1. mud brick houses with common walls and courtyard 2. varied diet 3. monumental architecture sign of wealth and centralized authority C. Math and Astronomy 1. by 2500 B.C. had multiplication tables, square root, cube root 2. used base 60 number system (geometry and time system) 3. place value notation system, but no zero 4. started practice of naming days of the week after sun, moon and planets 5. invented the calendar, lunar calendar, which is still in use (Jewish and Islamic Calendar)