Chapter 25-27.doc
advertisement

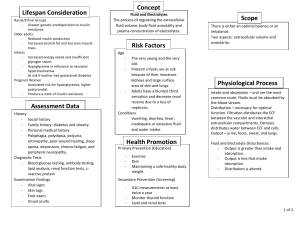
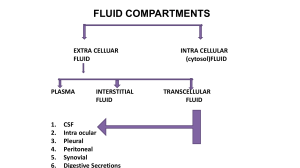
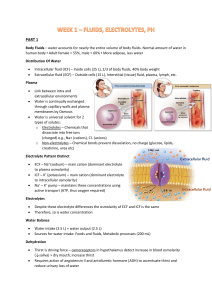
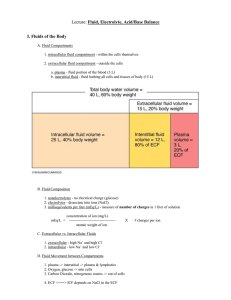
Houston Community College Town and Country Plaza A&P Biology 2402 Human Anatomy and Physiology I1 Instructor: Dr. H. I. Chukwu ================================================================ Study Guide for Chapters 25 – 27 Chapter 25 Define nutrients, calorie, Kilocalories, monosaccharides, disaccharides, Polysaccharides What are Lipids, cholesterol, Phospholipids Proteins and the functions of proteins What are the Recommended Amounts for CHO, proteins and lipids What are the importance of vitamins, which are water soluble - fat soluble Minerals and their functions, organic vs. inorganic Define catabolism, anabolism (examples), metabolism, Energy is used for? Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration Cori cycle is? Number of ATP produced at glycolysis. Kreb cycle and electron transport chains ammonia is produced as a by-product of oxidative deamination, how removed from the body Metabolism of Amino Acid Interconversion of Nutrient Molecules, define: Glycogenesis, Lipogenesis, Glycogenolysis, Gluconeogenesis Components of Metabolic Rate Body temperature and heat exchange? Regulation of set point is by the? Heat is exchanged by Chapter 26 Functions of Urinary System The External Anatomy of the kidney Internal Anatomy of Kidneys Locations and functions of Ureters, Urinary bladder, Urethra, Sphincters Filtration, Renal filtrate, Filtration pressure Which substances are transported actively and passively Urine Production Hormonal Mechanisms: ADH, Aldosterone, Renin, Atrial natriuretic hormone Autoregulation vs. Sympathetic Stimulation Plasma clearance vs. Tubular load Tubular maximum Urine Flow and Micturition Reflex What is Micturition Reflex Effects of Aging on Kidneys 1 Chapter 27 Body Fluids The difference between Intracellular and extracellular fluids Body Fluid Compartments Approximate volumes of body fluid compartments: infants, adult male, adult female Concentration of major solutes in body fluid compartment How does the body regulate it’s water content? Sources of water, Regulation processes, Routes of water loss Regulation of Extracellular Fluid Osmolality Increased ECF vs. Decreased ECF Regulation of Electrolytes in ECF Hypernatremia vs. Hyponatremia Regulation of Chloride, Potassium, Magnesium Ions Hyperkalemia vs. Hypokalemia Regulation of Calcium Ions Hypocalcemia vs. Hypercalcemia Symptoms of decreased or elevated levels of ions in the body Haw are Calcium ions regulated? Define acid, base, buffer Types of buffer systems Respiratory Regulation of Acid-Base Balance Hypoventilation vs. Hyperventilation Renal Regulation of Acid-Base Balance Acidosis and Alkalosis 2