C08: Star Properties
advertisement

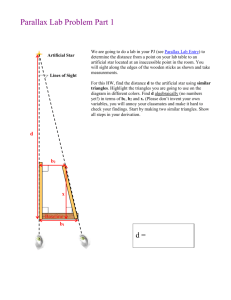
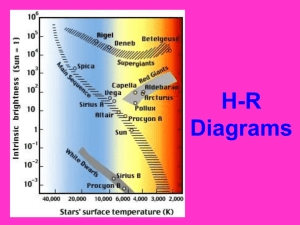
Star Properties (Chapter 8) Student Learning Objectives • Classify stars • Explain how star properties are related. What is the parallax method for measuring distance? Stellar parallax is a change in an object’s apparent position caused by a change in the observer’s position. Distance in parsecs is inversely related to the parallax angle in arcseconds. d= 1 p Example: Sirius is a very bright star in our sky. It has a parallax angle of 0.379 arcseconds. Practice Calculate the distance in Light Years (1 pc = 3.26 LY) 1) Parallax angle = 0.2 arcseconds 2) Vega: Parallax angle = 0.12 arcseconds 3) Polaris: Parallax angle = 0.01 arcseconds How are stellar properties related? Magnitudes are a measure of brightness, and brightness is the direct result of energy output. Brightness refers to the number of photons. Intrinsic to Star Apparent on Earth Mathematical relationship between brightness & energy B= L 4pd2 Magnitudes & Distance Absolute Magnitude is Magnitudes can be used the magnitude a star to determine distance. would have at a distance of 10 parsecs. m – M = 5log10(d) Luminosity and Flux measure energy from the star. L = (Area)sT4 The more mass a star has, the greater the energy output. L = M3.5 Mass → Temperature → Energy → Brightness Practice Star A: Large Surface Area at 6,000 K Star B: Small Surface Area at 6,000K 1) Which would have a greater luminosity? 2) Which would have a greater flux? 3) Which would be brighter if both were the same distance from us? What does a star’s spectral class indicate? The spectral class is determined from a star’s atomic spectrum. All stars have similar compositions Stars have different temperatures OBAFGKMLT Type Color Temperature O B Blue-Violet Blue 30,000+ K 18,000 K A F G K Blue-White White Yellow Orange 10,000 K 7,000 K 5,500 K 4,000 K M L T Orange-Red Red Dark Red 3,000 K 2,000 K 700-1,300 K http://www.atnf.csiro.au/outreach/education/senior/astrophysics/spectral_class.html What is shown by an H-R diagram? An H-R diagram is a graph of luminosity compared to temperature. The locations of the stars on the graph indicates where they are in the stellar evolution process. HR Graph Shows Distance Radius Mass Luminosity Class Age of Cluster Globular Cluster M55 Cluster Ages The HR Diagram is further divided into Luminosity Classes based on line width. I Super Giants II Bright Giants III Giants IV Sub Giants V MainSequence Why are binary stars important? The mass of a binary system can be determined from the orbital period. (m1 + m2)P2 = a3 Visual Binaries See orbital periods Spectroscopic Binaries Doppler shift leads to orbital period Eclipsing binaries Light curves lead to orbital periods