DStroupTalk2.ppt
advertisement

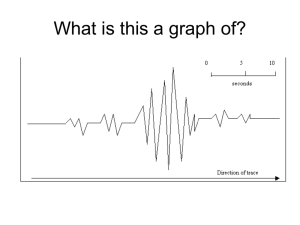
Seismographs By Danielle Stroup Definition • • • • Record zigzag trace Detect earthquakes all over the globe Time, location, and magnitude Goal: to accurately record motion History • Chinese and Egyptians • Devices allowed marbles to fall • 132 AD: Chinese scientist Chang Heng invented seismoscope • Invention called a dragon jar Seismograph Advances • Modern seismograph invented in the 1800s • 1855: Luigi Palmeri of Italy • Recorded time, intensity, and duration for the first time of small earthquakes • 1880: JA Ewing invents pendulum seismograph • HO Wood and J Anderson: mass suspended by torsion Mathematical Theory • 1841: Earliest mathematical theory by Forbes • Considered only simple non-oscillatory ground displacements • 1877: Response of a seismograph to arbitrary, periodic, ground motion written in Japan; had little influence on the development of seismographs Theory • Tilting was neglected in the early development of the seismograph. • Forced damped harmonic-oscillator seismographs were presented by Perry, Ayrton, and Lippmann • Had little effect on the construction of seismographs • 1890's: the importance of tilt was much debated • 1900: become convinced that the effect of tilting could usually be neglected. Improvements • • • • Press-Ewing seismograph Records long period waves Widely used around the world Press-Ewing pendulum seismograph uses the Milne pendulum Seismographs • • • • Compact, light weight, battery operated Performs self-tests Very detailed computer vibration analysis Utilized four channels for signals Blasting seismograph – Monitor, record, analyze, display, and print ground vibration and airblast – Measures seismic wave – Data from blast events represented – Displayed on a liquid crystal display (LCD) Components • Attached to seismograph to collect data • Vibration sensor (geophone): three sensors • Vibration sensor has internal weight that when moved, creates a voltage • Measures absolute velocity • Microphone to measure airblast Data • Shows peak particle velocity, displacement, and the frequency of movement • Require different standards and limits depend on the type of structures • Technology is increasingly utilized • Sensors are placed very close to the blast Conclusion • Instruments have been used for over eighteen hundred years • From seismoscopes to seismographs suitable for detailed studies of earth motion