Personality_Children
advertisement
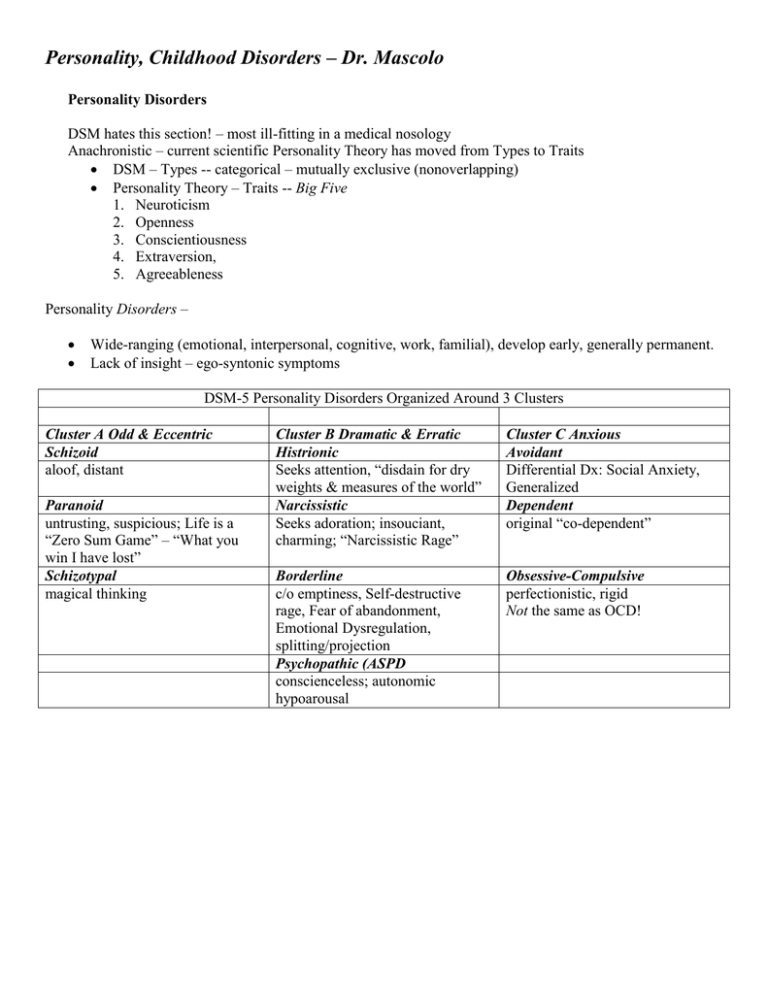
Personality, Childhood Disorders – Dr. Mascolo Personality Disorders DSM hates this section! – most ill-fitting in a medical nosology Anachronistic – current scientific Personality Theory has moved from Types to Traits DSM – Types -- categorical – mutually exclusive (nonoverlapping) Personality Theory – Traits -- Big Five 1. Neuroticism 2. Openness 3. Conscientiousness 4. Extraversion, 5. Agreeableness Personality Disorders – Wide-ranging (emotional, interpersonal, cognitive, work, familial), develop early, generally permanent. Lack of insight – ego-syntonic symptoms DSM-5 Personality Disorders Organized Around 3 Clusters Cluster A Odd & Eccentric Schizoid aloof, distant Paranoid untrusting, suspicious; Life is a “Zero Sum Game” – “What you win I have lost” Schizotypal magical thinking Cluster B Dramatic & Erratic Histrionic Seeks attention, “disdain for dry weights & measures of the world” Narcissistic Seeks adoration; insouciant, charming; “Narcissistic Rage” Cluster C Anxious Avoidant Differential Dx: Social Anxiety, Generalized Dependent original “co-dependent” Borderline c/o emptiness, Self-destructive rage, Fear of abandonment, Emotional Dysregulation, splitting/projection Psychopathic (ASPD conscienceless; autonomic hypoarousal Obsessive-Compulsive perfectionistic, rigid Not the same as OCD! Personality, Childhood Disorders – Dr. Mascolo Childhood Disorders Work with kids, work with their families Harbor negative countertransferential feelings of parents – may lose the patient. Issues of law:– e.g., the holder of the privilege (confidentiality), consent to tx. Confidentiality – technically, parents have a right to know the content of the sessions. Nature of SXs – Not inherently pathological – instead developmentally inappropriate Need to know developmental milestones Not always a delay. Focus on function, rather than topography of the behavior. Verbal Skills/Insight – weak; Candor -- strong Dx – consequences of a false positive -- but also -- a false negative “Sensitivity” it may be subtle, but the clinician makes the diagnosis “Specificity”– it may seem obvious, but the clinician does not make the diagnosis ADHD -- maybe is an example of a trait, not a type 3 subtypes – primarily inattentive, primarily hyperactive, combined Inattention – kid playing video games for hours? Autism – Neurodevelopmental Disorder – like Schizophrenia “spectrum disorder” – acknowledges huge variation in severity and symptoms Typical sx’s include social isolation, stereotypic interests & behaviors, language problems Oppositional Defiant Disorder – ODD All kids are sometimes noncompliant (disobedient) ODD is extreme – for example not just noncompliant -- actually defiant ODD may “graduate” to Conduct Disorder (CD), which may graduate to Antisocial Personality Disorder (ASPD) Conduct Disorder worse than just noncompliant – or even defiant – actually violate the rights of others prelude to ASPD?






