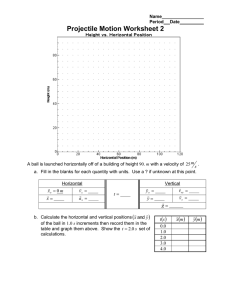
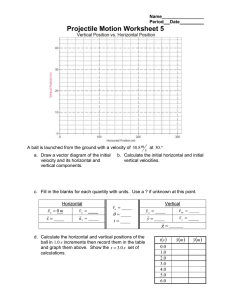
Document 15232716
advertisement
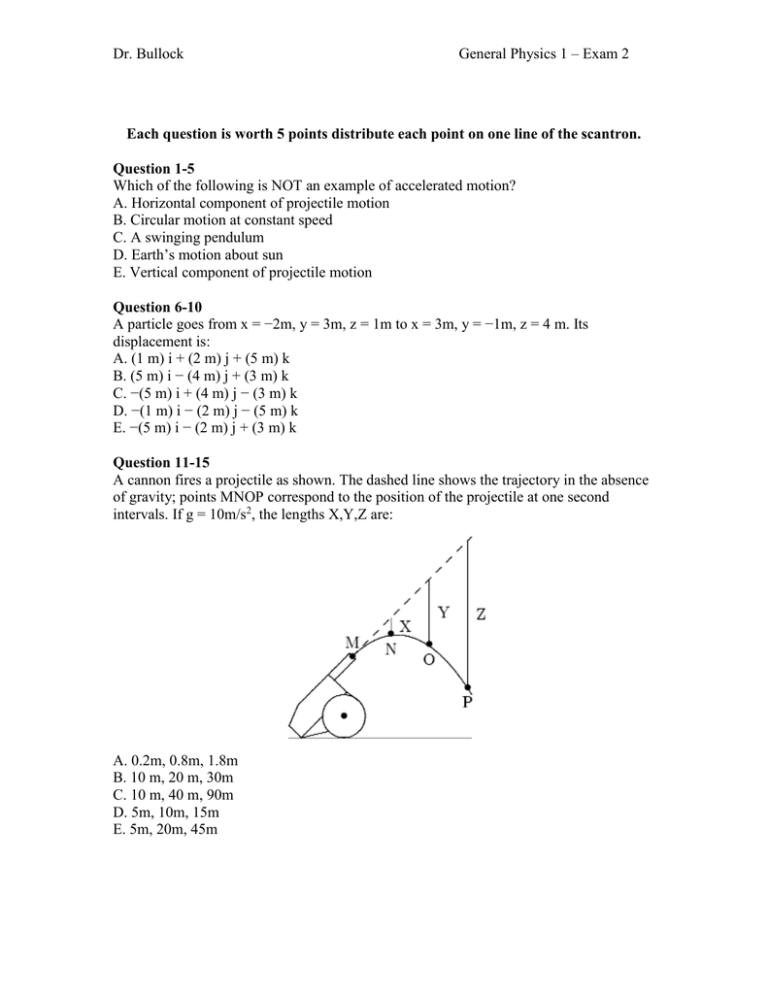
Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 Each question is worth 5 points distribute each point on one line of the scantron. Question 1-5 Which of the following is NOT an example of accelerated motion? A. Horizontal component of projectile motion B. Circular motion at constant speed C. A swinging pendulum D. Earth’s motion about sun E. Vertical component of projectile motion Question 6-10 A particle goes from x = −2m, y = 3m, z = 1m to x = 3m, y = −1m, z = 4 m. Its displacement is: A. (1 m) i + (2 m) j + (5 m) k B. (5 m) i − (4 m) j + (3 m) k C. −(5 m) i + (4 m) j − (3 m) k D. −(1 m) i − (2 m) j − (5 m) k E. −(5 m) i − (2 m) j + (3 m) k Question 11-15 A cannon fires a projectile as shown. The dashed line shows the trajectory in the absence of gravity; points MNOP correspond to the position of the projectile at one second intervals. If g = 10m/s2, the lengths X,Y,Z are: A. 0.2m, 0.8m, 1.8m B. 10 m, 20 m, 30m C. 10 m, 40 m, 90m D. 5m, 10m, 15m E. 5m, 20m, 45m Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 Question 16-20 A toy racing car moves with constant speed around the circle shown below. When it is at point A its coordinates are x = 0, y = 3m and its velocity is (6m/s)ˆi. When it is at point B its velocity and acceleration are: A. −(6m/s) j and (12m/s2) i, respectively B. (6m/s) i and −(12m/s2) i, respectively C. (6m/s) j and (12m/s2) i, respectively D. (6m/s) i and (2m/s2) j, respectively E. (6m/s) j and 0, respectively Question 21-25 A boat is able to move through still water at 20m/s. It makes a round trip to a town 3.0 km upstream. If the river flows at 5m/s, the time required for this round trip is: A. 120 s B. 150 s C. 200 s D. 300 s E. 320 s Question 26-30 What is an order of magnitude estimate for the weight of a person? A. 10 N B. 150 N C. 10,000 N D. 1,000 N E. 5,000 N Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 Question 31-35 Two forces, one with a magnitude of 3N and the other with a magnitude of 5N, are applied to an object. For which orientations of the forces shown in the diagrams is the magnitude of the acceleration of the object the least? Question 36-40 A 9000-N automobile is pushed along a level road by four students who apply a total forward force of 500 N. Neglecting friction, the acceleration of the automobile is: A. 0.055 m/s2 B. 0.54 m/s2 C. 1.8 m/s2 D. 9.8 m/s2 E. 18 m/s2 Question 41-45 A 1-N pendulum bob is held at an angle θ from the vertical by a 2-N horizontal force F as shown. The tension in the string supporting the pendulum bob (in newtons) is: A. cos θ B. 2/ cos θ C. √5 D. 1 E. none of these Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 Question 46-50 A man weighing 700 Nb is in an elevator that is accelerating upward at 4m/s2. The force exerted on him by the elevator floor is: A. 71N B. 290N C. 410N D. 700N E. 990N Question 51-55 A brick slides on a horizontal surface. Which of the following will increase the magnitude of the frictional force on it? A. Putting a second brick on top B. Decreasing the surface area of contact C. Increasing the surface area of contact D. Decreasing the mass of the brick E. None of the above Question 56-60 A block of mass m is pulled at constant velocity along a rough horizontal floor by an applied force T as shown. The magnitude of the frictional force is: A. T cos θ B. T sin θ C. zero D. mg E. mg cos θ Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 Question 61-65 A heavy wooden block is dragged by a force F along a rough steel plate, as shown below for two possible situations. The magnitude of F is the same for the two situations. The magnitude of the frictional force in (ii), as compared with that in (i) is: A. the same B. greater C. less D. less for some angles and greater for others E. can be less or greater, depending on the magnitude of the applied force. Question 66-70 An object of mass m and another object of mass 2m are each forced to move along a circle of radius 1.0m at a constant speed of 1.0m/s. The magnitudes of their accelerations are: A. in the ratio of √2 : 1 B. in the ratio of 2 : 1 C. in the ratio of 4 : 1 D. zero E. equal Question 71-75 The iron ball shown is being swung in a vertical circle at the end of a 0.7-m long string. How slowly can the ball go through its top position without having the string go slack? A. 1.3m/s B. 2.6m/s C. 3.9m/s D. 6.9m/s E. 9.8m/s Dr. Bullock SHOW ALL YOUR WORK! General Physics 1 – Exam 2 NAME In the figure below a ball is thorwn up onto a roof, landing 5 s later at a height of 15 m above the release level. The ball’s path just before landing is angled at = 600 with the roof. (a) Find the horizontal distance d it travels. What are the (b) magnitude and (c) angle (relative to the horizontal of the ball’s initial velocity? (10 POINTS) Dr. Bullock General Physics 1 – Exam 2 SHOW ALL YOUR WORK! NAME A puck of mass m = 3 kg slides in a circle of radius r = 20 cm on a frictionless table while attached to a hanging cylinder of mass M = 4.0 kg by a cord through a hole in the table. What speed keeps the cylinder at rest? (10 Points)