Identify lameness in horses, and make and fit appropriate shoes
advertisement

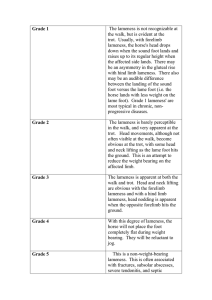
1610 version 5 Page 1 of 3 Identify lameness in horses, and make and fit appropriate shoes Level 5 Credits 40 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to identify the site of lameness in a horse's limb, and identify the particular lameness condition, and make and fit shoes. Subfield Equine Domain Farriery Status Registered Status date 25 September 2003 Date version published 25 October 2007 Planned review date 31 December 2011 Entry information Open. Accreditation Evaluation of documentation and visit by NZQA and industry. Standard setting body (SSB) Primary Industry Training Organisation Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0018 This AMAP can be accessed at http://www.nzqa.govt.nz/framework/search/index.do. Special notes 1 Legislation relevant to this unit standard includes but is not limited to the Health and Safety in Employment Act 1992, and its subsequent amendments. 2 All work practices must comply with industry standards, and not contravene the Code of Recommendations and Minimum Standards for the Welfare of Horses, Code of Animal Welfare No. 7, available from http://www.maf.govt.nz/biosecurity/animalwelfare/codes. 3 Industry standards are defined as work having been performed within Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) regulations, and performed in a timely manner which has an economic outcome for the farrier. Such work must not require any immediate adjustment. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 1610 version 5 Page 2 of 3 Elements and performance criteria Element 1 Identify the site of lameness in a horse’s limb. Performance criteria 1.1 Observation of the features of horse's action identifies the lame limb. Range 1.2 features – nodding head, shortened gait, dropping of one side of hindquarters. Site of lameness is pinpointed by observation and touch. Range heat, pain, swelling, loss of function, redness. Element 2 Identify the particular lameness condition, and make and fit shoes in consultation with veterinarian. Performance criteria 2.1 Foot and leg problems that can be corrected by trimming are identified, and hoof is trimmed to correct the problem. Range 2.2 problems – stone bruise, punctured sole, contracted heels, thrush, cracked heels, mud fever, sandcracks, corns, false quarters, weak/sheared heels, club foot, seedy toe, sidebone, curb, spavin, windgalls. Foot and leg problems are identified, veterinarian is consulted and corrective shoe made and fitted helps to correct the problem. Range laminitis, ringbone, pedalostitus, broken pedal bone, navicular, splints, bowed tendons. Please note Providers must be accredited by NZQA, or an inter-institutional body with delegated authority for quality assurance, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by NZQA before they can register credits from assessment against unit standards. Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against unit standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those standards. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 1610 version 5 Page 3 of 3 Accreditation requirements and an outline of the moderation system that applies to this standard are outlined in the Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP). The AMAP also includes useful information about special requirements for organisations wishing to develop education and training programmes, such as minimum qualifications for tutors and assessors, and special resource requirements. Comments on this unit standard Please contact the Primary Industry Training Organisation standards@primaryito.ac.nz if you wish to suggest changes to the content of this unit standard. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016