Test3LearningObjectives.docx
advertisement

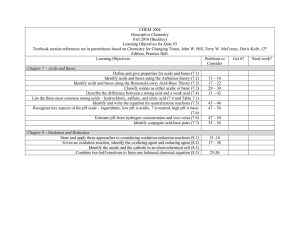
Learning Objectives For Test 3 November 18, 2010 General Chemistry II (CHEM 1474) Sample Exercises Acid-base equilibria (Chapter 16) Review of current acid-base concepts Arrhenius Theory (16.1) Identify substances as Bronsted-Lowry acids or bases (16.2) Identify conjugate acid-base pairs (16.2) Determine relative acidity or basicity of substances (16.2) The autoionization of water Given hydronium or hydroxide concentration, determine the other (16.3) The pH scale Given hydronium, hydroxide, pH, and/or pOH determine the other values (16.4) Calculations involving strong acids and bases Determine hydronium, hydroxide, pH, and/or pOH values given a concentration of a strong acid or base (16.5) Calculations involving weak acids Given sufficient information, determine hydronium, hydroxide, pH, pOH, Ka, and/or percent ionization for a weak acid solution (16.6) Calculations involving weak bases Given sufficient information, determine hydronium, hydroxide, pH, pOH, Ka, and/or percent ionization for a weak base solution (16.7) 16.15-16.16 16.17-16.24 16.25-16.28, 16.107 16.29-16.34 16.35-16.42, 16.111 16.43-16.50, 16.110, 16.112, 16.122-16.123 16.51-16.70, 16.10516.106, 16.113-16.115, 16.130 16.71-16.78, 16.11816.119,16.127 ↓↓↓↓↓Test 3 Begins Here↓↓↓↓↓ Relationship between Ka and Kb Determine Ka and Kb for a conjugate acid/base pair given one of them (16.8) Acid-base properties of salt solutions Given sufficient information, determine hydronium, hydroxide, pH, pOH, Ka, and/or percent ionization for a salt solution (16.9) Acid-base behavior and chemical structure Identify factors that affect acid and base strengths (16.10) Evaluate the relative acidity or basicity of a series of compounds (16.10) Lewis acids and bases Identify materials as Lewis acids or bases (16.11) 16.79-16.82 16.83-16.90, 16.116 16.91-16.92 16.93-16.98, 16.120 16.99-16.104, 16.125 Got it? Needs work Learning Objectives For Test 3 November 18, 2010 General Chemistry II (CHEM 1474) Sample Exercises Other Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria (Chapter 17) Common ion effect Identify “common ions” in a given solution (17.1) 17.13-17.14 Calculate the pH and associated quantities in systems made with compounds 17.15-17.18 containing common ions (17.1) Buffered solutions Define and identify buffer systems (17.2) 17.19-17.20 Calculate the pH and associated quantities in buffer systems (17.2) 17.21-17.26 Calculate changes in pH when acids and bases are added to buffer solutions (17.2) 17.27-17.28 Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to buffer systems (17.2) 17.29-17.32 Acid-base titrations Recognize titration curves for strong acid-strong base, weak acid-strong base, and 17.33-17.38 weak base-strong acid titrations (17.3) Generate titration curves for strong acid-strong base, weak acid-strong base, and 17.39-17.46 weak base-strong acid titrations (17.3) ↑↑↑↑↑↑Test 3 Ends Here↑↑↑↑↑↑ Solubility equilibria Given any chemical equation expressing the dissolution of a solid, write the mathematical expression for the Ksp (17.4) Given sufficient information, calculate missing information related to a solubility situation (17.4-17.5) Predict solubility based on the introduction of common ions (17.5) Qualitative analysis for metallic elements Given results of particular steps in Figure 17.22, state conclusions regarding the presence or absence of specific ions (17.7) Mastering Chemistry Homework Sets include HW13 through HW 16 17.51-17.52 17.49-17.50, 17.5317.56, 17.59-17.62 17.57-17.58 Got it? Needs work