– 2007 Assessment Schedule Agricultural Science: Describe management practices used in pasture /
advertisement
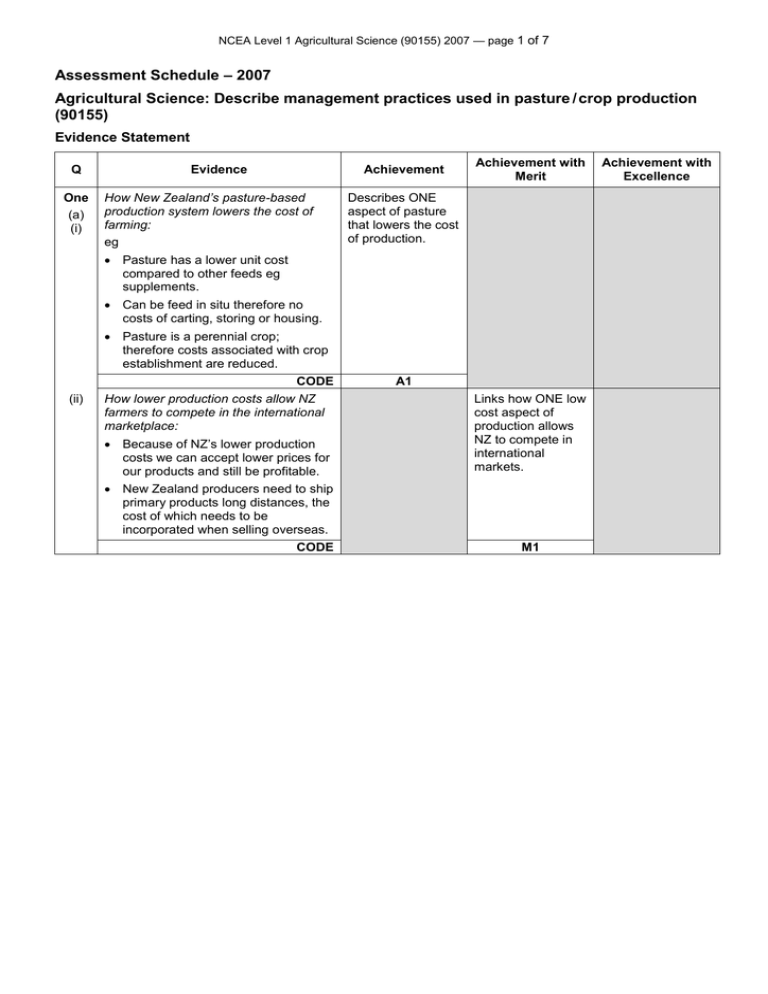
NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule – 2007 Agricultural Science: Describe management practices used in pasture / crop production (90155) Evidence Statement Q One (a) (i) Evidence How New Zealand’s pasture-based production system lowers the cost of farming: eg Achievement Achievement with Merit Describes ONE aspect of pasture that lowers the cost of production. Pasture has a lower unit cost compared to other feeds eg supplements. Can be feed in situ therefore no costs of carting, storing or housing. Pasture is a perennial crop; therefore costs associated with crop establishment are reduced. CODE (ii) How lower production costs allow NZ farmers to compete in the international marketplace: A1 Because of NZ’s lower production costs we can accept lower prices for our products and still be profitable. Links how ONE low cost aspect of production allows NZ to compete in international markets. New Zealand producers need to ship primary products long distances, the cost of which needs to be incorporated when selling overseas. CODE M1 Achievement with Excellence NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 2 of 7 One (b) (i) How pasture improves soil fertility: Pasture contains clovers which fix nitrogen / nitrate from the air. Grazing animals return nutrients to the soil through dung and urine excretion. Describes one aspect of pasture that improves soil fertility. Decaying plant material increases soil organic matter. Topdressing of pasture supplies nutrients. CODE (ii) How farmers benefit from improved soil fertility: Links increase in soil fertility to increased pasture production allowing increased animal production / financial returns or costs. eg 1. Annual pasture production is increased resulting in increased milk / meat / venison production therefore more product for sale and more financial returns. 2. With increased nitrogen levels (as nitrate) in the soil, farmers do not have to rely on expensive nitrogen-based fertilisers to maintain productivity. CODE A1 Explains how increased soil fertility benefits NZ farmers. M1 NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 3 of 7 Q One (c) (i) Evidence Disadvantages of pasture as principal feed source: Achievement Achievement with Merit Describes ONE disadvantage. Variation in pasture growth-rates throughout the year. Pasture quality varies throughout the year. Diseases caused by grazing pasture, eg footrot / bloat/ facial eczema. Stock are always outdoors and are exposed to adverse weather conditions. CODE (ii) How this disadvantage decreases farmers’ financial returns: The requirement to feed out supplements incurs additional costs eg machinery / labour / purchasing feed/ sowing fodder crops. A1 Explains how the selected disadvantage decreases financial returns. Decreased quality decreases energy / protein values, this decreases animal production therefore decrease in financial returns / money. Cost from treating (medicines / labour) and preventing sickness in animals eg bloat – cost of prevention and financial loses due to death of animal. Higher energy expenditure to keep warm (alive) therefore lower production rates / increased death rates, therefore decrease in financial returns. CODE M1 Achievement with Excellence NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 4 of 7 Two (a) Descriptions and explanations: Management practices that impact on the seedbed being fine, firm, weedfree, moist, warm and level include: Cultivation Conventional cultivation: Describes a management practices that is required to prepare a suitable seedbed. Explains how the management practice produces suitable seedbed conditions. Breaks up soil aggregates into a fine soil structure allowing contact between soils and seed. Firming of the seedbed so that the seed is not buried too deep. Spraying with herbicides: Produces a weedfree non competitive seedbed environment. Sub surface drainage / spray irrigation: Maintains optimum seedbed moisture levels, ensuring a warm moist environment for germination. CODE 2 X A2 2 X M2 NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 5 of 7 Q Two (b) (i) Evidence Achievement Management practices to prevent the spread of broadleaf weeds: eg Dig out the isolated weeds by hand. Spot spray weeds with a herbicide / chemical using a backpack sprayer. Achievement with Merit Describes ONE plausible management practice of weed control. Graze with stock that will not carry the seed in their fleece. Increase stocking rate by mob stocking / grazing. CODE (ii) A2 How preventing the spread of broadleaf weeds would improve pasture growth: Explains how reduced competition allows more inputs required for plant processes, thereby increasing yield. Competition from weeds for nutrients / light / water limits the growth rate of pasture. eg Without competition, all pasture plants will have light for photosynthesis, therefore increasing pasture growth. CODE (c) (i) Topping: eg Pasture is cut using a mower at an elevated cutting height. Cutting off the seedheads using a mower. CODE (ii) How topping increases milk production: Encourages leaf growth (high protein), reduces the stem (higher digestibility); therefore more nutrients for improved milk production. CODE M2 Describes a method used to top. A2 Correct explanation. M2 Achievement with Excellence NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 6 of 7 Q Three Evidence Achievement Option that will maximise the farmer’s financial returns: Reducing stock numbers by selling some young stock eg Pros: More market opportunities for young stock, for example selling to farmers to fatten therefore increasing financial returns. The farmer can sell poor genetic stock. Describes what is involved in the selected management practice. Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Explains how the selected management practice can maximise financial returns. Justifies the selected management practice by explaining why it is a better option than the others being considered. Critical thinking drives the award of excellence and must consider the development of new pasture. Cons: Young stock cause less damage to developing pasture because they are lighter. The farmer would be selling off replacement stock and possibly losing favourable genetics. Selling breeding cows in calf eg Pros: Selling of heavier stock reducing pugging and pasture damage. Decreases stock units as one cow is equivalent to four / five calves (depending on breed) Cons: Less productive base as farmer only has 2-year-old cows as replacements. Buying in more feed eg Pros: Don’t lose genetic base in stock. Cons: Logistics of feeding out (machinery). Hay and silage is not high enough in nutritive value to grow out young stock. Availability of feed. Cost of feed. Other factors that could be considered What finance is available to the farmer? What machinery is available to feed silage? Feed storage. Availability of breeding records. CODE A2 M2 E NCEA Level 1 Agricultural Science (90155) 2007 — page 7 of 7 Judgement Statement Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Achievement plus Merit plus 2 A1 2 M1 2 A2 2 M2 1E







