Block 4 Pacing Guide
advertisement

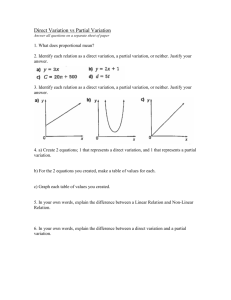
Pre Algebra/CCSS 7th Grade Math Pacing Guide 2011-2012 Instructional Block 4: Graphing & Geometry Recommended Time: 7 weeks Start Date: March 12 Estimated End Date: May 4 Utah Core 2.1: Model and illustrate meanings of ratios, percents, and decimals. a. Graph proportional relationships and identify the unit rate as the slope of the related line. 2.3: Recognize similar polygons and use properties of similar triangles to solve problems and define the slope of a line. d. Define the slope of a line as the ratio of the vertical change to the horizontal change between two points, and show that the slope is constant using similarity of right triangles. 3.3: Graph coordinates and linear equations (incl. slope and intercept) a. Identify approximate rational coordinates when given the graph of a point on a rectangular coordinate system. b. Graph ordered pairs of rational numbers on a rectangular coordinate system. c. Graph linear equations using ordered pairs or tables. d. Recognize that all first order equations produce linear graphs. e. Model real-world problems using graphs, tables, equations, manipulatives, and pictures, and identify extraneous information. 4.2: Derive formulas for surface area and volume. a. Derive formulas for and calculate surface area and volume of right prisms and cylinders using appropriate units. b. Explain that if a scale factor describes how corresponding lengths in two similar objects are related, then the square of the scale factor describes how corresponding areas are related and the cube of the scale factor describes how corresponding volumes are related. c. Find lengths, areas, and volumes of similar figures, using the scale factor. d. Select appropriate two- and three-dimensional figures to model real-world objects, and solve a variety of problems involving surface areas and volumes of cylinders and prisms. Actual End Date: _______ Common Core 7.RP.2: Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities. a. Decide whether two quantities are in a proportional relationship, e.g., by testing for equivalent ratios in a table or graphing on a coordinate plane and observing whether the graph is a straight line through the origin. b. Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships. c. Represent proportional relationships by equations. For example, if total cost t is proportional to the number n of items purchased at a constant price p, the relationship between the total cost and the number of items can be expressed as t = pn. d. Explain what a point (x, y) on the graph of a proportional relationship means in terms of the situation, with special attention to the points (0, 0) and (1, r) where r is the unit rate. 7.G.1: Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale. 7.G.4: Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle. 7.EE.3: Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation. Bolded Utah Core has no overlap in CCSS 7th grade mathematics