Lectures/notes/lecture 35 Holography.pptx
advertisement

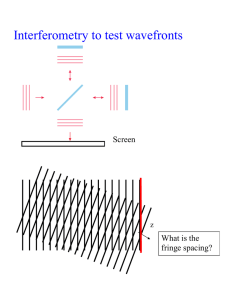
Holography Traditional imaging Image, record intensity distribution in 2-d plane Holography From Gr, “holos”: Record the interference pattern (fringes) between coherent object beam and reference beam. Then we get phase and amplitude information. Why does 3D look 3-D? O Holography Coherence lengths required for reference beam? Hologram recording Simple example Object wave can be made up by summing plane waves. Imagine one of these coming at angle ob vs the z axis. Put film at z = 0. Illuminate also with reference beam along z. E Eref exp ik z z Eob exp ik y y ik z z E Eref Eob exp ik sinob y Spacing h of fringes on screen: when k sinob y changes by 2p hy sin ob Hologram recording Three different angles of plane waves give three interference patterns, but same angle to reference beam I(y) depends on phase and amplitude of Eob . Expose a film 2 I y A Eob Eref 2 2 Eob Eref cos k sinobj y Hologram reconstruction The film becomes a grating of spacing hy . Send a reconstruction beam along z: What diffraction angles do we get out? For the first order, we get out exactly ob ! I(y) for two object waves (and reference) Imagine infinite number of gratings superposed from all object angles...The reconstruction diffraction creates all the object angles again. A zone plate is a crude hologram of a point source of light! Hologram reconstruction When we shine the reference beam on the film, we get 1) undeflected part of the reconstruction beam, with no image information (m = 0) 2) reconstructed object beam (m = 1) 3) “conjugate” reconstruction beams that form a real “image” that is inside out! (m = -1) What coherence lengths are needed for reconstruction beam? Hologram as superposition Film requirements Resolution: 1000-2000 fringes/mm (almost down to ) Need a special nonlinear transparency of film: 2 T I E Normal (linear) film: film exposure exposure so Holography needs Etransmitted I exposure so Tfilm I 2 exposure E 4exposure Etransmitted I exposure Reflection holography Object and reference beam come from opposite sides of holographic plate. Reconstructing beam from same side as viewer: reflection Reflection holography White-light holograms Recorded with coherent light. Reconstructed with incoherent light 15-20mm thick (“volume” hologram). Use “Bragg-plane” interference to give constructive interference for only a narrow band of wavelengths (like photonic crystal) 2d sin Rainbow thin reflecting holograms for white light exposure Slit near object. 3-D appearance only along one axis. Rainbow in other direction.