Click here for powerpoint notes

THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Power Point Notes
What Do I Need To Know (pages 270-280)?
1. Identify and give the functions for each of the following:
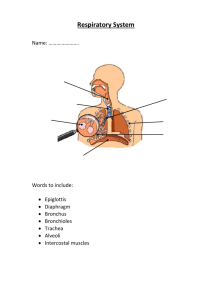
Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Diaphragm & ribs, Pleural membranes, and Thoracic cavity.
2. Compare and contrast the mechanics of the processes of inhalation and exhalation .
3. Explain the relationship between the structure and function of the alveoli.
4. Explain the roles of the cilia and mucous in the respiratory tract.
5. Describe the interaction of the lungs, pleural membranes, ribs, and diaphragm in the breathing process.
6. Explain the roles of carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions in stimulating the breathing centre in the medulla oblongata.
7. Describe the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen during internal and external respiration.
8. Distinguish between the transport of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood by explaining the roles of oxyhemoglobin, carboxyhemoglobin, reduced hemoglobin, and bicarbonate ions.
VOCABULARY
_____ Alveoli
_____ Bicarbonate ions
_____ Breathing
_____ Bronchi
_____ Bronchioles
_____ Carbaminohemoglobin(HbCO
2
)
_____ Carbon dioxide
_____ Carbonic anhydrase
_____ Carboxyhemoglobin (HbCO
2
)
_____ Cartilage
_____ Cellular respiration
_____ Chemoreceptors
_____ Cilia
_____ Diaphragm
_____ Epiglottis
_____ Esophagus
_____ Exhalation/Expiration
_____ External respiration
_____ Hemoglobin
_____ Hydrogen ions
_____ Inspiration/Inhalation
_____ Intercostal muscles
_____ Internal respiration
_____ Larynx
_____ Lipoproteins (surfactant)
_____ Medulla oblongata
_____ Mucous
_____ Nasal sinus
_____ Nose hairs
_____ Oxyhemoglobin (HbO
2
)
_____ Pharynx
_____ Pleural membrane
_____ Pneumothorax
_____ Pulmonary capillaries
_____ Reduced hemoglobin (HHb)
_____ Sinus
_____ Stretch receptors
_____ Surface tension
_____ Thoracic cavity
_____ Trachea
_____ Vocal cords
THE PARTS YOU NEED TO KNOW:
The Nasal Sinus:
The _______________ is surrounded by a lot of ________ __________ and _____________ glands.
Because it is one of the major entry ways into the body it has many things to help keep us safe
1. _____________ : with the aid of mucous, these hairs ____________________________ .
The debris that is trapped in this manner is discharged through the nose.
2. There are _________________________ here to recognize and destroy foreign objects.
3. _______________ are released here as an allergic response when foreign irritants are encountered. This causes runny nose.
Pharynx/Throat:
This is the common passageway for ____________________
Epiglottis:
This is a ________________ that covers the top of the
______________ when ________________ to ensure that food enters the esophagus and not the lungs.
Larynx:
When the epiglottis is opened, the air is able to pass through the __________
____________________ and into the trachea.
The larynx contains the _______________ (two tendons that adjust the pitch of sounds according to how taut they are).
When a guy goes through puberty, his vocal chords and voice box (larynx)
___________________ , and begins to stick out at the front of the throat.
This lump is called the __________________ .
Trachea:
This is the ________________ .
This passageway is held open by the presence of Cshaped rings of ________________ .
This is a ______________ adaptation.
The trachea conducts air into the _____________.
• _________________ filter the air as it moves through the trachea.
• The mucous ____________ and other particles, and the cilia ___________ to the back of the ______ so we swallow it into our digestive system
CONDITIONING OF THE AIR
Several things happen to the air on its way to the alveoli. It is:
1. Adjusted to ___________________: By the time it arrives at the alveoli the air has been in contact with many tissues and is 37 o C.
2. Adjusted to _________________ . As inhaled air passes over the mucous passageways, it becomes saturated with water.
3. __________________ in a 2 part process .
1. Nose hairs and mucous in the nasal passageways.
2. Mucous and Cilia in Trachea and bronchi. *Note: cilia do not filter!
BRONCHI:
The trachea splits into __________ and takes the air into each lung. These branches also have _____________ around them, for the same reason. The bronchi conducts air into smaller branching passageways called _____________.
BRONCHIOLES:
The bronchioles are branching passageways that carry air to its ultimate destination, the ______________________ .
ALVEOLI:
These are the blind ___________ endings at the end of the bronchioles.
There are approx. ____________ __________ in the human lung.
This is the __________________ .
______ leaves the alveoli and ___________________________ to be taken around the body.
______ does the opposite and is ________________ .
Why are they so special?
1. ____________ : Each adult lung contains millions of alveoli. This provides lots of _________
__________ for the gases to be exchanged.
2. ___________: The walls of alveoli are only _________ thick .
3. _______________________: They have stretch receptors that ____________ when the
_________________ enough (stretched). They send a message to the brain to start
_____________________ .
4. _______: They are very moist and this helps gas exchange.
5. VERY __________________: They have a close association with many blood capillaries so oxygen and carbon dioxide can be exchanged ______________ .
DIAPHRAGM:
This is __________ ____________ that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
When you _________ _________________.
When you _ ________ _________________.
6. LINED WITH ____________
______________(surfactant) on their inner surface. This helps to maintain surface tension, thus _____________
___________________ and sticking together during exhalation.
RIBS AND MUSCLES:
These are the bones that are connected to the vertebral column and sternum.
These are ___________________ between the ribs, which help to move the ribs…
1. _____________________________________
2. _____________________________________
MEDULLA OBLONGATA:
Our control of the breathing process is only voluntary to a point.
The _________________of the brain is sensitive to the concentration of ____________ ________________in the blood.
When the concentrations of H + and CO
2
_________________, the breathing center in the medulla oblongata is ____________ and sends nerve impulses to the __________
________________________________________________.
TO INHALE:
When the brain realizes there is ______________ in our blood, it sends a message to the rib muscles and diaphragm to
______________.
The ribs move ____________ , the diaphragm ____________ .
This creates __________ in the lungs ( _________ air pressure) and ____________ to fill that space.
This is called ____________________ .
TO EXHALE:
When the ________________ __________ (full of air), they send a message to the brain to ______________________.
The brain tells the muscles to _________ and the ribs move back
______________ , while the diaphragm moves ____________ .
This ____________ the amount of _______ in the lungs and the air is ________________ .
This is called ____________________ .
PLEURAL MEMBRANES:
These are membranes that _______________________ .
The ____________ pleural membrane _______________________
________________________ & the diaphragm.
The ____________ pleural membrane is _____________________ .
The two lie very close to each other.
The pleura _________________ ____________ so when the lungs inflate, a ___________________ is created and this causes air to rush in.
These membranes also stick the lungs to the chest cavity walls, so
_____________________________________________.
PNEUMOTHORAX:
A ____________ to the chest wall, piercing the pleural membrane (even without damaging the lung itself), will result in a ______________________ , or
________________________________ .
In a situation like this, the negative pressure effectively draws air in through the puncture wound, putting pressure on the surface of the lung instead of inside it and the lung collapses.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM:
Respiration is the set of processes involved with the __________________________________ and the removal of the waste product CO
2
.
There are four aspects to respiration:
1. __________________ : the inspiration and expiration of air.
2. __________________ : gas exchange at the alveoli.
3. __________________ : gas exchange at the tissues.
4. __________________ : mitochondria turn O
2
and glucose into CO
2
and H
2
O and ATP energy.
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION:
Happens at the _____________ .
It is the diffusion of _______________ pulmonary capillaries
( __________ ) and the diffusion of ______________
__________________ to be exhaled with the air.
Because there is a lot of CO
2
returning to the lungs, and not very much in the alveoli, the _______________________________ down its concentration gradient and ________________________ to be breathed out.
Because there is a lot of O
2
in the fresh air in the alveoli, and not much in the deO
2
blood, the
___________________________ down its concentration gradient and ________________________ .
INTERNAL RESPIRATION:
Happens at the _____________ .
It is the diffusion of ________ ____________ cells, and the diffusion of ____________ ______________ capillaries.
The CO
2
is then returned to the heart and sent to the lungs to be removed during exhalation.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION:
INTERNAL RESPIRATION (con’t):
At the venule end of the capillary bed, when __________________ into the blood by
________________ , _______________________ .
Carbon dioxide can be transported in three ways:
1. _____________________
2. _____________________
3. _____________________
Because the hemoglobin now _____________ , they join to form ____________________.
CO
2 also joins with ________ to make the _________________ . There is an enzyme in the red blood cells called ___________ ___________________ which catalyzes this reaction.
The ____________________ from the water is now free. This is BAD as it is _________ and can eat through the blood vessel walls.
So, hemoglobin acts as a _______________ and joins with the hydrogen ion to make
________________________ .
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION (con’t):
When the blood returns to the lungs, the conditions change again, and _______________
_________________ & wants to _________________ again.
So all of the reactions happen in _________________ .
At this point, all that is left to be excreted at the lungs is _______________________
So the CO
2
_____________________ and is ________________ .
The water will either:
1. Be ____________ in the air
2. Enter the alveoli to keep them
___________
3. Remain in the ______________