Announcements 3/28/12 Prayer Exam review problems for sign-up Calvin & Hobbes
advertisement

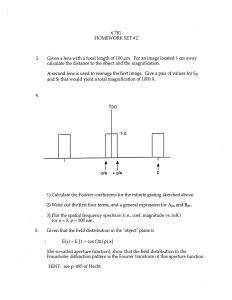
Announcements 3/28/12 Prayer Exam review problems for sign-up Calvin & Hobbes Reading Quiz A lens placed after a diffraction aperture causes the Fraunhofer pattern to be produced: a. before the focal length b. at the focal length c. after the focal length (but at a finite distance) d. at infinity Lenses Lenses What it object is not at infinity? a. What appears at q? b. What appears at f? Object at f: f f f f “Fourier transform plane” Lens Fourier Transforms at focus of lens From Hecht “Fourier Transform smoothing” Before From Hecht After Reading Quiz What does the “Rayleigh criterion” tell us? a. The angle at which both light polarizations have equal reflection coefficients b. The angle at which p-polarized light has minimum reflection c. The angular separation resolvable by an imaging system d. The number of orders produced by a diffraction grating Reading Quiz The Rayleigh criterion for resolving two point light sources comes from: a. Fourier transforms of delta functions. b. Jinc functions’ maxima and minima. c. Lagrange multipliers. d. Parallax of stars. Simple Telescope Circular Aperture, again What do you get in this situation? What if there’s a lens in the hole? What if there isn’t a board? What if you have two light sources? pattern at infinity f superimposed pattern at focus patterns at focus board with hole Rayleigh: 2nd peak at position of first minimum Rayleigh Criterion Curve is (J1(x)/x)2 plotted vs (krb/f), = qD/l (using sinq q) Mathematica “FindRoot” command: q/l = 1.21967… qmin.resolve 1.22 l (= first zero of J1(x)) D Rayleigh Criterion