The Interaction Design of Microsoft Windows CE Sarah Zuberec Ugur Kuter
advertisement

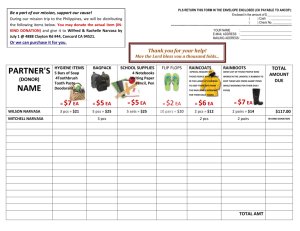
The Interaction Design of Microsoft Windows CE Sarah Zuberec Productivity Appliance Division, Microsoft Corp. Presented By: Ugur Kuter Dept. of Computer Science, Univ. of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742 Outline Introduction User Interface (UI) Design Goals Evolution of Design Handheld PC (H/PC) Palm PC (P/PC) Auto PC (A/PC) Comparison: Windows CE vs. PalmPilot Conclusions Introduction – Windows CE An operating system designed to run on computers that are considerably smaller than PCs portable devices designed to be a “Desktop Companion” products that support TV-, Internet-related applications Outline Introduction User Interface (UI) Design Goals Evolution of Design Handheld PC (H/PC) Palm PC (P/PC) Auto PC (A/PC) Comparison: Windows CE vs. PalmPilot Conclusions User Interface Design Goals Achieve consistency rather than predictability Make use of users’ existing PC expertise Support user tasks on various platforms Develop systems that are easy to integrate with existing PC systems Outline Introduction User Interface (UI) Design Goals Evolution of Design Handheld PC (H/PC) Palm PC (P/PC) Auto PC (A/PC) Comparison: Windows CE vs. PalmPilot Conclusions Evolution of Windows CE Design: Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] The first H/PC prototype contained concepts of desktop PCs but did not have much affinity Screen size 480 x 240 pixels Input/Output Methods A keyboard for touch-typing A touch screen for navigation on the interface Silk-screened buttons that enabled global functionality Single-tap activation for the applications Evolution of Windows CE Design Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] Usability Testing: Controlled Experiments People found the size of certain targets too small People were not able to identify the active areas on the interface People were confused with the selection / activation model In other words, the interface design is failed! Evolution of Windows CE Design Handheld PCs (H/PCs) [1995] New interface that strongly resembles Windows Desktop The same input/output characteristics, tasks and product goals Usability Testing Most targets are perceived as too small to hit Single-tap activation is efficient Auto-save model fails Evolution of Windows CE Design Palm PC (P/PC) [1998] Design Goals Fit the H/PC interface into a smaller size 320 x 240 pixel screen Provide quick information look-up and entry Enable information customization Make it smaller and easy to carry Alternative Input/Output methods to H/PC Hardware buttons for scrolling up/down Handwriting recognition and voice recording Evolution of Windows CE Design Palm PC (P/PC) [1998] Usability Testing: Controlled Experiments Data entry using a small on-screen keyboard is tedious The use of keyboard is rated as easiest to use Subjects were the fastest and most accurate with the keyboard In general, handwriting recognizer is rated low as an input method Evolution of Windows CE Design Auto PC (A/PC) [1998] First product that deviates from the Windows 95 look designed to support tasks of a mobile professional while driving Uses New forms of Input/Output Methods No stylus and no touch screen A numeric keypad for character inputs Speaker-independent voice command interface Sound feedback about the state of the system Infrared connections to H/PCs and P/PCs Evolution of Windows CE Design Auto PC (A/PC) [1998] Usability Testing: Field Studies Interoperability of in-car equipment was compelling People usually plan their tasks before getting into the car They need to be kept informed about schedule changes The data is then synchronized at the office/home Outline Introduction User Interface (UI) Design Goals Evolution of Design Handheld PC (H/PC) Palm PC (P/PC) Auto PC (A/PC) Comparison: Windows CE vs. PalmPilot Conclusions Windows CE vs. Target audience: PC users Palm Designed as a Desktop companion Target audience: PC users Consistency Application switching Multiple taps required to access information Does not emulate PC design Predictability No application switching Quick and instant access to information Outline Introduction User Interface (UI) Design Goals Evolution of Design Handheld PC (H/PC) Palm PC (P/PC) Auto PC (A/PC) Comparison: Windows CE vs. PalmPilot Conclusions Conclusions Implemented in a way to achieve consistency Take something that users understand and use And copy it Familiarity and functionality is satisfied; but not usability Interface consistency is not enough to ensure success Long-term usage is hampered Conclusions Despite these facts Respect must be given to desktop Windows when creating Windows CE interfaces One cannot ignore Windows to create successful products So, the saga continues….