Motion Capture
advertisement
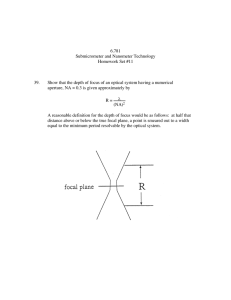
CS 6353 Computer Graphics and Multimedia Motion Capture By Vanitha Kowdeed Overview: Definition of Motion Capture History of Mocap Rotoscoping Types of Motion Capture Prosthetic Optical Electromagnetic Acoustic Marker Placement Production Pipeline Objects for Mocap Skin Deformation Examples References What is Motion Capture? A process by which a movement can be recorded digitally. Or Motion Capture of an object involves sensing, digitizing, and recording that object in motion – Whole body – Hands – Face • One way of acting out an animation Originally used for military tracking purposes. In sports, motion capture acts as a tool for biomechanic research that is focused on the mechanical functioning of the body, like how the heart and muscles work and move. History of Motion Capture The Motion Capture began in late 1800’s when Etienne Jules Marey and Eadweard Muybridge performed motion studies on various animals and humans. History of Motion Capture (Contd.) Etinne Jules Marey’s Motion Capture Suit Eadweard Myubridge •Historically, Motion Capture in animated movies was created using the extension of "ROTOSCOPING" technique. Rotoscoping is an animation technique in which the animators trace over liveaction film movement frame by frame, for use in animated films. The pre-recorded liveaction film images are projected onto a frosted glass panel and are re-drawn by an animator. This project equipment is called rotoscope. Tom Goes To The Mayor There are primarily five methods in motion capture. They are : Prosthetic (or Electromechanical) Acoustic Electromagnetic Optical fiber Optical Prosthetic Motion Capture uses Potentiometers on the aforementioned plastic exoskeleton that an actor must “wear”, and then act out his or her movements. This is very accurate and transmits real-time data at a far greater range than any other technology. A gypsy3 prosthetic suite Fiber Optic sensors Rotation based on transmitted light This approach has a central magnet with several receivers attached to the actor’s body. The receivers capture and record the actors movements and save them to the computer. This motion capture method can be hindered by nearby metal objects if they are large enough and depending on the power of magnets being used. A suit with magnetic sensors Acoustic Motion Capture uses audio transmitters on the actor’s body that make a “clicking” sound when activated by movement. Receivers measure the time it takes for the sound to reach them and triangulate the data to indicate a point on a 3D plane. This method has a problem of audio interface that effects the accuracy of the motion capture. And the other disadvantages are as follows: Limited Rage Limited number of sensors Cables on body •Reflective Markers •Multiple Cameras that digitize different views of performance. Inside-In Motion Capture Systems Inside-Out Outside-In •Electromechanical •Optical Fiber •Electromagnetic •Acoustic •Optical Location should move rigidly with joints Stay away from bulging muscles Production Pipeline Sensor Calibration Compute the position and orientation of camera/transmitter Mapping to characters Direct Mapping or retargetting Subject Calibration Place markers on body, compute skeleton structure(lengths of links) Convert to Joint Angles Occlusion and correspondence problems Record Movements Marker positions (and orientations) varying over time Marker Data Cleanup Occlusion and correspondence problems Details to be taken Care of at time of Motion Capture: •What we need is – Position and orientation of the root segment – Joint angles – Length of each link (is it possible ?) – Skeleton connectivity – Skin deformation • The mocap system actually provides – Marker positions on the skin, or – The positions and orientations of markers Types of Objects that can be had motion capturing •Human whole body •Portions of body •Facial animation •Animals •Puppets •Other objects What is Captured ? Skin Deformation: References: •Motion Capture- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_capture •A Brief History of Motion Capture for Computer Character Animationhttp://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/HyperGraph/animation/character_ animation/motion_capture/history1.htm •Computer Graphics World- http://www.cgw.com/ME2/dirmod.asp?sid=&nm=&type=Publishing&mod=Publi cations%3A%3AArticle&mid=8F3A7027421841978F18BE895F87F791&tier=4 &id=A8B4004315A84A5089255A2E366E2E78 •Motion Capture- What is it? - http://www.metamotion.com/motioncapture/motion-capture.htm •ACCAD-Motion Capture Lab-Home, information and documentationhttp://accad.osu.edu/research/mocap/mocap_home.htm References (contd..) •Motion Capturehttp://www.postmagazine.com/ME2/dirmod.asp?sid=&nm=&type=Publishing& mod=Publications::Article&mid=8F3A7027421841978F18BE895F87F791&tier =4&id=C715B81DD6674D62BD666D304D2E8D0B •Motion Capturehttp://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/ee476/FinalProjects/s2005/Motion_Cap ture_KHY6_DCL34/Motion_Capture.htm •Practical Motion Capture in Everyday Surroundingshttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V0yT8mwg9nc •Motion Capture- http://web.mit.edu/comm-forum/papers/furniss.html •Motion Analysis Studios- http://www.mastudios.com/index.html Any Questions ???????? Thanks !!!!