CHY 4U1 – Image Analysis
CHY 4U1 – Image Analysis
The Scientific Revolution – Isaac Newton and the Laws of Motion
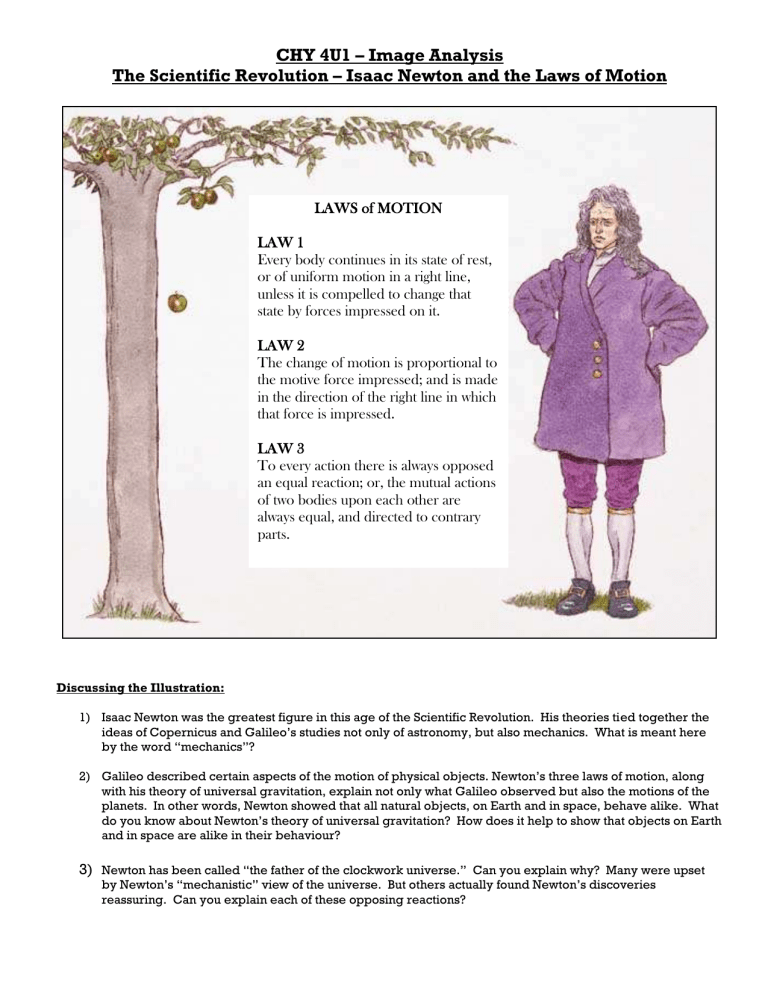
LAW 1 parts.
LAWS of MOTION
Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed on it.
LAW 2
The change of motion is proportional to the motive force impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.
LAW 3
To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction; or, the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary
Discussing the Illustration:
1) Isaac Newton was the greatest figure in this age of the Scientific Revolution. His theories tied together the ideas of Copernicus and Galileo’s studies not only of astronomy, but also mechanics. What is meant here by the word “mechanics”?
2) Galileo described certain aspects of the motion of physical objects. Newton’s three laws of motion, along with his theory of universal gravitation, explain not only what Galileo observed but also the motions of the planets. In other words, Newton showed that all natural objects, on Earth and in space, behave alike. What do you know about Newton’s theory of universal gravitation? How does it help to show that objects on Earth and in space are alike in their behaviour?
3) Newton has been called “the father of the clockwork universe.” Can you explain why? Many were upset by Newton’s “mechanistic” view of the universe. But others actually found Newton’s discoveries reassuring. Can you explain each of these opposing reactions?






