STATISTICS (COMMON DISTRIBUTIONS)
advertisement

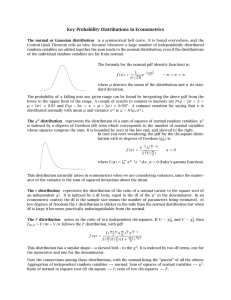
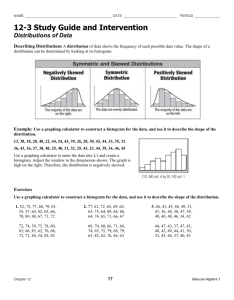
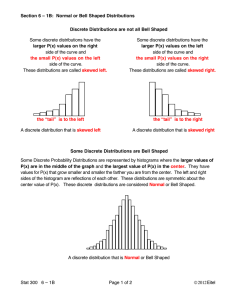
STATISTICS (COMMON DISTRIBUTIONS) Frequency distributions show the frequency of each outcome in a given situation. There are several types of common distributions. NORMAL DISTRIBUTION In a normal distribution, the data are distributed symmetrically about the mean (bell–shaped). The mean, median, and mode are close in value and are located at the centre of the distribution. Ex. SKEWED DISTRIBUTION A non–symmetrical (or lopsided) distribution of data. A skewed distribution has the appearance of a normal distribution that has been pushed to one side of the mean. The data can be clustered on the right or left side of the mean (right skewed or left skewed). Ex. BIMODAL DISTRIBUTION A distribution that contains two equally likely measures of central tendency (two modes) within the data and is symmetrical about both the centres. Ex. Unit 8 Lesson 6 Page 1 of 2 Example 1: In each case, predict the shape of the data distribution. a) the heights of the members of the Toronto Raptors basketball team b) the cost of 1L of gas in a city in Ontario c) the masses of players on the Canadian Olympic men’s and women’s hockey teams Homework: p.153–155 #1–7 Unit 8 Lesson 6 Page 2 of 2