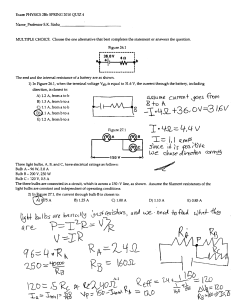
Electricity Review
advertisement

Electricity Review Static Electricity: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is static electricity? What is the law of attraction and repulsion? How do charged objects attract neutral objects? Explain the difference between a negatively and positively charged object? How do conductors and insulators differ from one another? What are some examples of each? 6. Explain why someone can get a charge by dragging their feet as they walk across the carpet? 7. What is charging by induction? Contact? Friction? 8. Know how to use the electrostatic series. 9. What is an electroscope? How does it work? 10. What is grounding? Why does all excess charge go into the ground? 11. What is discharging at a point? 12. How does lightning work? 13. What is similar between a spark and a lightning bolt? Current Electricity: 1. What is current electricity? How is it different from static? 2. What are the four basic parts that make up a circuit? 3. What is the difference between an open and closed circuit? 4. What is the difference between AC and DC? 5. Define current, potential difference, resistance, coulomb, charge and circuit. 6. Explain the difference between an ammeter, voltmeter and multimeter. 7. How is a voltmeter connected to a circuit to measure the potential difference across a light bulb? How is an ammeter connected to a circuit to measure the current? Use a diagram to clarify your answer. 8. List 4 characteristics that affect total resistance. 9. Why are insulators used to cover the conducting wires in electrical cords? 10. Draw the circuit symbols for the following: switch, four cell battery, motor, lamp, connecting wire, grounding, 110 V outlets, ammeters, voltmeters 11. What is the advantage of hooking cells up in series and in parallel. 12. What information does the Energuide provide? Energy Star Symbol? 13. What is a circuit breaker? How does it work? 14. Know how to calculate for the following: current, potential difference, resistance, power and percent efficiency. 15. Have a general understanding of all the different types of electricity: fossil fuels, hydroelectric, nuclear, wind, geothermal, biomass and solar. 16. Know how to solve for resistance, voltage and current in series and parallel circuits: a. Series Current IT = I1 = I2 = I3 Voltage VT = V1 + V2 + V3 Resistance Re = R1 + R2 + R3 b. Parallel Current Voltage Resistance IT = I1 + I2 + I3 VT = V1 = V2 = V3 1/Re = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 Circuit Diagrams: 1. Draw a schematic diagram of a 5 cell battery connected in series to three light bulbs in parallel and a voltmeter connected to one light bulb to measure its potential difference. 2. Draw a schematic diagram of a 110 V outlet, two bulbs connected in parallel, two bulbs connected in series, one open switch controlling the whole circuit and one closed switch controlling one of the bulbs connected in parallel. Include an ammeter. 3. Draw a schematic diagram of a 3 cell battery, with three bulbs in parallel, two motors in series, one switch controlling everything and a voltmeter across the second bulb. 4. Draw a schematic diagram of a 2 cell battery, with two bulbs in series, three bulbs in parallel, 3 open switches each controlling one of the bulbs in parallel, an ammeter and a motor. Current Electricity Problems: 1. If 300 C of charge pass a point in a conductor in 4.0 min, what is the current through that point in the conductor? 2. How much chemical energy is converted to electrical energy when there is 30 C of negative charge of the negative terminal causing a potential difference of 20 V? 3. A flashlight bulb has a resistance of 4.0 ohms. What current passes through the bulb if it is connected to a 1.5 V dry cell? 4. If the current flowing through a conductor is 0.7 A, how much time is required for a charge of 450 C to pass through? 5. Calculate the efficiency of a compact fluorescent light bulb if it produces 40 J of light energy, while using 105 J of electrical energy. 6. How much energy does a 1500 W clothes dryer use when it runs for 45 minutes? 7. What is the charge on the negative terminal if the chemical energy of a battery is 70 J and the potential difference between the 2 terminals is 6 V? 8. A light bulb passes a current of 0.85 A when the potential difference across the bulb is 130V. What is the electrical resistance of the bulb in ohms? 9. A laptop uses 85 W adapter when it is plugged in. Electricity cost 0.06 $ per kW▪h. Calculate how much it would cost to operate the laptop for one year for 20 hours per day. 10. The power of a microwave is 1200 W. What current passes through it when it is connected to an outlet of 120 V? 11. A gasoline-powered generator consumes 16 000 J of energy in 6.0 min. How much power did it produce in this time?