The Animal Kingdom: The Deuterostomes 4/23/2012
advertisement
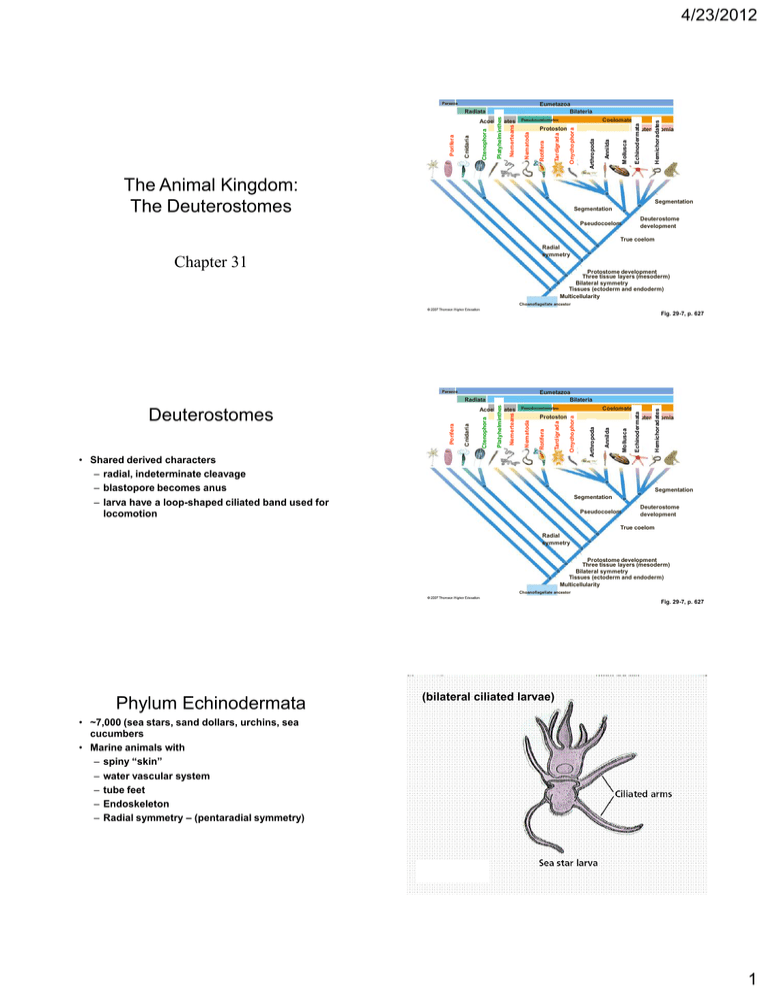
4/23/2012 Parazoa Eumetazoa Bilateria The Animal Kingdom: The Deuterostomes Echinodermata Mollusca Annilda Deuterostomia Arthropoda Tardigrada Onychophora Protostomia Hemichoradates Coelomates Pseudocoelomates Rotifera Nemerteans Ctenophora Porifera Cnidaria Acoelomates Nematoda Platyhelminthes Radiata Segmentation Segmentation Deuterostome development Pseudocoelom True coelom Radial symmetry Chapter 31 Protostome development Three tissue layers (mesoderm) Bilateral symmetry Tissues (ectoderm and endoderm) Multicellularity Choanoflagellate ancestor Fig. 29-7, p. 627 Parazoa Eumetazoa Bilateria • Shared derived characters – radial, indeterminate cleavage – blastopore becomes anus – larva have a loop-shaped ciliated band used for locomotion Echinodermata Mollusca Annilda Deuterostomia Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Rotifera Protostomia Hemichoradates Coelomates Pseudocoelomates Nematoda Nemerteans Ctenophora Porifera Acoelomates Cnidaria Deuterostomes Platyhelminthes Radiata Segmentation Segmentation Pseudocoelom Deuterostome development True coelom Radial symmetry Protostome development Three tissue layers (mesoderm) Bilateral symmetry Tissues (ectoderm and endoderm) Multicellularity Choanoflagellate ancestor Fig. 29-7, p. 627 Phylum Echinodermata (bilateral ciliated larvae) • ~7,000 (sea stars, sand dollars, urchins, sea cucumbers • Marine animals with – spiny “skin” – water vascular system – tube feet – Endoskeleton – Radial symmetry – (pentaradial symmetry) • Larvae exhibit bilateral symmetry 1 4/23/2012 Class Asteroidea • Sea stars – central disc with five or more arms – use tube feet for locomotion Class: Asteroidea (sea stars) • skin gills • carnivorous (mollusks, annelids) • metabolic wastes exits by diffusion • water vascular system • able to regenerate appendages • Endoskeleton covered by thin epidermis • coelom Madreporite - complete digestive system Stone canal • no brain - - nerve rings around mouth • sexes separate - external fertilization • Poorly developed circulatory system Ampulla Sea Star Body Plan Fig. 31-1, p. 669 2 4/23/2012 Parazoa Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum: Hemichordata Echinodermata Mollusca Annilda Deuterostomia Arthropoda Tardigrada Onychophora Protostomia Hemichoradates Coelomates Pseudocoelomates Rotifera Nemerteans Ctenophora Porifera Cnidaria Acoelomates Nematoda Platyhelminthes Radiata Sedentary worm-like marine animals Segmentation Segmentation Deuterostome development Pseudocoelom True coelom Radial symmetry Protostome development Three tissue layers (mesoderm) Bilateral symmetry Tissues (ectoderm and endoderm) Multicellularity Choanoflagellate ancestor Fig. 29-7, p. 627 Parazoa Hemichoradates Echinodermata Mollusca Annilda Deuterostomia Arthropoda Onychophora Tardigrada Protostomia Rotifera Nemerteans Coelomates Pseudocoelomates Nematoda Platyhelminthes Ctenophora Porifera Cnidaria Acoelomates Choradates Eumetazoa Bilateria Radiata Phylum Chordata: Characteristics • At some time during life cycle have: Segmentation Segmentation Pseudocoelom Deuterostome development True coelom Radial symmetry – – – – – flexible, supporting notochord dorsal, tubular nerve cord pharyngeal (gill) slits muscular postanal tail endostyle (or thyroid gland) Protostome development Three tissue layers (mesoderm) Bilateral symmetry Tissues (ectoderm and endoderm) Multicellularity Choanoflagellate ancestor Fig. 29-7, p. 627 Chordate Body Plan Phylum Chordata • Subphylum Urochordata (Invertebrate) • Subphylum Cephalochordata (Invertebrate) • Subphylum Vertebrata (Vertebrate) 3 4/23/2012 Chordate Evolution Subphylum Urochordata • Tunicates – Invertebrate – marine animals with tunics – suspension-feeders • Larvae are free swimming – Most adults are sessile Incurrent siphon Ganglion Oral tentacles Pharynx with slits Excurrent siphon Atrium Endostyle Tunic Intestine Esophagus Testis Digestive gland Ovary Heart Stomach Fig. 31-5b, p. 672 Tunicate 4 4/23/2012 Pharynx with slits Incurrent opening Larva Atrium Excurrent opening Nerve cord Adhesive papilla Notochord Heart Stomach 0.5 mm Subphylum Cephalochordata • Lancelets – Invertebrate, small, segmented, fishlike animals Vertebrata Cephalochordata (lancelets) Urochordata (tunicates) Chordata Hemichordata (acorn worms) Echinodermata (sea stars, sea urchins) Fig. 31-5c, p. 672 Deuterostome ancestor Fig. 31-5a, p. 672 Chordate Evolution Vertebrate Evolution 5 4/23/2012 Vertebrate Characteristics • Vertebral column: skeletal axis of body • Cranium: braincase • Neural crest cells: determine development of many structures • Pronounced cephalization • Complex brain • Muscles attached to endoskeleton for movement Vertebrate Evolution KEY CONCEPTS • Shared derived characters of vertebrates include a vertebral column, cranium, neural crest cells, and an endoskeleton of cartilage or bone Jawless Fishes • Ostracoderms (extinct) – among earliest known vertebrates • Agnathans (hagfishes) – class Myxini • Lampreys . class Cephalaspidomorphi • no jaws or paired fins; cartilage, gills, notochord Jawless Fish: Hagfish Vertebrate Evolution 6 4/23/2012 Lampreys Vertebrate Evolution Class Chondrichthyes (Cartilaginous Fishes) • Includes sharks, rays, skates • Cartilaginous fishes have – jaws – two pairs of fins – placoid scales Shark Structure Early Jawed Fishes 7 4/23/2012 More developments of Cartilaginous fishes: - development of sense organs • Oviparous • electrorecptors in head • lateral line organs Shark Reproduction – lay eggs (all fish) • Ovoviparous • Internal fertilization – young enclosed by eggs – incubated in mother’s body • Viviparous – young develop in mother’s uterus – nutrients transferred from mother’s blood Vertebrate Evolution Bony fishes – “Osteicthyes” 24,000 spp. 8 4/23/2012 Characteristics of Bony fishes Bony Fishes • • • • • Class Actinopterygii – ray-finned fishes • Class Actinistia – coelacanths skeleton of bone most oviparous swim bladder (not all) bony dermal scales Modern bony fishes • Class Dipnoi – lungfishes Lung fishes (3 genera (lungs – enamel) Ray-finned Lobe-finned (lungs) Lobe-finned fishes (1) (Coelocanth) bony ancestor (lungs) Modern Bony Fishes Modern day boney fish Swim bladder Nerve cord Dorsal fins Kidney Ureter Caudal fin Brain Nostril Pharynx Gills Heart Gonad Liver Stomach Pelvic fin Intestine Urinary bladder Anal fin Cloaca Fig. 31-13, p. 680 Lung fish branch: Sarcopterygii We used to think • Gave rise to – lungfishes (class Dipnoi) Lungfishes – coelacanths (class Actinistia) 9 4/23/2012 Sarcopterygii Vertebrate Evolution • Lungfishes gave rise to tetrapods – land vertebrates • Tiktaalik - transitional between fishes and tetrapods Early Tetrapods • Early amphibians – mainly aquatic – moved onto land to find food, escape predators – had limbs strong enough to support body weight on land Class: Amphibia - salamanders, frogs, toads, caecilians • metamorphosis aquatic larvae terrestrial adult!!!! • lungs + skin for gas exchange • chambered heart: systemic circulation pulmonary circulation • most oviparous - Water!! 10 4/23/2012 Amniote Evolution Have body covering that retards water loss Have physiological mechanisms that conserve water Amniotic membrane Amniotic Egg (from drying out – temperature) • Protection • Keeps from drying out • Temperature regulation Class Reptilia • A paraphyletic group – dinosaurs, turtles, lizards, snakes, alligators • Biologists classify amniotes in two main groups: diapsids and synapsids Amniotes • Diapsids – turtles, ichthyosaurs, tuataras, squamates (snakes and lizards), crocodiles, pterosaurs, saurischian dinosaurs, birds Diapsids • Many biologists consider birds as feathered dinosaurs – classify birds and most reptiles as diapsids • Synapsids – gave rise to therapsids, which gave rise to mammals 11 4/23/2012 Therapsid Amniote Evolution 4 Groups of Extant Reptiles Reptile Characteristics 1. Turtles, terrapins, tortoises 2. Snakes • Reproduction – internal fertilization – leathery protective shell around egg – embryo develops protective membranes (including amnion) 3. Tuataras 4. Crocadiles, alligators, caimans Reptile Characteristics Class: Aves (birds) around 9,000 species - derived from dinosaurs • Dry skin with horny scales • Lungs with many chambers • Three-chambered heart – some separation of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood - adaptations to flight • feathers • streamlined bodies • light bones (fenestrated) • No teeth - efficient lungs and circulatory systems - 4 chambered heart 12 4/23/2012 Modern Birds Archaeopteryx Reptile-like - reptile teeth - long tail - wings w/claws Bird-like -wings - feathers - furcula Birds Birds • Adaptations for powered flight – feathers – wings – light, hollow bones containing air spaces • Excrete solid metabolic wastes (uric acid) • Four-chambered heart • Well-developed nervous system • Very efficient lungs • Excellent vision and hearing • Endotherms – maintain constant body temperature 13 4/23/2012 Mammal Evolution Mammals • Characterized by – – – – hair mammary glands differentiated teeth three middle-ear bones • Have highly developed nervous system and muscular diaphragm • Are endotherms Subclass: Holotheria (monotremes) **** Oviparous!!!! Subclass: Metatheria (Marsupials) - Marsupium -- Viviparous Marsupials (Subclass Metatheria) • Include pouched mammals – kangaroos, opossums • Young are born in embryonic stage • Complete development in mother’s marsupium – nourished with milk from mammary glands 14 4/23/2012 Placental Mammals (Subclass Eutheria) • Characterized by placenta – for exchange between embryo and mother Subclass: Eutheria (Placental mammals) Viviparous - Placenta (organ of exchange between mother and embryo) No loss of eggs Maternal bond Resources MYA On seeing the marsupials in Australia for the 1st time and comparing them to placental mammals: 200 225 290 “An unbeliever might exclaim „surely two distinct creators must have been at work” C. Darwin 350 Mammalia mammals (4,600 species) Aves birds (9,000 species) Reptilia reptiles (6,500 species) Amphibia amphibians 400 Osteicthyes Bony fishes (4,000 species) 400 Chondricthyes Cartilagenous fishes (850 species) 450-500 Agnatha Jawless fishes (24,000 species) (60 species) 15





