8.2 Review Name________________________________ Period_______Date_____________________
advertisement

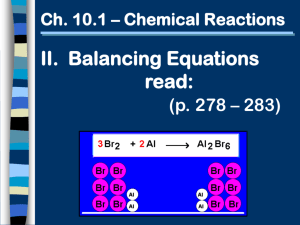
8.2 Review Name________________________________ Chemical Equations Period_______Date_____________________ DIRECTIONS: Refer to the unbalanced chemical equation below to answer the following questions. Write your answers in the space provided. Al(NO3)3 + FeCl2 → Fe(NO3)2 + AlCl3 1. Write the names of the reactants in this equation: _______________________________________ _____________________________________ 2. Write the names of the products in this equation: _______________________________________ 3. Balance the equation above. _____________________________________ What is the coefficient for Al(NO3)3? ___________ What is the coefficient for FeCl2? ___________ What is the coefficient for Fe(NO3)2? ___________ What is the coefficient for AlCl3? ___________ 4. How many oxygen atoms are there on each side of the balanced equation? __________ 5. What should you do if an equation you have written cannot be balanced? ________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 6. How is balancing an equation related to the Law of Conservation of Matter? _____________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Describe the correct way to balance an equation: ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 8. How are the physical states of the reactants and products indicated in a chemical equation? __________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ DIRECTIONS: Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions. Indicate the physical state of the reactants and products (ex – s,g,l,aq). 9. Hydrogen gas reacts with nitrogen gas to produce ammonia gas (NH3). 10. Hydrogen bromide gas reacts with oxygen gas to produce liquid water and bromine gas. 11. When a solid piece of magnesium is placed in hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas bubbles off and magnesium chloride is left in solution. 12. Hydrochloric acid can be added to calcium carbonate to produce calcium chloride in solution, carbon dioxide gas and water. 13. Solid carbon disulfide can be used to form carbon dioxide gas and sulfur dioxide gas when it reacts with oxygen gas. 14. Solid manganese dioxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce manganese (II) chloride, liquid water and chlorine gas.